What Is A Dividend: Your Guide To Investment Income
Understanding what is a dividend is crucial for a smart investor's portfolio. It shows a company's choice to give part of its earnings to shareholders. This sharing reflects the company's health and rewards for investors. Dividends can be in cash or additional stock and they boost a financial portfolio.
Not all companies give out dividends; some prefer investing in growth. The dividends definition thus echoes a firm’s financial strategy. It demands careful review by investors who view dividends as key to their investments.
Key Takeaways
- Dividends are payouts that companies make to shareholders, and they can come as cash, additional stock, or even property.
- Dividends are often indicative of a company's financial health and stability, commonly associated with established and mature companies.
- Intricacies like dividend dates, including ex-dividend and payment dates, play a crucial role in the investment cycle.
- Analysing dividend yield and payout ratios helps investors evaluate the potential return on their investments and the sustainability of a company's dividend policy.
- Reinvesting dividends through DRIPs can significantly enhance long-term investment growth due to the compounding effect.
- Knowing the tax implications associated with dividend income is critical for investors to optimize their after-tax returns.
- Companies with a history of increasing dividends, such as the S&P 500 dividend aristocrats, are often sought after for their potential to deliver growing income streams to investors.
Understanding the Basics of Dividends
For investors, learning about dividends is key to good investment choices. Dividends are part of a company's profit shared with its shareholders. They are not just income; they also show if a company is doing well financially and succeeding in its operations.
Definition of a Dividend
A dividend is a payment a company makes to its shareholders out of its earnings. These payments could be in cash, stock, or other assets. It all depends on the company's financial plan and how stable its earnings are. In short, dividends let shareholders enjoy a piece of the company's profits.
Importance in Investing
Grasping what dividends mean is vital for making smart investment choices. Here's why they're so important:
- Indicators of a strong company: Regular dividends show a company is stable and profitable. This is usually the case with well-established companies.
- Making a stock more appealing: Dependable dividends make a stock more attractive. They offer a chance at steady income, along with the potential for the investment to grow in value.
- Building your investment: Reinvesting dividends can let investors buy more shares. This could make their investment worth more over time.
So, dividends mean a lot more than just sharing profits. They show a company's dedication to its shareholders and its optimism about its financial future. Also, knowing how dividends work can really help with growing your investments, especially when it comes to earning income and strategically expanding your portfolio.
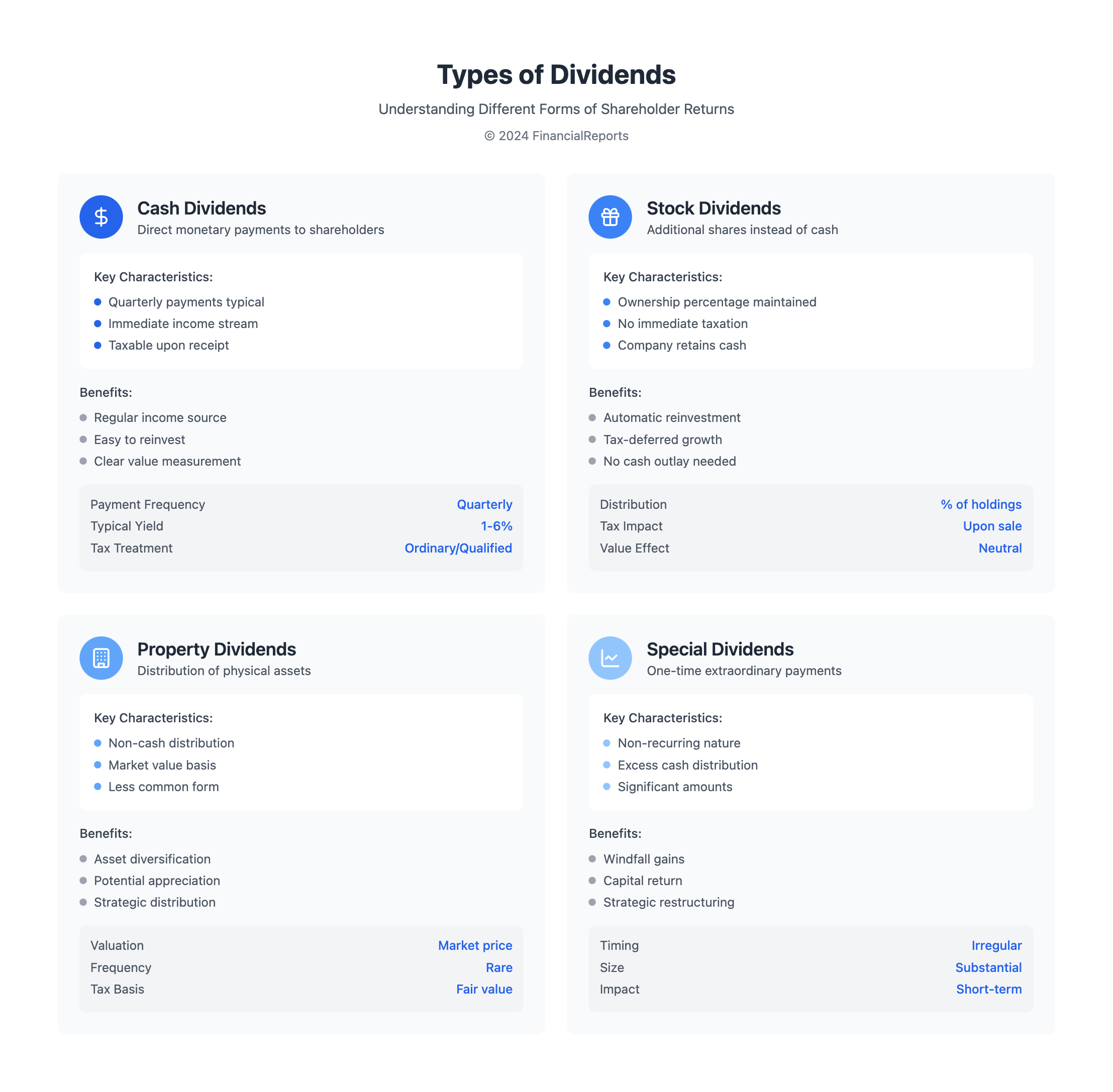
Types of Dividends
Dividends are a portion of profit a company shares with its investors. There are mainly three types: cash, stock, and property dividends. Each kind caters to investors' different needs and tax situations. They heavily influence investment decisions.
Cash Dividends
Cash dividends are very common among companies. They give this directly from their earnings, usually four times a year. This payout is a sign of a company’s good health and its ability to make money. But, they are taxable in the year you get them.
Stock Dividends
Stock dividends give you more shares instead of cash. This increases your share without immediate taxes. Understanding how do stock dividends work is key. For instance, a 10% stock dividend gives you 1 extra share for every 10 you own. They're mostly found in growing companies, keeping cash for expansion. They aren't taxed until sold.
Property Dividends
Property dividends are rarer but offer distinct value. These dividends can be real estate, inventory, or stakes in other businesses. They're appraised at market value. This can include items with potential to grow in value, unlike cash dividends.
Each dividend type offers unique benefits and suits different investment strategies. They reflect a company's performance and investor's tax planning. This makes them crucial for investment decisions and managing a portfolio.
How Dividends Work
Dividends are vital for investors looking to benefit from profit sharing in their portfolios. They are a way companies give profits to their shareholders, following several important steps.
Declaration Date
On the declaration date, a company's board decides to pay a dividend. They set the dividend rate, record date, and payment date. Figuring out dividend payments involves looking at the announced rate, which is a share price percentage or a set amount.
Ex-Dividend Date
The ex-dividend date decides who gets the next dividend. To get dividends, you must own the stock before this date. This deadline helps firms manage dividend payments effectively. Dividend payment frequency depends on the company’s policy, often quarterly.
Payment Date
When are dividends paid? After the ex-dividend and record dates comes the payment date. This is when dividends are given to shareholders. Companies usually use the Depository Trust Company (DTC) for distribution. Shareholders get dividends via direct deposit or checks from their brokers.
Understanding the dividend process is key for all investors. Knowing these dates and their effects can boost dividend income. It’s also crucial to know the different payment frequencies for smart investment strategies.
Dividend Yield Explained
For investors focusing on making money through their investments, understanding dividends is vital. The yield shows the income potential of an investment. It also offers insights into a company's financial health and stability.
Calculating Dividend Yield
Calculating dividend yield is about finding the annual dividends per share and dividing it by the stock's market price. For example, if a company pays a quarterly dividend of $0.255 per share, you multiply by four to get $1.02. If the stock is priced at $20, then the yield is 5.1%.
To get dividend per share more accurately, don't just look at the latest payment. It's better to use the most reliable, regular dividends.
Importance of High Yield
Investors often look for high-yield stocks to boost their income from investments. But, it's important to weigh the risks that come with high yields. A high yield might look good, but it could point to problems like a poor business model or a falling share price.
Mature companies or those in sectors like utilities tend to offer higher, stable yields. This is because of their steady cash flow and lower growth chances. On the other hand, very high yields from struggling companies could mean financial troubles.
Here's how different sectors stack up in terms of dividend yields:
| Sector | Typical Dividend Yield |
|---|---|
| Mature Industries | 4-6% |
| Utilities | 3-5% |
| Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) | 5-7% |
| Consumer Staples | 2-4% |
| Technology | 1-3% |
The table shows that sectors with steady cash flow often have higher yields. These numbers are key for investors looking for reliable income, especially when they want to reduce risk and ensure steady returns.
In conclusion, while dividend yields are key in picking investments, they need to be seen in a bigger picture. This includes looking at the company's health, the stability of its sector, and the overall market conditions.
The Impact of Dividends on Stock Prices
Dividends are key in investment strategies, especially their effect on stock prices. Knowing how dividends change stock market trends helps investors make smart choices. We look at the immediate impact of dividend news and the long-term results of continuous dividend strategies.
Short-Term Effects
Stock prices usually react in a predictable way to dividend news. Announcing a dividend often makes stock prices rise before the ex-dividend date. This is because people want to buy the stock to get the dividend. After the stock goes ex-dividend, its price typically falls about the same amount as the dividend. This drop is due to the dividend being paid out, not the company losing value.
Long-Term Trends
Over time, companies that steadily pay dividends are seen as financially healthy. This leads to a slow increase in their stock prices. Dividends are viewed as signs of a company's strong earnings and growth. This boosts investor confidence. Long-term investors are very interested in which stocks pay dividends and how these payments affect stock prices over the years.
| Statistic | Impact on Stock Prices |
|---|---|
| Percentage increase in stock prices following dividend announcements | Varies by industry, generally 1-5% increases within a month |
| Percentage of companies viewed favorably post-dividend announcement | Around 80% perceived as more stable |
| Overall effect on stock price volatility | Reduction in volatility due to perceived stability from regular dividends |
Long-term stock price growth is also boosted by dividend reinvestment plans. Asking "how do you get dividends?" and then reinvesting them leads to direct income and possible stock price rises from the compounding effect. Such plans highlight the link between steady dividends and stock price stability and growth. They appeal to both income-seekers and those who prioritize growth.
Overall, dividends and stock prices are closely connected, impacting investment decisions greatly. The effects can be immediate after dividend news or unfold over time, showing stability and growth. Dividends are a crucial part of planning your investment strategy.
Benefits of Investing in Dividend Stocks
Investing in dividend stocks is useful for all kinds of investors. Whether you're looking for stable income or opportunities to grow your investments, dividend stocks are key. They offer two major benefits, making them a must in a balanced investment portfolio.
Steady Income Stream
Dividend stocks can give you regular cash. This cash normally comes to shareholders every quarter. It helps provide a reliable income, which can be very helpful in retirement.
The payments are a sign of a company's health and stability. So, dividend stocks are a smart pick for those needing steady income.
- Dividend payments are usually quarterly
- Income from dividends can be used to cover living expenses
- Companies with a history of consistent and increasing dividends are often financially robust
Compound Growth Potential
You can also reinvest dividends for more growth. Through reinvestment, you get more shares, increasing your investment over time. This strategy helps grow your investment portfolio, particularly with companies that raise their dividends regularly.
- Reinvestment can accelerate portfolio growth
- Compounding increases the total return on investment, factoring in both capital gains and dividends
- Regularly increasing dividends signify company growth and financial strength
This table shows different dividend stocks, their yields, and growth potential. It highlights how diverse options suit different investment goals:
| Stock Type | Average Yield | Growth Outlook | Dividend Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large Cap Stocks | 1% - 3% | Stable with moderate growth potential | Quarterly |
| High Dividend Yield Stocks | 4% - 6% | Moderate, with potential risk of dividend cut | Quarterly or Annually |
| Growth-focused Stocks | Below 1% | High, with potential for significant long-term gains | Irregular |
| International Stocks | Varies, sometimes higher than U.S. averages | Depends on regional market conditions | Quarterly or Annually |
By understanding when dividends are paid, you can use reinvestment as a tool for growth and stability. Dividend stocks offer solid financial benefits. They are a wise choice for both earning immediate income and achieving long-term investment objectives.
Risks Associated With Dividends
Dividends look like a good way to get steady money, but they have risks. Investors should be careful about risks like lower dividends and market changes. These could really change how much money they make.
Dividend Cuts
Dividend cuts are a big risk for those who invest for dividends. Companies can cut dividends if they're short on money or want to reinvest. For example, REITs or utilities may lower dividends if they don't have enough cash. It's key to know how to determine dividends paid. This means looking at free cash, past payouts, and the company's health.
Market conditions, like higher interest rates, can also lead to dividend cuts. When rates go up, bonds look better than dividends. This can cause people to move money out of dividend stocks. This was clear when the Federal Reserve raised rates, showing how interest rates affect dividends.
Market Fluctuations
Investors need to think about how the market affects dividends. Established companies usually offer more stable dividends. But, they too can struggle during bad market times. On the ex-dividend date, a stock's price often drops by the dividend amount. This can impact the company's value and investor returns.
The global market impact on dividends is also key. Economic trends can change how companies perform. Keeping an eye on these trends helps investors see potential dividend risks.
)))
| Indicator | Impact on Dividends |
|---|---|
| Rising Interest Rates | Makes bonds more attractive, leading to decreased attractiveness of dividend stocks. Sectoral impacts e.g., REITs, could see decreased cash flows resulting in potential dividend cuts. |
| Economic Downturns | Increases the likelihood of reduced earnings; affecting the company's ability to sustain dividend payouts, especially for high-yield stocks, which might be an indicator of financial distress. |
Managing dividend risks isn't just about current yields. It's about deep market and company research. This approach helps investors get dividends without facing big losses.
Popular Dividend Stocks to Consider
Investing in dividend stocks is smart for steady income and high returns over time. You might like tech stocks, consumer goods, or Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) dividends. Understanding their performance and history is key to choosing the right stocks. Here's a look at important sectors for dividend investment.
Technology Sector
Technology companies stand out for their growth and innovation. Many offer great dividends. Investing here can bring income and grow your capital. Yet, it's important to check if their dividends can last despite fast changes in the industry.
Consumer Goods Sector
Consumer goods companies often give steady dividends, thanks to constant demand. Their products are always needed, making their dividends reliable. These companies usually do well, even when the economy doesn't.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
REITs must give most of their income to shareholders, which makes their dividends very attractive. They can yield high returns. When picking REITs, consider their location, sectors, and management's performance.
| Company | Sector | Dividend Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Walgreens Boots Alliance (WBA) | Consumer Goods | 10.47% |
| CME Group (CME) | Financial | 9.73% |
| Altria Group (MO) | Consumer Goods | 7.58% |
| LyondellBasell (LYB) | Materials | 7.29% |
| Dow (DOW) | Materials | 7.01% |
| Crown Castle (CCI) | Real Estate | 6.90% |
| Verizon Communications (VZ) | Telecommunications | 6.79% |
| Pfizer (PFE) | Healthcare | 6.53% |
| Franklin Resources (BEN) | Financial | 6.25% |
These examples show the variety and promise in dividend investing across different sectors. Choosing the right dividend stocks requires a good look at market trends, company success, and economic signs. The goal is to maximize both income and growth from your investments.
How to Build a Dividend Portfolio
Starting to build a dividend portfolio means planning carefully. You'll need to understand how to spread out your investments. We'll cover the key steps to get the best out of your dividends. This will help make sure your investment brings in a steady income.
Diversification Strategies
It's very important to diversify when making a dividend portfolio. You should spread your investments over many sectors. This reduces risk by not putting all your eggs in one basket. Experts suggest a few tips for a solid portfolio:
- Investing in around 20 to 60 stocks lessens risks tied to any single company.
- Keeping less than 25% of your portfolio in one sector helps avoid too much risk.
- Picking companies that consistently raise dividends, like those in the S&P "Dividend Aristocrats."
- Adding stocks from sectors like technology and utilities, which offer varied dividend growth rates.
By following these tips, you can lower the chance of losing from dividend cuts or market ups and downs. This makes your investment more secure and profitable.
Reinvestment Plans
Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRIPs) are key for a dividend portfolio. DRIPs let you automatically buy more shares with your dividends. This can really help your investment grow over time. DRIPs have a few major benefits:
- They allow you to buy more shares without paying extra fees.
- They automate buying new shares so you don't miss out on any chance to invest your dividends right away.
- Investing in companies with growing dividends increases the value of your portfolio and your future income.
Using DRIPs can help meet your long-term financial goals. The compound interest from reinvesting adds up, especially for retirement.
To sum up, building a portfolio that gives a steady income takes careful planning. You need to diversify and use Dividend Reinvestment Plans effectively. These steps help your investment grow. They also provide a reliable income over the years, which is key for financial success in the long run.
Tax Implications of Dividends
Investing means dealing with tax rules that change based on the type of dividends you get. It's key to know the difference between qualified dividends and ordinary dividends. Qualified ones are taxed less, while ordinary ones follow the usual tax rates. For people earning up to $47,025, or $94,050 for married couples, there's no tax on qualified dividends in 2024.
Smart investors understand the value of knowing these rules. This helps them keep more money after taxes. Knowing the tax rules for dividends can really pay off.
Qualified Dividends vs. Ordinary Dividends
To get tax benefits, you must figure out if your dividends qualify for lower taxes or not. Some dividends, like those from certain stocks or funds, need to be held for a while to get this benefit. If you're single making over $44,625 or a couple making $89,250, you'll be taxed at least 15% on these gains in 2023.
It's key to plan well and know the rules. This way, you can make smart choices and save on taxes.
Tax Strategies for Dividend Income
Tax experts suggest careful planning, especially if you're in a higher tax bracket. Say you or your spouse earns more than $518,900. You could then face a 20% tax on capital gains. By using tax-friendly accounts or mixing dividends with growth stocks, you can lower your tax hit.
There's also an extra 3.8% tax on investment money for high earners. Smart investors set aside money for taxes or choose certain investments to benefit from better tax rates. This can help you keep more of your earnings in the long run.
FAQ
What is a dividend and how does it contribute to investment income?
A dividend is part of a company's profits given to shareholders. It is often paid every three months. This sharing of profits helps investors gain from the company's success. Dividends can be in cash, additional shares, or other properties.
How do dividends work and why are they important for investing?
Dividends reward shareholders with company profits. They are key for a steady income from investments. They show a company is doing well and that it believes in future success.
What are the various types of dividends?
There are main types like cash, stock, and property dividends. Cash dividends are money paid directly to shareholders. Stock dividends are extra shares given to shareholders. Property dividends are physical assets given as dividends.
What is the process for dividend distribution?
The dividend process has three important dates. First is the declaration date when it’s announced. Next, the ex-dividend date decides who gets the dividend. Last, on the payment date, dividends are given out.
How can an investor calculate and understand dividend yield?
Dividend yield is the yearly dividend divided by the stock's price, times 100. This shows the income a stock can generate compared to its price.
What impact do dividends have on stock prices?
In the short term, stock prices can drop about the amount of the dividend on the ex-dividend date. Over time, consistent dividends can make stocks more valuable. They show a company is stable and builds investor trust.
Why invest in dividend stocks?
Dividend stocks can provide a constant income and chances for growth if dividends are reinvested. They are vital for a diverse investment portfolio.
What are the risks associated with dividends?
Drawbacks include possible dividend cuts if a company is struggling, leading to a stock value drop. Market changes can also affect dividend payments.
Which sectors offer popular dividend stocks to consider?
Notable sectors for dividend stocks include technology, consumer goods, and Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs). While tech focuses on growth, consumer goods bring stability. REITs are notable for high yields because they must pay out most earnings.
How can one build a successful dividend portfolio?
A strong dividend portfolio needs diversity across sectors, picking stocks with good dividend histories and growth potential. Using Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRIPs) to reinvest dividends boosts the effect of compounding.
What are the tax implications of dividends?
Taxes on dividends differ. Qualified dividends get a lower tax rate than ordinary dividends. Investors should use strategies to enhance after-tax returns.