What Are Retained Earnings? A Simple Guide
Retained earnings are crucial for a company's finances. They show both past success and future promise. These earnings are what's left after paying dividends to shareholders. They can be used to invest back into the company or saved for future needs. You can find them in the equity section of the balance sheet. They change after each accounting period, showing how well a company is doing. Investors and financial experts pay close attention to retained earnings. They know this number can tell more about a company's future than just its net income.
The formula to calculate them is simple yet important: Current Retained Earnings + Profit/Loss - Dividends = Retained Earnings. A new business might start with $0 in retained earnings. This number changes as the business makes or loses money. For example, if a company earns $1,000 and pays no dividends, its retained earnings increase by $1,000. This improves the company's financial report and makes it more attractive to investors.
But retained earnings are more than just a number. They show if a company has been profitable over time. This is attractive to investors looking for a good future return. The size of retained earnings can be affected by how old the company is, its dividend policy, its seasonality, and how profitable it is. Each of these factors adds to what retained earnings reveal about a company.
Key Takeaways
- Retained earnings are a cumulative measure reflecting profits not distributed as dividends.
- The calculation of retained earnings is integral to understanding a company's ability to reinvest in itself.
- A strong balance in retained earnings can signal consistent profitability and forecast future growth.
- Investors and creditors scrutinize retained earnings for insights into financial health and investment risk.
- Efficient management of retained earnings can lead to debt reduction, expansion, and even influence shareholders' dividends.
- Real-world corporate situations, like Coca-Cola's financial results, provide concrete examples of retained earnings’ impact on a company’s financial narrative.
Understanding Retained Earnings
Retained earnings are vital for any business, showing the net gains reinvested, not given to shareholders. These earnings reflect a company's profit and long-term health. Knowing about retained earnings on balance sheet and statements of changes in retained earnings helps understand fiscal stability and growth potential.
Definition of Retained Earnings
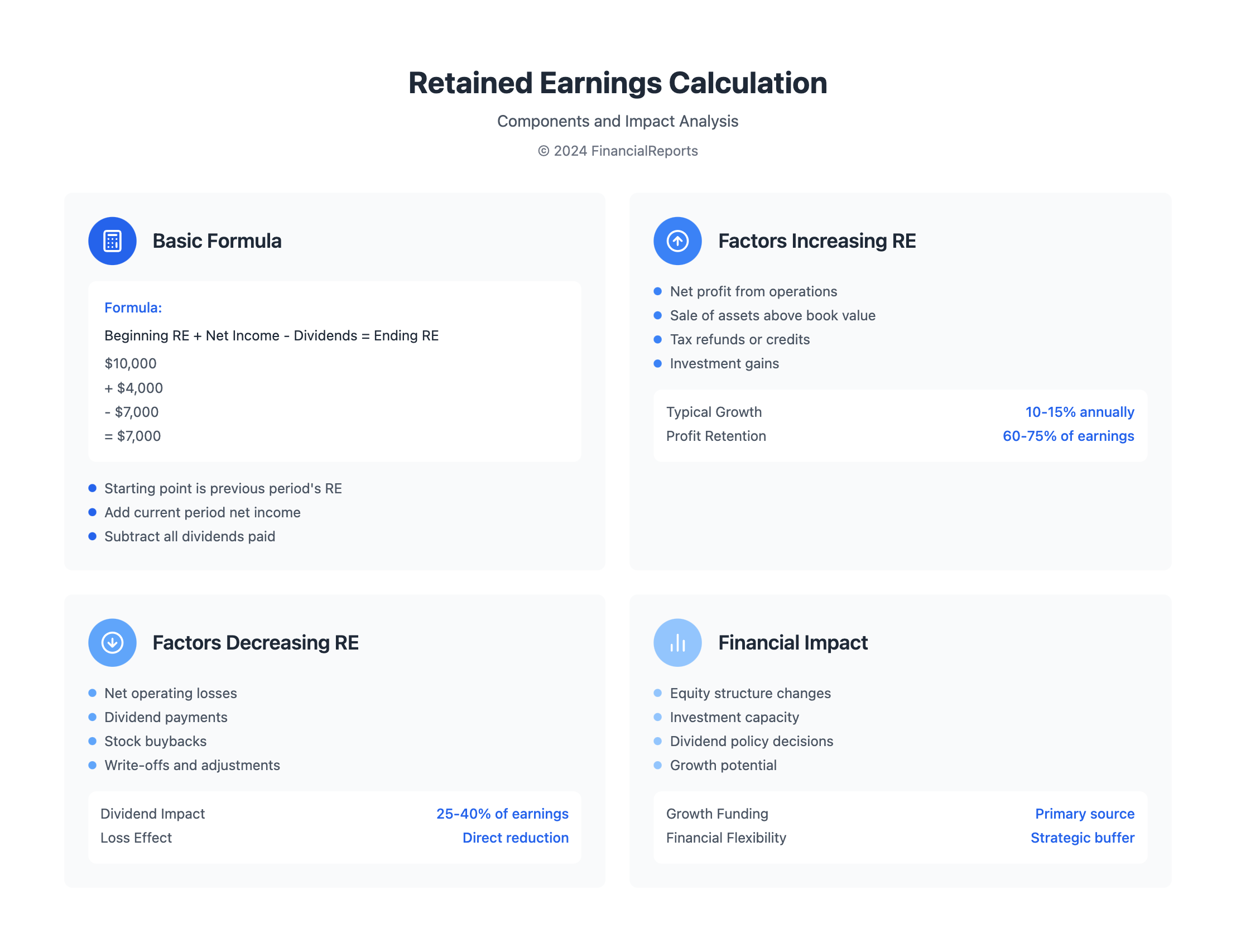
Retained earnings are the total income a company keeps and invests back into the business instead of paying as dividends. This amount changes after every accounting period and shows up under shareholder’s equity. The calculation is simple: Retained Earnings = Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income − Dividends.
The Importance of Retained Earnings
Retained earnings are crucial for a company's growth. They fund research, marketing, better infrastructure, and lowering debt. This investment is key for the company's future earnings and adding value for shareholders.
| Financial Metric | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Retention Ratio | (Net Income – Dividends Distributed) / Net Income | Indicates what proportion of earnings is retained versus paid out as dividends. |
| Retained Earnings to Total Assets Ratio | Retained Earnings / Total Assets | Measures how much of a company’s assets are financed through reinvested earnings. |
| Dividend Payout Ratio | Dividends Distributed / Net Income | Shows the percentage of earnings distributed to shareholders as dividends. |
Reviewing the retained earnings statement offers valuable insight for investment and policy making. For growing businesses, a rise in retained earnings shows potential for expansion. On the other hand, high retained earnings in stable companies could mean reallocating funds, perhaps by raising dividends or stock buybacks.
Digital tools like Datarails FP&A software make analyzing retained earnings easier. They help in making informed decisions, boosting financial procedures, and enhancing strategic financial planning.
How Retained Earnings Are Calculated
Finding out retained earnings is key for companies to understand their financial health and future plans. We look into the retained earnings formula and explain its main parts.
Formula for Calculating Retained Earnings
The formula for retained earnings is simple but tells a lot about a business. It involves adjusting the starting balance with the earned net income or loss, then subtracting any dividends. Here is the formula:
- Beginning Retained Earnings: The total retained profit from past financial periods.
- Net Income/Loss: The profits or losses for the current period, influencing retained earnings.
- Dividends Paid: The dividends given to shareholders, deducted from total earnings.
This method lets stakeholders know a company's financial situation clearly. It shows the company's careful management of its finances.
Components Influencing Retained Earnings
Several things affect retained earnings, shaping financial strategies for companies:
| Component | Impact on Retained Earnings |
|---|---|
| Net Income | Goes up with more profits. |
| Dividends Paid | Goes down when more dividends are given out. |
| Business Cycles | Changes with the economy and company performance. |
| Operational Expenditures | Influences net income and thus retained earnings. |
| Retention Ratio | Shows the amount of profit kept versus given as dividends. |
To know retained profit means seeing how business moves and market conditions change the formula. This knowledge helps in planning and predicting future finances and stability.
Each part of this process highlights a commitment to being open and honest financially. This ensures everyone involved knows the company's position and how it can use retained earnings for growth and security in the future.
The Role of Retained Earnings in Financial Statements
Retained earnings are crucial in financial reports. They connect past outcomes with future possibilities. These earnings are found in income statements, balance sheets, and shareholder equity statements. They show how essential they are in financial documentation and strategy.
Income Statement Influence
Retained earnings show a company's total profit or loss over time. They start with the net income on the income statement. This figure helps decide how much earnings the company keeps or gives out as dividends.
Balance Sheet Representation
Where are retained earnings on a balance sheet? They're in the shareholders’ equity section, usually at the bottom. This spot highlights the connection between retained earnings and a company's value. It shows how past profits, kept in the company, boost its financial health.
Statement of Shareholder Equity Impact
An example of a retained earnings statement shows earnings changes during an accounting period. It explains these changes due to kept profits and paid dividends. This statement really shows how a company manages its finances.
| Financial Statement | Role of Retained Earnings | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Income Statement | Source of Net Income | Initial calculation basis |
| Balance Sheet | Part of Shareholders' Equity | Reflects financial health |
| Statement of Shareholder Equity | Tracks adjustments in retained earnings | Shows financial strategy effectiveness |
Including retained earnings in major financial statements shows their value in analyses. It helps stakeholders make smart choices about the company's financial policies and growth plans.
Key Differences Between Retained Earnings and Dividends
Understanding the difference between retained earnings and dividends is key. They are essential in a company's financial strategy. They influence how a company grows or pays its shareholders.
Definition of Dividends
Dividends are what a company pays its shareholders from its profits. They share the company's success with its owners. But, these payments are only made if profits are enough.
How Earnings Are Distributed
Retained earnings, unlike dividends, are not given out. Instead, they are kept to grow the company's core business or pay off debts. The formula Retained Earnings = Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income - Dividends Paid shows their purpose. They fund growth or save for future needs.
| Financial Strategy | Impact on | Utilization |
|---|---|---|
| Retained Earnings | Company Growth | Reinvestment, Liability Reduction, Emergency Fund |
| Dividends | Shareholder Wealth | Profit Distribution |
Choosing between boosting retained profit and giving out dividends depends on several factors. These include the company's financial health and its goals. A strong calculate net retained earning signals good management and long-term planning.
Getting the retained earnings meaning helps experts assess a business. It shows how well it manages its finances and its potential for success.
Why Retained Earnings Matter for Businesses
Understanding retained earnings is key for businesses looking to grow and stay ahead. These earnings help fund projects internally, avoiding more debt. They're not just about profit but are crucial for a company’s financial well-being.
Funding Growth Opportunities
Retained earnings are vital, especially during growth stages. They let businesses invest in new tech, grow operations, or tackle new markets without outside money. This keeps the debt-to-equity ratio low, making the company more attractive to investors and partners.
Financial Stability Indicator
A healthy balance of retained earnings shows good management to investors and stakeholders. It means a company can grow and stay stable. Showing the calculations of these earnings from financial statements builds trust with financial partners and shareholders.
Deciding how much to reinvest versus distribute as dividends is complex. It impacts short-term shareholder value and long-term goals. Let's check how retained earnings affect key financial areas:
| Financial Indicator | Description | Impact of Retained Earnings |
|---|---|---|
| Return on Equity | Measurement of a company's profitability that reveals how much profit a company generates with the money shareholders have invested. | Higher retained earnings can significantly improve ROE, indicating proficient business management and profitable operations. |
| Debt-to-Equity Ratio | Indicator of the relative proportion of shareholders' equity and debt used to finance a company's assets. | Lower ratios can manifest due to increased retained earnings, suggesting greater financial autonomy and lesser reliance on debt. |
| Retention Ratio | Shows the percentage of net income retained to reinvest in the business, as opposed to being paid out as dividends. | Retained earnings improvements reflect a higher retention ratio, displaying a dedicated reinvestment in company growth. |
Managing retained earnings well can give a business a strong financial base and room to grow. Using these earnings wisely avoids financial issues and makes a company competitive in its field.
How Retained Earnings Impact Shareholder Value
Retained earnings are key for a company's growth and reinvestment. They show how well a company can use its profits to grow. Understanding the accumulated retained earnings withdrawal impact on income statement is vital. It shows how these actions affect shareholder value.
Retained Earnings as a Growth Signal
Reinvesting retained earnings shows confidence in a company's future. It can include starting new projects or improving operations. This smart use of funds boosts accumulated retained earnings withdrawal impact on the operation. It raises investor confidence and can increase stock value.
Effect on Stock Prices
Investor views on a company's financial health affect stock prices. If retained earnings grow and are used well, it signals strong future earnings. The accumulated retained earnings withdrawal should be clearly explained. This builds trust and can improve shareholder returns.
Good management of retained earnings can greatly affect a company's value. It's important to find a balance between paying dividends and reinvesting. This balance is key for long-term growth and benefitting shareholders.
Common Misconceptions about Retained Earnings
People often simplify retained earnings too much. This can mislead others and hide true financial meanings. We need to correct wrong ideas about this key part of financial statements. We'll focus on what the balance in retained earnings represents and clear up misunderstandings about a retained deficit.
Retained Earnings Are Not Savings
Thinking of retained earnings as just a business's savings is a common mistake. This view doesn't see the strategic importance of these earnings. They're not just sitting idle. Retained earnings are used for important purposes. Things like research, paying off debt, and growing the company benefit from these funds. They are the profits left after dividends are paid, not just unused cash.
The Relationship with Profitability
Retained earnings are closely linked to how profitable a business is over time. A high balance usually means the company has made money in the past. But, it doesn't always show if the company is doing well now or will in the future. A retained deficit could mean losses or big spending that went beyond earnings.
| Financial Aspect | Description | Impact on Retained Earnings |
|---|---|---|
| Net Income | The profitability after all expenses have been deducted from revenues | Increases retained earnings |
| Dividends Paid | Distributions to shareholders | Decreases retained earnings |
| Retained Deficit | Occurs when cumulative losses and dividends exceed profits | Reduces retained earnings below zero |
| Funding Investments | Using retained earnings for expansion or debt reduction | Shifts retained earnings into asset growth or liability reduction |
Retained earnings show how a company manages its profits for development and value. It's crucial to understand this for financial planning or investment. Knowing the balance in retained earnings represents more than just saved money. It's about strategic choices that affect a company and its stakeholders.
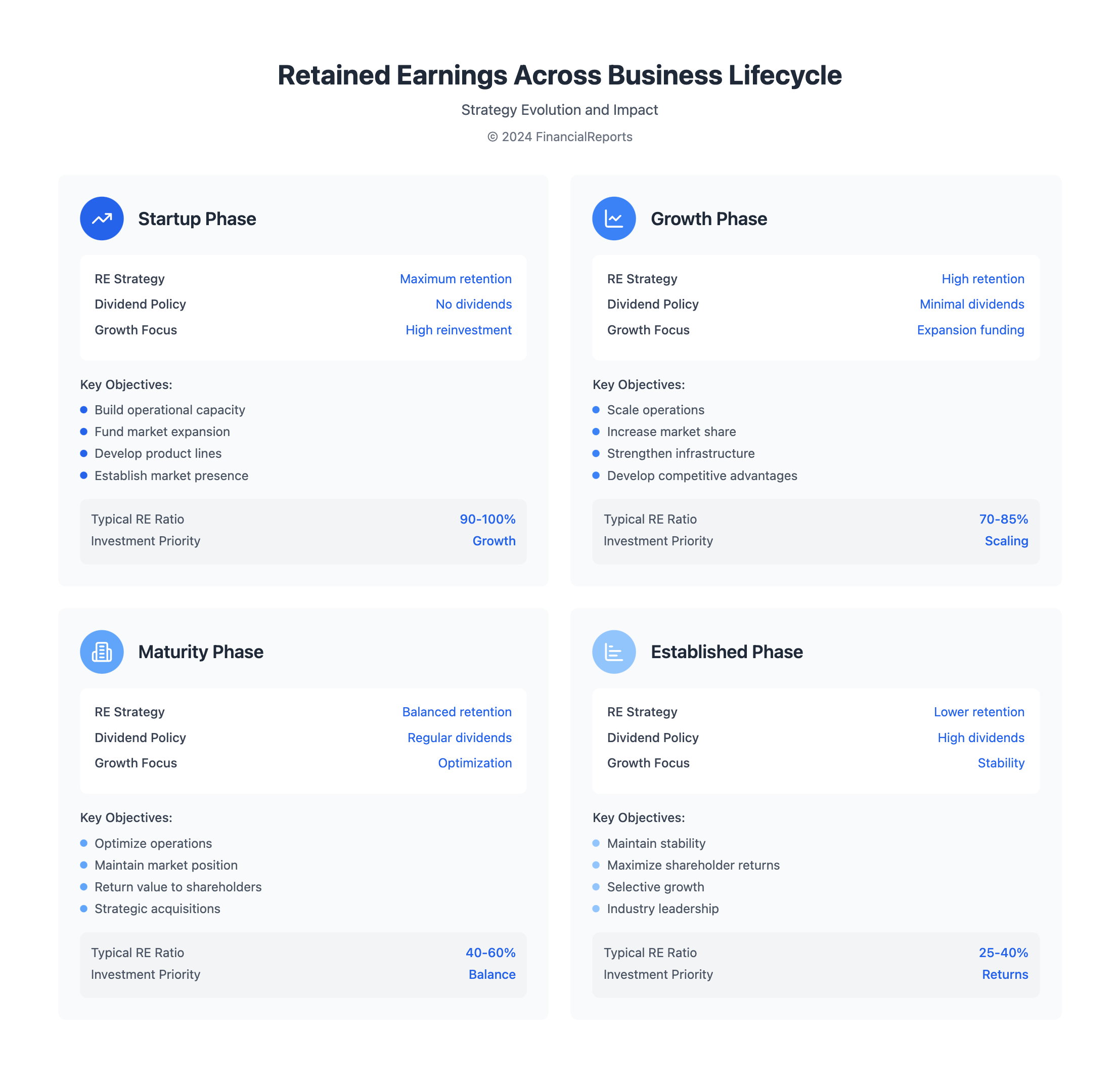
Retained Earnings and Business Lifecycles
It's essential to understand the role of retained earnings across business stages. These reserves are key for financial tactics and flexibility. Knowing the initial amount of retained earnings helps companies manage changes smoothly. This affects reinvestment and dividend decisions deeply.
Startups and Early Growth Phases
In the beginning or early growth stages, startups rely on retained earnings for reinvestment. They might not make much profit at first. Yet, they often use any retained earnings to grow and reach more customers. To figure out retained earnings, just follow: Retained Earnings = Start Retained Earnings + Net Income – Dividends.
This method boosts quick innovation and helps them stay ahead without needing outside funds.
Established Businesses
When companies mature, how they use retained earnings changes. Established businesses have a positive history with these earnings. They use them for smart investments or to give dividends. This stage sees strategic use of retained earnings for growth or rewards to shareholders.
Choosing between keeping earnings or giving dividends affects the company's future and shareholder happiness. Knowing the starting amount of retained earnings is critical for good planning. It keeps the company's equity strong.
| Financial Aspect | Startups | Established Businesses |
|---|---|---|
| Use of Retained Earnings | Reinvestment for Growth | Diversification, Expansion, Dividends |
| Impact on Financial Health | Building Reserves | Enhancing Stability and Shareholder Value |
| Challenges | Limited Resources | Optimal Resource Allocation |
Retained earnings management changes as a company grows. Effective management is key, no matter the stage. It boosts both the financial health and appeal to investors of the business.
Factors That Can Diminish Retained Earnings
Knowing what can lower retained earnings is key for managing a firm's finances well. We'll look at the main reasons retained earnings might fall on a balance sheet.
Business Losses and Write-offs
Big losses and write-offs can really hurt retained earnings. This happens when companies don't do well operationally or face market drops. These lead to less revenue and net income. This makes it hard to keep a good level of retained earnings.
Also, big write-offs of assets that are too old or valued too high can quickly reduce retained earnings. These adjustments show changes in asset values that impact the company's financial health.
Dividend Payments
Paying out dividends to shareholders also lowers retained earnings. When companies pay dividends, they share some of their net income with shareholders. This means there's less retained earnings left.
To grasp how these factors play out, here's a table showing how retained earnings can drop because of business losses, write-offs, and dividends:
| Year | Beginning Retained Earnings | Net Income | Dividends Paid | End Retained Earnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | $5,000,000 | -$2,000,000 (loss) | $500,000 | $2,500,000 |
| 2022 | $2,500,000 | $1,000,000 | $800,000 | $2,700,000 |
| 2023 | $2,700,000 | $500,000 | $300,000 | $2,900,000 |
This table shows how retained earnings change based on how well a company handles its income and expenses, along with its decisions about dividends. It's crucial for stakeholders to keep an eye on these changes to understand the company's financial path.
In summary, knowing how to figure out retained earnings and what causes them to decrease is vital. This knowledge helps in making wise financial and operational choices. Such choices support a company's growth and stability.
Effective Management of Retained Earnings
The management of retained earnings is key for growth and shareholder value. Knowing how to figure out retained earnings and using them wisely lets companies reach their full potential. We will explore how to retain earnings and find a balance between them and dividends.
Strategies for Retaining Earnings
Managing retained earnings starts by understanding a statement of retained earnings example. It helps decide how much profit to reinvest or give to shareholders. Some strategies include:
- Putting earnings into projects with high returns to grow organically.
- Making the company's financial base stronger for stability and future chances.
- Using retained earnings for smart buys or investments that fit long-term goals.
Balancing Retained Earnings and Dividends
It's crucial to find a middle ground between reinvesting profits and paying dividends. This choice affects investor happiness and future fund raising. Companies need to think about:
- The current market situation and what shareholders expect.
- What’s more important—long-term goals or quick returns for shareholders.
- The company's financial strength, looking at the retention ratio and performance history.
| Criteria | Impact on Retained Earnings | Impact on Dividends |
|---|---|---|
| Market Conditions | Dictates reinvestment needs based on operational demands and growth opportunities. | Influences dividend rate adjustments in response to investor expectations and industry standards. |
| Strategic Goals | Targets earnings reinvestment in core areas critical for long-term success. | Aligns dividend policies with long-term capital strategy and shareholder value creation. |
| Financial Health | Assess ability to fund future projects without compromising operational integrity. | Ensures dividends are sustainable, reflecting the company’s true profitability and operational achievements. |
Learning how to figure out retained earnings helps businesses plan better. Every retained or given dollar must match the firm's financial and strategic goals. A smart approach balances immediate needs with long-term growth.
Reporting Retained Earnings: What You Need to Know
Accurate reporting of retained earnings shows a company's financial health. It's key to understanding shareholder equity. It gives us a look into the company's past and future financial potential.
Key Guidelines for Reporting
Companies must follow specific guidelines for reporting retained earnings. It's important to know how to calculate retained earnings from the balance sheet. This step mixes different financial data points together.
- The retained earnings formula is vital: Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income - Dividends Paid = Ending Retained Earnings.
- At each period's end, companies should report retained earnings in a statement. This summary shows the financial changes during that time.
- Records need to show beginning retained earnings, the period's net income or loss, dividends paid, and ending retained earnings.
Using this formula and its data keeps financial reporting clear. This allows everyone to track how well a company manages and plans financially over time.
Importance of Transparency in Reporting
Being clear in financial reporting, especially with retained earnings, is crucial. It builds trust with investors and shows a company's commitment to good financial management.
- Companies should disclose any big restrictions, like loan agreement terms that could limit dividends from retained earnings. This shows the complete financial status and decision freedom.
- Clear reporting of retained earnings helps set the right expectations with investors about the company’s growth and financial plans.
This honest reporting is key for solid financial planning. It showcases how well management uses retained capital for growth, even in tough economic times.
| Component | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Beginning Retained Earnings | Funds retained at the start of the period | $10,000 |
| Net Income | Profit earned during the period | $4,000 |
| Dividends Paid | Dividends distributed to shareholders | $7,000 |
| Ending Retained Earnings | Funds retained at the end of the period | $7,000 |
By sticking to these rules, companies meet regulatory standards. They also build trust with investors. Savvy investors look for clear use of retained earnings. They see it as a sign of a company's long-term success and good management.
Real-World Examples of Retained Earnings
Understanding retained earnings is key for strong financial moves. Market leaders show how keeping profits leads to growth and trust. Apple Inc. is a prime example of this strategy.
From 1995 to 2012, Apple kept all its profits to support its growth and innovation. After starting to share dividends in 2012, they still reinvested 70-75% of earnings.
Successful Companies and Their Retained Earnings Strategies
In its 2022 report, Apple showed $49.25 billion in retained earnings. This result came from smart reinvestment. Many companies follow a formula to decide how much profit to keep. This helps them grow steadily.
For instance, Winnie’s Web Design, LLC used this formula wisely. They ended the year with $125,000 more in retained earnings. The right calculation can make a big difference.
Lessons Learned from Failures in Retained Earnings Management
Yet, managing retained earnings isn't always successful. Bad investments can disappoint investors. But many small businesses find success by reinvesting 60% of their profits, according to the Harvard Business Review.
A local bakery raised its retained earnings from $10,000 to $35,000. They did it by managing profits and dividends well. Mastering retained earnings is crucial for smart planning and making wise choices.
FAQ
What Are Retained Earnings?
Retained earnings are the money a company keeps instead of giving it to shareholders as dividends. This money is either put back into the company or saved for later.
How Are Retained Earnings Calculated?
To calculate retained earnings, start with the beginning balance. Add any profit or subtract any loss. Then subtract any dividends given out.
What Is the Importance of Retained Earnings?
Retained earnings show a company's financial strength and profit-making ability. They tell us how a company uses its earnings for growth and new chances.
What Is the Impact of Retained Earnings on the Income Statement and Balance Sheet?
Retained earnings don't show up on the income statement. But, they are influenced by the net income or losses reported there. On the balance sheet, they're listed under shareholders' equity. This shows the profits put back into the company.
How Do Dividends Affect Retained Earnings?
Dividends lower retained earnings because they share the company's profits with shareholders. When dividends are paid, it reduces the retained earnings amount.
Why Do Retained Earnings Matter for Businesses?
Retained earnings are crucial because they fund growth, innovation, and stability. They do this without needing extra debt or new investors.
How Can Retained Earnings Impact Shareholder Value?
Retained earnings can boost shareholder value by funding activities that lead to more profit and growth. This can make the stock price go up.
Are Retained Earnings the Same as Savings?
No, retained earnings are different from savings. Even though they are not given out as dividends, they are planned for use in operating, growing, and expanding the company.
What Is the Relationship Between Retained Earnings and Profitability?
Retained earnings directly show a company's profitability. If retained earnings are positive, it means the company has been making profits. A deficit means there have been losses or too much given out in dividends.
How Do Business Lifecycles Affect Retained Earnings?
Business lifecycles have a big impact on how retained earnings are used. New and growing companies might put all their profits back into growing fast. Older companies might share profits with shareholders and reinvest some.
What Factors Can Diminish Retained Earnings?
Less retained earnings can result from business losses, big one-time costs, and dividends to shareholders.
What Are the Strategies for Effectively Managing Retained Earnings?
Good strategies involve a balance between putting money back into the business and giving dividends to shareholders. It's also about sticking to long-term goals and being clear with investors.
What Are the Key Guidelines for Reporting Retained Earnings?
Important rules for reporting retained earnings include showing them at the end of each period on the balance sheet. And being clear about any changes to these earnings.
Can You Give Real-World Examples of Companies That Successfully Manage Retained Earnings?
Apple Inc. has done a great job with its retained earnings. They've used the money for new products and expanding their market. This has led to a higher stock price and more value for shareholders.