Unlocking the Power of the Price to Book Ratio
The price to book ratio is a key financial tool. It compares a company's market value to its book value. This gives investors insights into whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued. It's a vital tool for making investment decisions.
This ratio helps investors understand a company's value. It also helps spot good investment chances. The price to book ratio is calculated by dividing the stock's current price by its book value. It's mainly used for companies like insurance, real estate, and investment trusts.
Key Takeaways
- The price to book ratio compares a company's market price per share to its book value per share.
- A low price to book ratio (less than 1) may indicate that a stock is undervalued, while a higher ratio (greater than 1) may indicate that it is overvalued.
- The price to book ratio is used to evaluate a company's current market value relative to its book value.
- Book value per share is calculated as total assets minus total liabilities divided by the number of outstanding shares.
- The comparison of price to book ratios is best done between companies within the same industry.
- The price to book ratio is a valuable tool for investors to assess company valuation and identify potentially good investments.
- High-value procurement projects, such as cost reduction initiatives and strategic sourcing, can help improve the price to book ratio.
What is the Price to Book Ratio?
The price to book ratio, or p/b ratio, is a way to check if a company's stock price is fair. It compares the current stock price to the company's book value. The book value is what you'd get if the company sold everything and paid off all debts.
This ratio is key for investors. It shows if a company's stock price is good compared to its financial health. A low p/b ratio might mean the stock is cheap. A high ratio could mean it's too expensive. For example, a ratio of one means the stock price matches the company's book value.
Definition and Explanation
To find the p/b ratio, you divide the stock price by the book value. This ratio helps compare companies but remember, it depends on the industry and company specifics. Companies with lots of debt or losses might have misleading ratios.
Importance in Financial Analysis
Analysts and investors use the p/b ratio to pick stocks. It's great for value investors looking for cheap stocks with growth chances. By looking at the p/b ratio with other numbers, investors can understand a company's worth better. This helps them make smarter choices.
How is the Price to Book Ratio Calculated?
The price to book ratio is a way to value a company. It compares the company's market value to its book value of equity. The price to book value formula is simple: just divide the stock's current price by the book value per share for the latest quarter. This can also be shown as: Market Capitalization / Net Book Value or Share Price / Net Book Value per Share.
This ratio is key for investors. It shows if a company's stock is cheap or expensive. A low p b ratio might mean the stock is a good buy. On the other hand, a high p b ratio could mean it's overpriced.
To figure out the price to book ratio, follow these steps:
- First, find the company's market capitalization. This is done by multiplying the current share price by the total shares outstanding.
- Then, calculate the book value. This is done by subtracting liabilities from assets.
- Lastly, divide the market capitalization by the book value to get the price to book ratio.
Significance of Price to Book Ratio in Investing
The Price to Book (P/B) ratio is key in investing. It shows how much investors pay for each dollar of assets. A good price to book ratio changes based on the industry and market. For example, a P/B ratio below 1 might mean a stock is undervalued. A ratio above 1 could show it's overvalued or has growth chances.
When looking at the stock book price, investors should check the P/B ratio with other financial numbers. This ratio can change with market ups and downs. It's important to keep an eye on it, even when the market is shaky. The pbr ratio is a basic tool but should be used with other financial data and industry trends.
Here are some key points to consider when using the P/B ratio in investing:
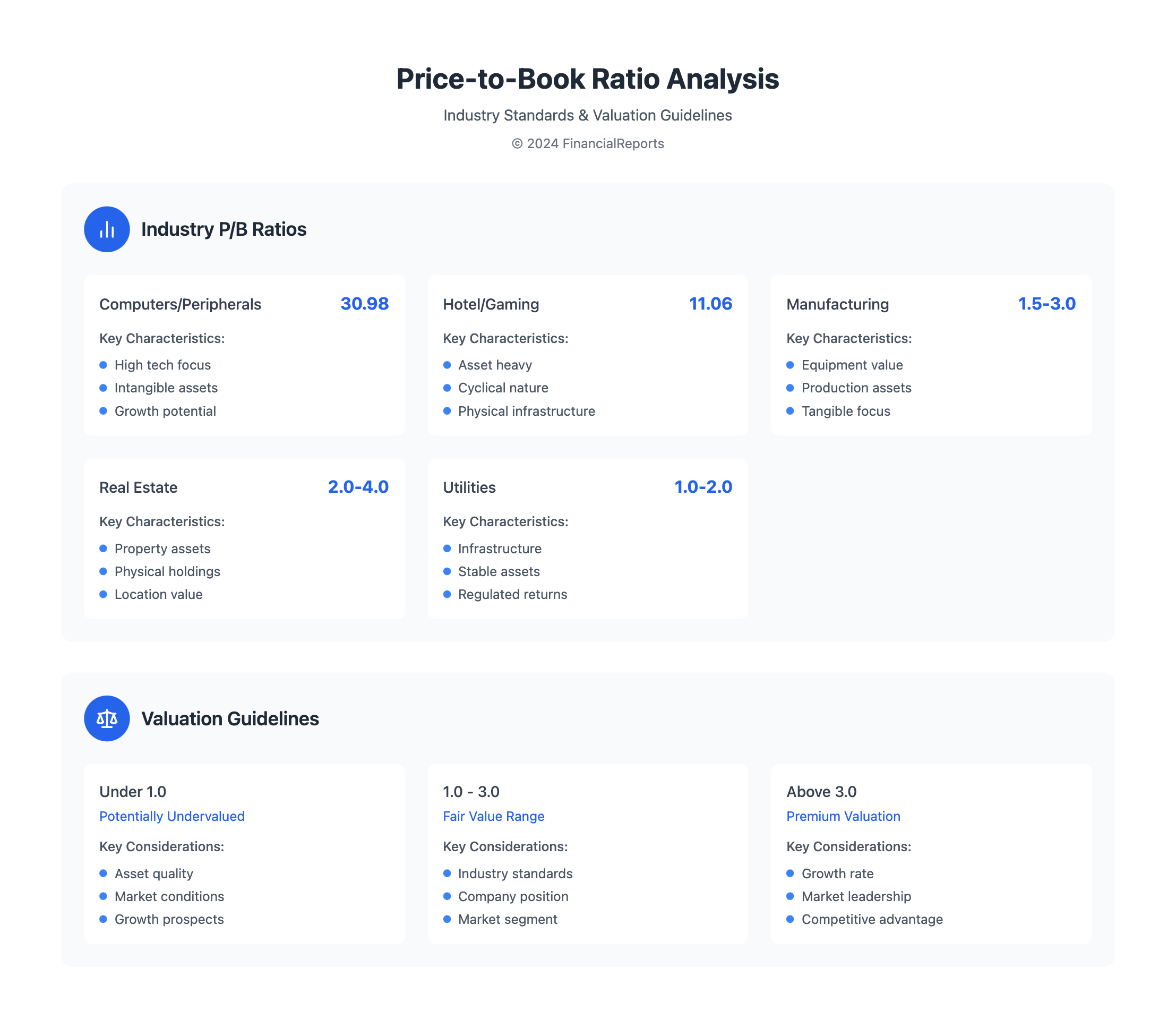
- The P/B ratio is useful for valuing companies in industries like manufacturing, real estate, and utilities.
- Investors can use the P/B ratio to find undervalued stocks for long-term investments.
- Value investors look for stocks where the market price is lower than the book value using the P/B ratio.
| Industry | Typical P/B Ratio |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 1.5-3.0 |
| Real Estate | 2.0-4.0 |
| Utilities | 1.0-2.0 |
Understanding the Price to Book ratio helps investors make better choices. They can spot undervalued stocks for long-term growth.
Interpreting Price to Book Ratio Values
To understand price to book ratio values, knowing the price to book formula is key. It helps grasp what makes a good price to book value. The value to book ratio compares a company's market value to its book value. A ratio under 1 might show the stock is cheap. A ratio over 1 could suggest it's overpriced.
When looking at the price to book ratio, keep these points in mind:
- Industry-specific ratios: Different industries have different price to book ratios. Tech companies often have higher ratios because of their intangible assets and growth.
- Book value: A company's book value can be influenced by intangible assets like copyrights and brand awareness. These can be a big part of a company's worth.
- Market expectations: A higher price to book ratio means investors think management will make more value from assets.
Understanding the price to book ratio helps investors spot undervalued stocks. It's important to use this metric with other financial ratios, like the price to earnings ratio. This way, you get a full picture of a company's value.
Limitations of the Price to Book Ratio
The price to book ratio is useful for checking a company's value. Yet, it has its downsides. A low ratio might mean a company is cheap, but it could also show financial problems. To really understand a company's worth, investors should use a calculator and look at other financial numbers too.
This ratio doesn't count intangible assets like patents or brand names. This can give a skewed view of a company's value, mainly for businesses with lots of these assets. Also, the ratio can change based on the industry. So, it's key to compare companies in the same field. By keeping these points in mind, investors can get a clearer picture of a company's value.
Some important things to think about when using the price to book ratio include:
- Comparing companies within the same industry to account for industry variability
- Considering intangible assets and their impact on a company's value
- Using a price to book ratio calculator to accurately assess a company's valuation
Knowing the price to book ratio's limits helps investors make better choices. It's one tool among many for understanding a company's financial health and value. By using it with other metrics, investors can make more informed decisions.
How to Use Price to Book Ratio Effectively
To use the price to book ratio well, mix it with other financial metrics like P/E and P/S ratios. This gives a full view of a company's value. The pb ratio formula is great for spotting cheap or pricey stocks.
When looking at the price to book ratio, think about the company's field and compare it to others. A low price to book ratio might mean a stock is cheap. A high ratio could mean it's too expensive. Here are some tips for investors:
- Use the price to book ratio with other metrics like P/E and P/S ratios.
- Compare the company's ratio to its industry and peers.
- Look at the company's growth, management, and other important factors before investing.
By using these tips and the price to book ratio wisely, investors can make smarter choices. This could lead to better returns on their investments.
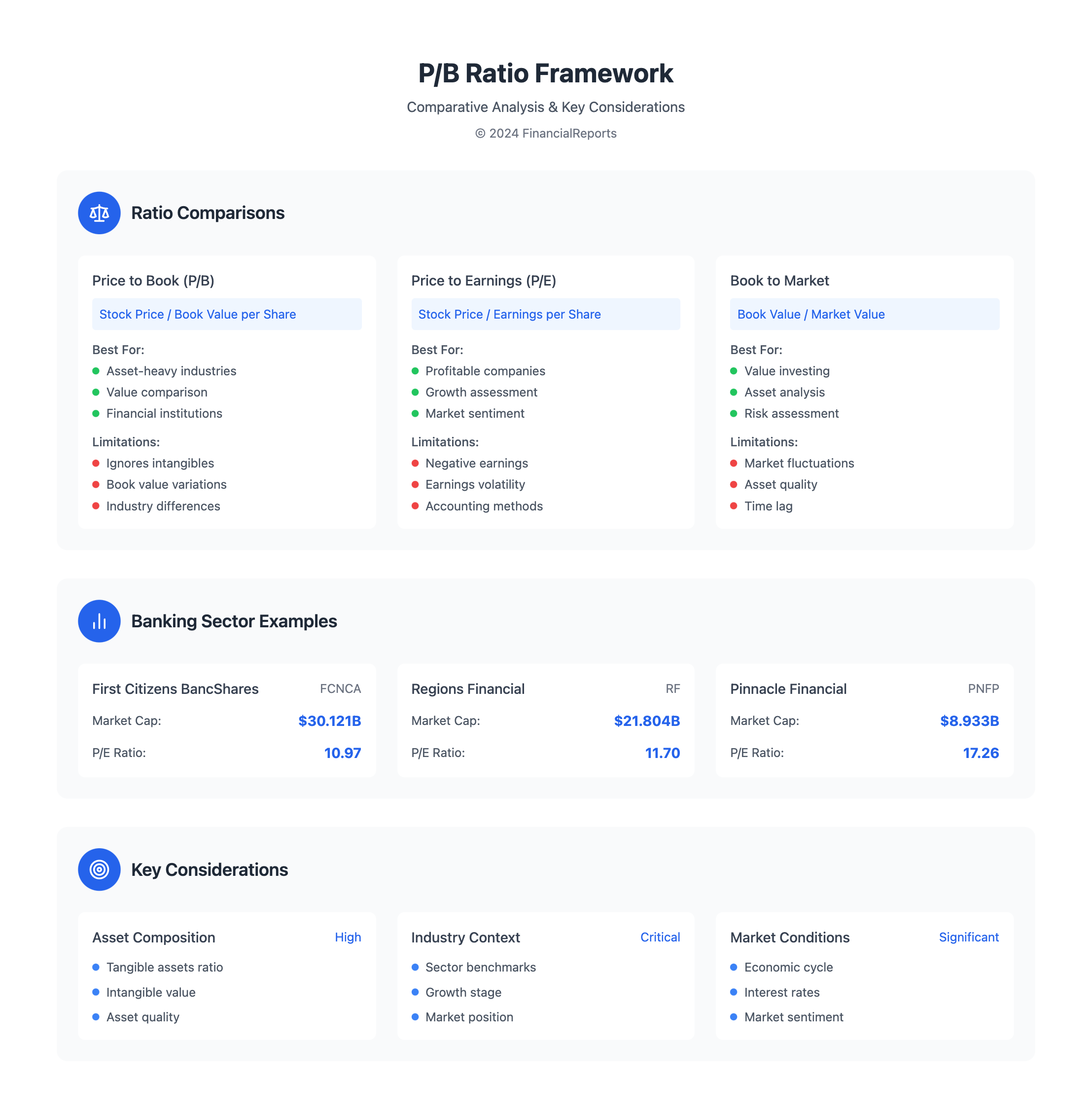
| Ratio | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Price to Book (P/B) | Stock price / Book value per share | Compares stock price to the value of a company's assets. |
| Price to Earnings (P/E) | Stock price / Earnings per share | Compares stock price to a company's earnings. |
| Price to Sales (P/S) | Stock price / Sales per share | Compares stock price to a company's sales. |
Historical Trends in Price to Book Ratio
The price to book value ratio has changed over time, due to many economic factors. It's key to look at long-term market trends to understand this. For example, the price to book sector data shows big differences. The Computers/Peripherals industry has an average ratio of 30.98, while the Hotel/Gaming industry has a ratio of 11.06.
Looking at companies like Popular Inc. gives us more insight. As of December 26, 2024, Popular Inc.'s ratio is 1.20. Over the last 10 years, its ratio has varied, from 1.32 in 2022 to 0.88 in 2023. This shows why the price to book value ratio is important for evaluating a company's worth.
When looking at the price to book ratio, it's important to consider the company's size and revenue. Here's a table showing this for Banks - Southeast industry sector companies:
| Company | Market Capitalization | Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| First Citizens BancShares (FCNCA) | $30.121 billion | $10.97 PE ratio |
| Regions Financial (RF) | $21.804 billion | $11.70 PE ratio |
| Pinnacle Financial Partners (PNFP) | $8.933 billion | $17.26 PE ratio |
By studying historical trends in the price to book ratio, investors can better understand a company's value. This helps in making smarter investment choices.
Case Studies of Price to Book Ratio in Action
The price to book value formula is key in making investment choices. It shows up in many case studies. A low ratio might mean a stock is cheap, while a high ratio could mean it's overpriced.
Looking at the pb ratio helps investors see a company's financial health. It compares the market price to the book value per share. This ratio is a big deal in the investment world.
Successful Investment Strategies
Value investors use the price to book ratio to find cheap stocks. Stocks with a ratio under 1.0 are often seen as good buys. But, stocks with a high ratio might not be the best choice.
Lessons from Market Failures
But, the price to book ratio isn't perfect. Other factors matter too. A low ratio doesn't always mean a stock is good. And a high ratio doesn't always mean it's bad.
| Industry | Average Price to Book Ratio |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 0.8 |
| Technology | 1.5 |
| Retail | 1.2 |
In conclusion, the price to book ratio is useful but not the only thing to look at. By understanding the formula and its uses, investors can make better choices.
Price to Book Ratio versus Other Ratios
The price to book ratio formula is a key tool for investors. It's not the only way to check a company's stock value. By comparing it to other ratios, like the price to earnings ratio, we get a fuller picture of a company's worth.
The price to earnings ratio can change due to share buybacks or accounting method shifts. These actions can alter the stock price. On the other hand, the book value of assets can be tweaked by adjusting cash reserves or buying back shares. This affects the price to book ratio.
A comparison of different financial ratios can be seen in the following table:
| Ratio | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Price to Book | Stock price / Book value per share | Compares a company's market value to its book value |
| Price to Earnings | Stock price / Earnings per share | Compares a company's market value to its earnings |
| Book to Market | Book value / Market value | Compares a company's book value to its market value |
Looking at several financial ratios helps investors understand a company's value better. This leads to smarter investment choices.
Future of the Price to Book Ratio in Investing
The financial world is always changing, and so is the role of the Price to Book (P/B) ratio. With more focus on intangible assets and tech companies, old ways of valuing stocks are being questioned. The P/B ratio, once a key tool, now faces the challenge of keeping up with these changes.
Evolving Financial Analysis Techniques
New methods like artificial intelligence and big data are changing how we use the P/B ratio. These tools could give us a better look at how a company's market value compares to its assets. This could lead to a deeper understanding of the P/B ratio's role in investment analysis.
Predictions and Trends to Watch
Experts say the P/B ratio's future depends on its ability to value companies with lots of intangible assets. This includes things like patents, brand value, and data-driven businesses. As accounting rules change to reflect these new values, the P/B ratio might need updates or new metrics to stay useful.
Investors need to watch for shifts in the global economy, changes in what investors want, and how new tech is used in finance. By keeping up with these trends and adjusting their use of the P/B ratio, investors can stay ahead in the ever-changing world of investing.
FAQ
What is the Price to Book Ratio?
The Price to Book (P/B) Ratio compares a company's market value to its book value. It helps investors understand a company's worth and find good investment opportunities.
How is the Price to Book Ratio calculated?
To find the P/B Ratio, divide a company's stock price by its book value per share. The formula is: P/B Ratio = Market Price per Share / Book Value per Share.
What is the significance of the Price to Book Ratio in investment analysis?
The P/B Ratio is key for investors. It helps them see if a company is overvalued or undervalued. It also lets them compare companies in different industries.
How should investors interpret high and low Price to Book Ratio values?
A low P/B ratio (below 1) might mean a company is undervalued. A high P/B ratio (above 3) could mean it's overvalued. But, the meaning changes based on the industry and other financial factors.
What are the limitations of the Price to Book Ratio?
The P/B Ratio might not fully show a company's value, like for companies with lots of intangible assets. Industry differences and accounting practices can also affect its accuracy.
How can investors effectively use the Price to Book Ratio in their investment strategies?
Investors should use the P/B Ratio with other metrics, like the Price to Earnings (P/E) Ratio. They should also consider qualitative factors for a full view of a company's value and growth.
How have historical trends in the Price to Book Ratio evolved over time?
The P/B Ratio has changed over time, influenced by the economy, industry shifts, and the growing role of intangible assets.
Can you provide real-world examples of how the Price to Book Ratio has been used in successful investment strategies?
There are examples of investors using the P/B Ratio to find undervalued companies and make money. There are also cases where relying too much on the ratio led to losses.
How does the Price to Book Ratio compare to other common financial ratios, such as the Price to Earnings (P/E) Ratio?
The P/B Ratio and P/E Ratio offer different views. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses, depending on the industry and investment goals. It's important to understand how they relate for a complete financial analysis.
What are the future implications for the Price to Book Ratio in investment analysis?
As the financial world changes, with more focus on intangible assets and tech companies, the P/B Ratio's role might need to evolve. It must stay relevant for making smart investment choices.