Unlock the Power of Share Ratio in Financial Data
Financial ratios, like share ratio and stock ratio, are key for checking a company's health and performance. They help experts and investors understand a company's liquidity, growth, and profitability. The share ratio is important for seeing how a company's stock price relates to its financials.
Using ratios like the current ratio and debt-to-equity ratio helps investors see if a company is stable and growing. For example, a P/E ratio of 35 might show a company is growing faster than one with a P/E ratio of 10. The P/S ratio, which compares stock price to revenue, shows if a stock is cheap or expensive. Knowing these ratios, including the share ratio, is key for smart investing.
Key Takeaways
- Financial ratios, including share ratio and stock ratio, are vital for analyzing a company's financial health and performance.
- The share ratio is a key metric for evaluating a company's stock price and its relationship to the company's financial statements.
- Financial ratios, such as the P/E ratio and P/S ratio, can show a company's growth and value.
- Understanding the share ratio and other financial ratios is essential for making informed investment decisions.
- Comparing companies within the same industry is most relevant when using the P/S ratio for analysis.
- The P/S ratio can indicate if a stock is undervalued or overvalued, providing valuable insights for investors.
- Financial professionals and investors can leverage the share ratio and other financial ratios to gain a competitive edge in the market.
Understanding Share Ratio: Definition and Importance
Share ratio is key in financial analysis. It shows a company's value, growth, and health. Knowing about share ratio helps in making smart investment choices. It's found by dividing shares outstanding by shares issued.
Share ratio falls under market value ratios. These include P/E, P/B, and dividend yield ratios. These ratios help investors see a company's value and growth. For example, a high P/E ratio might mean the stock is too expensive.
What is Share Ratio?
A share ratio shows how many shares are out there compared to all issued. It's a tool for investors to check a company's performance. The formula is: Share Ratio = Total Shares Outstanding / Total Shares Issued.
The Role of Share Ratio in Investments
The share ratio is important for investors. It helps them understand a company's value, growth, and health. By looking at the share ratio, investors can see a company's financial strength and growth chances.
For instance, a high share ratio might mean more shares are out, which could lower earnings. But a low share ratio could show a strong financial position and less risk. The stock ratio is also key, showing a company's financial performance and value.
How to Calculate Share Ratio
To find the share ratio, you need to know the formula and use it right. This ratio is key in finance. It shows how much a company's shares are worth compared to its earnings.
The formula is simple: share ratio = stock price / EPS. Let's say a company's stock is $50 and its EPS is $5. The share ratio would be 10. This means people are ready to pay $10 for every $1 of earnings.
Formula for Share Ratio Calculation
The formula works for different situations, like mergers and acquisitions. In these cases, the exchange ratio is found this way: exchange ratio = offer price for target's shares / acquirer's share price.
Example of Share Ratio Calculation
For example, if the offer price for the target company's shares is $21.63 and the acquirer's share price is $11.75, the exchange ratio is 1.84. This means the acquirer must give 1.84 of its shares for every 1 of the target company's shares. Knowing how to calculate the share ratio is important for investors and financial experts.
Types of Share Ratios in Finance
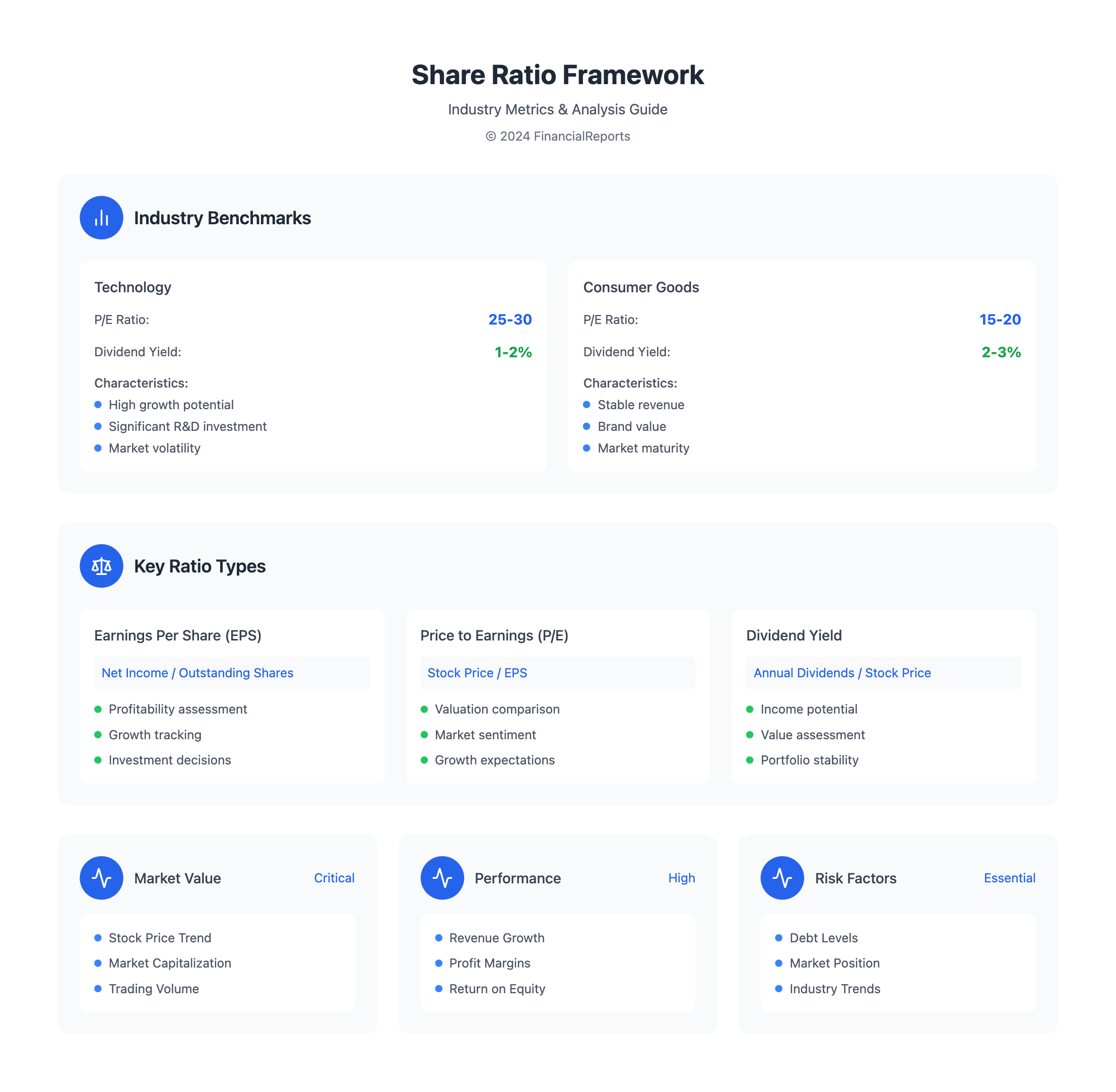
Financial experts and investors use share ratios to understand a company's stock. The stock ratio shows a company's financial health and value. Ratios like book value per share, dividend yield, earnings per share, and price-earnings ratio help evaluate stock prices.
Some common types of share ratios include:
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): a measure of a company's profitability on a per-share basis
- Price to Earnings (P/E) Ratio: a metric that helps investors gauge a stock's valuation relative to its earnings
- Dividend Yield: a measure of the return on investment for dividend-paying stocks
By looking at these ratios, investors can better understand a company's financial performance. The stock ratio is key in this analysis. It offers insights into a company's stock price and financial health.

The Impact of Share Ratios on Stock Valuation
Share ratios are key in stock valuation. They give investors and analysts insights into a company's financial health and growth. The share ratio helps judge a company's worth and compare it to others. This way, investors can see how attractive an investment is.
It's important to compare share ratios among competitors. This helps investors see if a company is fairly valued or not. For example, a company with a lower share ratio might be a good buy. On the other hand, a company with a higher ratio might be overvalued. By looking at these ratios, investors can make smarter choices.
When looking at share ratios, consider a few things:
- Industry averages and trends
- Historical data and performance
- Financial metrics, such as earnings per share and dividend yield
By analyzing share ratios thoroughly, investors can understand what affects stock value. This knowledge helps them make better investment choices.
Share Ratio Trends and Analysis
When looking at share ratio trends, it's key to compare a company's ratios to its peers. We look at ratios like return on assets and debt-to-equity to see how a company stacks up. This helps us understand how well a company is doing compared to others in its field.
Looking at historical trends in ratios like P/E and dividend yield is also important. These trends can tell us about the overall economy and market feelings. For example, a high P/E ratio might mean a stock is too expensive. On the other hand, a low dividend yield could show a company isn't making enough money to pay out dividends.
Industry-Specific Share Ratios
It's also vital to look at ratios specific to each industry. Different sectors have their own benchmarks. For instance, tech companies often have higher P/E ratios than consumer goods companies. This is because tech companies usually grow faster and have higher valuations.
| Industry | Average P/E Ratio | Average Dividend Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | 25-30 | 1-2% |
| Consumer Goods | 15-20 | 2-3% |
By studying these industry-specific ratios, investors can better understand a company's performance. The stock ratio is a key part of this analysis. It helps us see how a company is valued and its growth possibilities.
Using Share Ratio in Investment Strategies
Investors use the share ratio to make smart choices. They look at the company's money performance and market trends. This helps them spot chances for growth or value.
The share ratio fits into many investment plans. For instance, a high ratio might show a company ready to grow. A low ratio could mean it's a good deal.
When using the share ratio, investors should think about a few things:
- Compare the ratio to what's normal in the industry.
- Look at the company's money health and market trends.
- Use the ratio with other money metrics together.
Adding the share ratio to investment plans can lead to better choices. Economist William F. Sharpe's work on the Sharpe ratio helps measure how well an investment does compared to its risk. It's all about getting the most from your money.
Common Misconceptions About Share Ratios
When looking at stock ratios, it's key to know what's real and what's not. Many think a low P/E ratio means a stock is cheap. But, this isn't always true. For example, a company growing fast might have a higher P/E ratio than one growing slower, but its shares could be cheaper.
Some also believe high dividend yields are always good. While dividend stocks can offer steady income, a high yield doesn't always mean a stock is a smart buy. Companies with high dividend payouts might not grow much, and a dividend cut can drop stock prices sharply.
To invest wisely, it's important to look at the stock ratio in the right context. This means comparing the P/E ratio to others in the same industry. It also involves checking the company's financial health, debt, and growth chances. This way, investors can steer clear of mistakes and make better choices.
| Company | P/E Ratio | Dividend Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Company A | 20 | 2.5% |
| Company B | 15 | 4% |
By grasping the limits of stock ratios and avoiding common errors, investors can make smarter choices. This helps them reach their financial targets.
The Role of Share Ratios in Financial Reporting
Financial ratios, like share ratio, are key in financial reports. They give useful info on a company's performance. Numbers from financial statements help analyze a company's health and growth.
Companies share share ratio info in reports. This helps stakeholders understand the company's financial state. Rules for sharing certain ratios, like Earnings Per Share (EPS), differ by place and stock exchange.
Share Ratio in Quarterly Reports
Share ratio is vital in quarterly reports. It lets investors and analysts see a company's financial health. The ratio is clear and easy to understand, helping stakeholders make smart choices.
Regulatory Requirements and Compliance
Following rules is key in financial reports, and share ratio is no different. Companies must follow rules, like those from the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), for clear and accurate reports. Here are some important rules and issues:
| Regulatory Requirement | Compliance Issue |
|---|---|
| SEC Disclosure Requirements | Companies must disclose share ratio info in reports |
| GAAP Accounting Standards | Companies must follow GAAP when reporting share ratio |
| Industry-Specific Regulations | Companies must follow specific rules, like for banks or healthcare |
In summary, share ratio is very important in financial reports. Companies must follow rules to keep reports clear and accurate.
Advanced Metrics: Beyond Basic Share Ratios
Investors often look beyond basic share ratios to understand a company's financial health. The price/earnings-to-growth (PEG) ratio is a key metric. It combines the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio with earnings growth rates. This gives a clearer view of a stock's future growth.
Other advanced metrics help predict market performance and find investment opportunities. These include:
- Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Equity (ROE), which measure a company's profit-making ability
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio, showing a company's debt level
- Interest Coverage Ratio, checking if a company can meet its interest payments
By using these metrics with basic share ratios, investors get a deeper understanding. The stock ratio offers insights into valuation and growth prospects.
| Metric | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PEG Ratio | Price-to-Earnings Ratio / Earnings Growth Rate | Combines P/E ratio with earnings growth rate to provide a clearer picture of a stock's future growth prospects |
| ROA | Net Income / Total Assets | Measures a company's ability to generate profits from its assets |
| ROE | Net Income / Shareholder Equity | Measures a company's ability to generate returns for its shareholders |
Resources for Further Learning on Share Ratios
Looking to learn more about share ratios and financial analysis? There are many resources available. Experts have picked out top books that give deep insights into share ratios and how they impact investments.
Recommended Books and Articles
"Analyzing Financial Statements" by Pamela Peterson Drake dives into financial ratios, including earnings per share (EPS) and price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio. Emily Wilson's article in the Journal of Portfolio Management, "Interpreting Share Ratios for Better Investment Decisions," offers practical advice on using share ratios in investments.
Online Courses and Workshops
Want to improve your skills in financial ratio analysis? Online courses and workshops can help. Sites like Coursera and Udemy have programs that cover share ratio calculation and application in investments. These courses offer a hands-on way to learn and master financial analysis.
FAQ
What is a share ratio?
A share ratio is a financial tool that shows how well a company is doing. It's found by dividing one financial number by another. For example, it might be the stock price divided by earnings per share.
Why are share ratios important in financial analysis?
Share ratios are key for those in finance and investors. They help see if a company is healthy, growing, and a good investment. These metrics also help compare companies in the same industry.
How are share ratios calculated?
To find share ratios, you use formulas like the P/E ratio. This is done by dividing the stock price by earnings per share. There are examples to show how this works.
What are the different types of share ratios used in finance?
Main share ratios include Earnings Per Share (EPS), Price to Earnings (P/E) Ratio, and Dividend Yield. Each ratio gives different insights into a company's success, value, and investor returns.
How do share ratios impact stock valuation and market perception?
Changes in share ratios can really affect how investors feel and stock prices. These metrics help figure out a company's worth and future growth. This can lead to changes in the market and investment choices.
How can I analyze share ratio trends over time and across industries?
Looking at historical trends in share ratios and comparing them to industry standards is helpful. It gives context for today's market and helps make smart investment choices.
How can I integrate share ratio analysis into my investment strategies?
You can use share ratio analysis in many investment plans. For example, in value investing, growth investing, or dividend investing. Real examples show how investors use these ratios to find good stocks, growth, or high dividends.
What are some common misconceptions about share ratios?
There are myths about share ratios, like thinking a low P/E ratio always means a stock is cheap. Or that high dividend yields are always good. It's important to understand these metrics well and in context.
How are share ratios used in financial reporting and regulatory compliance?
Companies put share ratio info in their financial reports. There are rules for sharing certain ratios. Knowing these rules is important for finance pros and investors.
What are some advanced financial metrics that complement share ratio analysis?
More complex ratios and techniques, like the PEG ratio, offer a deeper look at a company's health and market performance. They work alongside share ratios for a fuller picture.
Where can I find resources to further my understanding of share ratios?
There's a list of books, articles, online courses, and workshops on share ratios and financial analysis. They're for all learning levels and preferences.