Understanding Traditional Income Statement Format
The traditional income statement, also known as the profit and loss statement (P&L), is key in financial reporting. It shows how well a company is doing financially, following the rules of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). This document lists all income, takes out the cost of goods sold (COGS), and shows the net result from all business activities as net income.
Companies worldwide use it to uniformly measure their operational success and efficiency over time. Its standardized format is crucial for comparing financial outcomes across different periods.
Key Takeaways
- Traditional income statements offer a comprehensive picture of financial performance over time.
- Following GAAP guidelines, these statements detail revenue, COGS, and other expenses to calculate net income.
- These statements are essential in reviewing company profitability and operational efficiency.
- Small businesses and large enterprises alike, produce income statements monthly, quarterly, or annually, affecting crucial financial decisions.
- The creation of traditional income statements requires meticulous attention to the accuracy of financial data.
- Integrating income statements with other financial documents is paramount for a holistic view of a company's finances.
- To aid in financial reporting, CPAs provide expertise in areas like interest expense and tax calculations.
What is a Traditional Income Statement?
A traditional income statement is an important financial document. It outlines a company's earnings, spending, and profit or loss over time. It follows GAAP rules. This information is crucial for people outside the company, like investors or banks.
Definition and Purpose
An traditional income statement shows how healthy a company's finances are. It lists all money coming in and going out, ending with the net income. This tells us if the company is doing well or facing problems. The statement is not just for checking profit. It's used to get funding, draw in investors, and plan business moves.
Key Components
The traditional income statement has several important parts. These detail the company's financial activity:
- Revenue: This is the money made from selling goods or services. It includes other income too.
- Expenses: Costs are both consistent and changing, like what it costs to make goods (COGS), overhead (SG&A), and loan interest.
- Net Income: This is what's left as profit or loss after handling all income and expenses. It shows if the company made money during the period.
Every part of the income statement is key to understanding a company's financial state. They help us see not just past and present health, but future prospects too. For more details and examples of a traditional income statement, you can look at this detailed guide.
In short, a traditional income statement is vital for financial reporting. It's designed to mirror a business's money movements based on GAAP. By studying this statement, stakeholders learn about where the company makes and spends money. This leads to understanding its total profit.
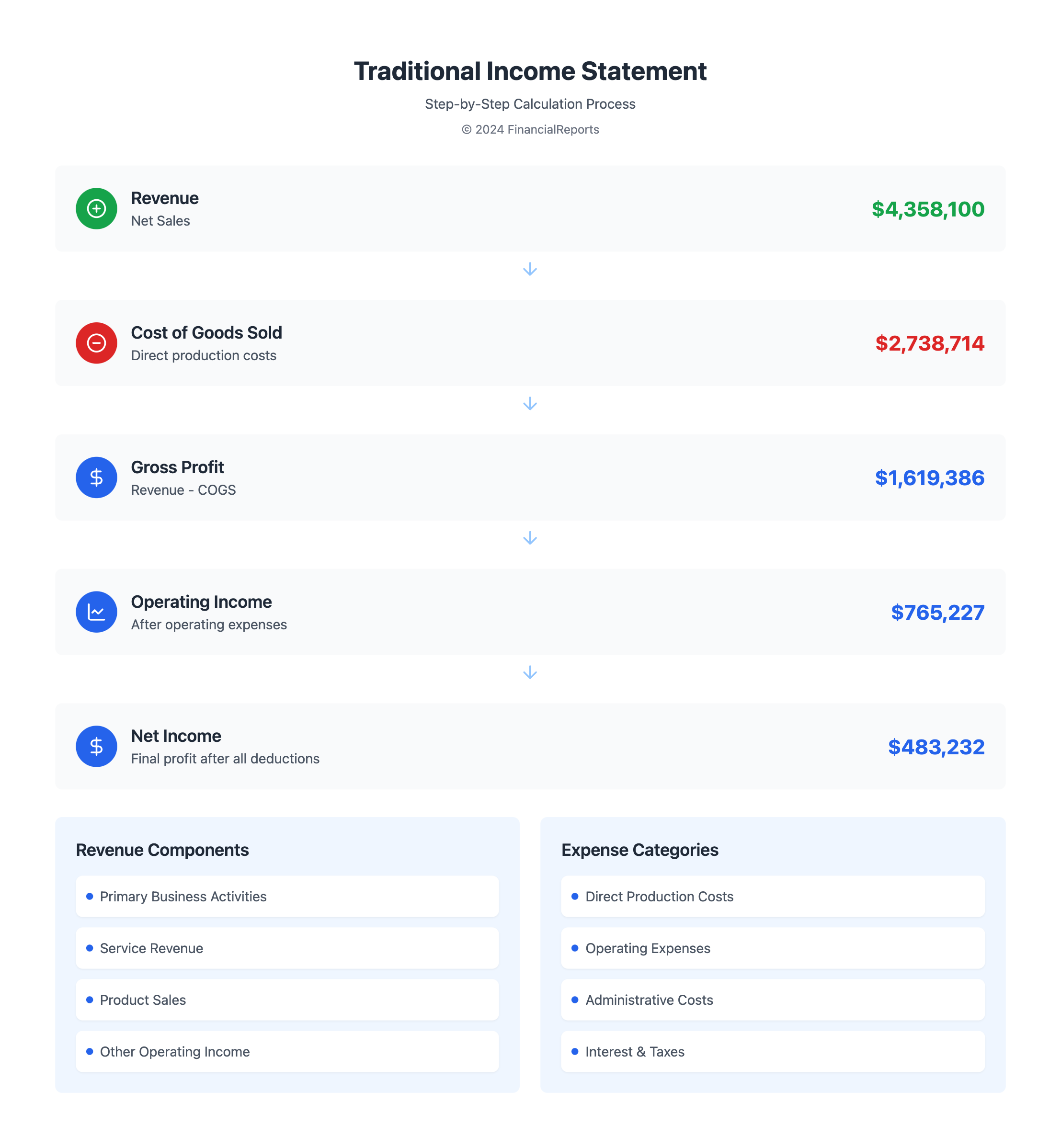
Structure of a Traditional Income Statement
The traditional income statement shows a company's financial performance over time. It is divided into revenue section, expense section, and net income calculation. Each section gives insights into the company's money health.
Revenue Section
In the revenue section, we find the total money made from main activities, like selling products or services. This starts with gross sales. Then, it subtracts returns and allowances to get the net sales. For example, Company B’s net sales were $4,358,100. This shows the earnings after subtracting sales reductions.
This part also includes money from extra sources. This boosts the company's total income.
Expense Section
The expense section shows all costs from running the business. This helps show how efficient the operations are. Direct costs, like the cost of goods sold (COGS), and other expenses like selling and admin costs are here. For Company B, COGS were $2,738,714.
It also covers indirect costs such as depreciation. Sharing these costs shows how they influence profit.
Net Income Calculation
The net income calculation part shows the company’s real earnings after deductions. Total revenue minus all operating and non-operating expenses gives us this number. For Company B, the operating income was $765,227. The final net income was $483,232 after taxes and other costs.
This final number is key for stakeholders. It helps them see the company’s profit and overall money health accurately.
Importance of Traditional Income Statements
Traditional income statements are key for analyzing a company's finances. They help in making big business decisions. Knowing how these statements work can make money matters clear and straightforward.
Financial Performance Overview
These statements break down revenue, expenses, and the bottom line. They show how a business is doing over a certain period. You can see if a company is making money and keeping costs low.
Gross profit and operating income tell a lot. They show if a company is good at making money and controlling expenses. This helps people stake in the business see if it's strong and can last.
Decision-Making Tool
Traditional income statements are crucial for managers. They highlight financial patterns and compare them over time. For example, looking at gross profit and expenses shows if things are getting better or worse.
This analysis helps with big decisions about costs, pricing, and growth. It shows if the business should expand or cut back. Plus, it guides decisions on dividends and investments by showing the net income.
| Financial Indicator | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Profit | Revenue minus cost of goods sold (COGS) | Measures efficacy of production and direct expenses |
| Operating Expenses | Sum of administrative and selling expenses | Indicates efficiency in managing regular business functions |
| Net Income | Difference between total revenue and total costs | Shows final profitability, influencing investment decisions and dividends |
In summary, traditional income statements are important. They help in looking at financial health and making smart choices. Their clear presentation of financial data is helpful for both managers and investors.
Differences Between Traditional and Other Income Statements
When looking at financial reports, there's a clear difference between traditional income statements and formats like multi-step and single-step statements. Each kind helps understand a company's financial health for specific needs.
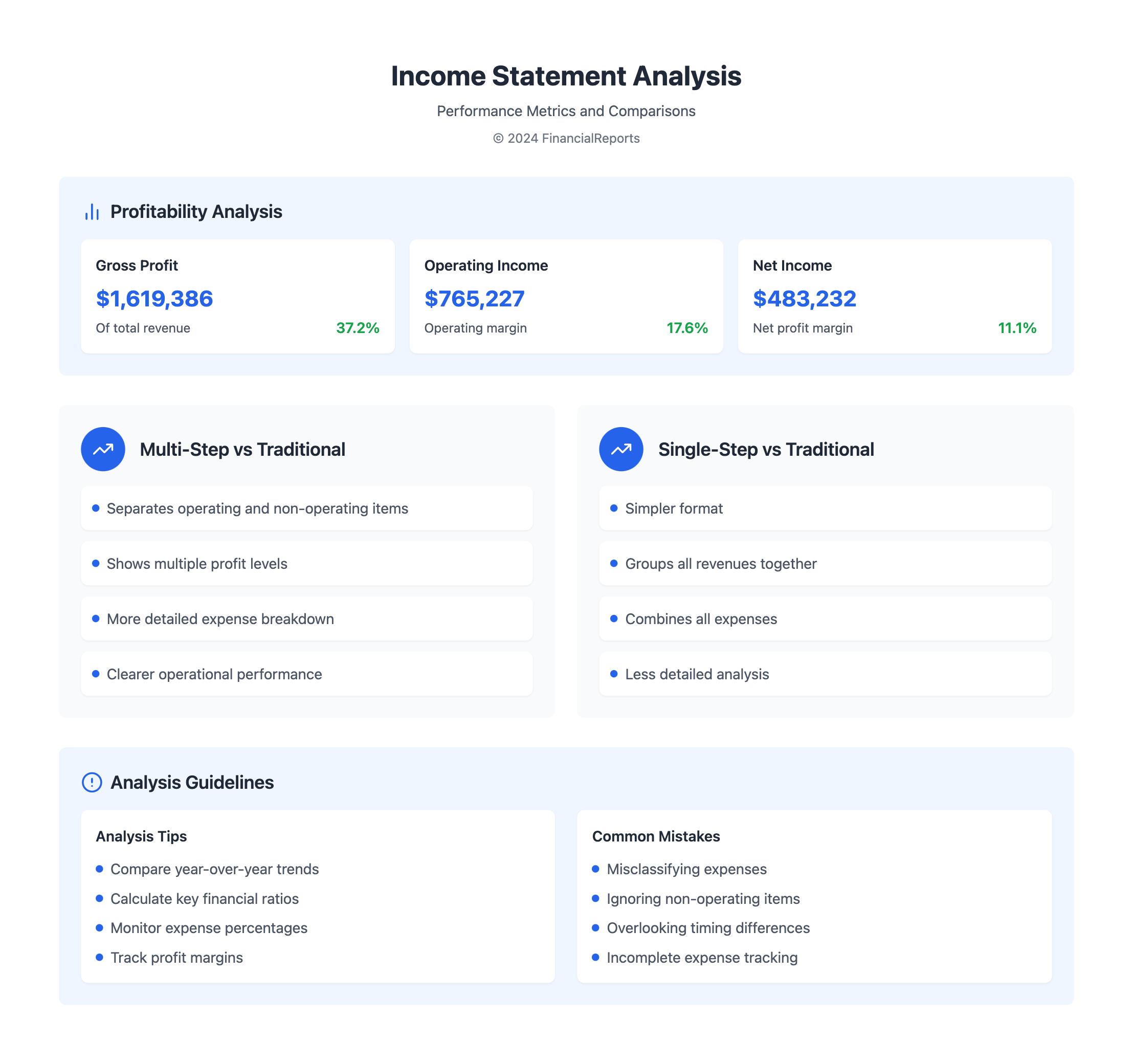
Comparison with Multi-Step Income Statements
The multi-step income statement breaks down operating and non-operating incomes and costs. This makes detailed financial analysis possible. For example, Widget Wizard Inc. showed a total revenue of $100 million and a net income of $32 million. This format separates things like gross profit ($70 million) and operating income ($45 million).
This method clearly shows different areas of performance, important for making strategic decisions. It separates selling and administrative expenses from the cost of goods sold. It also lists other incomes and expenses, like a $5 million interest expense.
Comparison with Single-Step Income Statements
The single-step income statement, on the other hand, is simpler. It puts all revenues and expenses into single categories. This makes it less detailed for thorough analysis. It could list total revenues and subtract all expenses to show net income.
This simplicity offers quick insights but misses the depth seen in traditional or multi-step formats. That depth is key for a full financial assessment and forecasting.
Financial professionals must understand these differences to use the data for investment decisions and policy-making. With Widget Wizard Inc., the traditional statement shows detailed info like gross and net profits. It also focuses on operational costs. Choosing the right income statement type is crucial for accurately interpreting financial data.
Key Terminology in Traditional Income Statements
Understanding the terms in traditional income statements is key for financial pros. They need this to accurately judge and share info on a company's financial health. We will look into important terms like gross profit, operating income, and net income. These are vital for understanding income statements and making financial decisions.
Gross Profit
Gross profit shows us the difference between what we earn and the cost of what we sell. It tells us how well a company manages its production and costs. Financial experts pay close attention to this to check on a company's financial health and how it operates.
Operating Income
Operating income, or profit, comes after we subtract operating expenses from gross profit. These expenses include things like sales, general costs, and administrative expenses (SG&A). This figure tells us how profitable a company's main business activities are. It does this without including money from investments, taxes, or other financial costs.
Net Income
Net income is often seen as the final profit line. It comes from taking out all costs, including operations, interest, and taxes, from our total earnings. Net income shows how profitable a company really is. Stakeholders use it to see how well the company is doing financially and to make wise investment choices.
| Term | Definition | Key Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Profit | Total revenue minus COGS | Measures efficiency of production and cost management |
| Operating Income | Gross profit minus operating expenses | Indicates profitability of core business activities |
| Net Income | Total profit after all costs | Ultimate measure of overall financial success |
Knowing these terms helps in the right reading and use of financial data in traditional income statements. It aids pros in making strategic decisions and evaluating performance.
How to Prepare a Traditional Income Statement
Learning how to prepare an income statement is key for true financial insight and smart business moves. We offer a step-by-step method to financial statement preparation. This ensures all financial activities are recorded in order.
Step-by-Step Guide
Starting this task involves some important steps:
- Gathering Data: Collect all your financial info. This includes sales, cost of goods, operating costs, and more.
- Calculating Gross Profit: Find your gross profit by subtracting the cost of goods from your total sales. If your sales are $4,358,100 and costs are 65% of that, gross profit would be $1,625,170.
- Detailing Operating Expenses: Note down all your operating costs. Things like salaries, rent, and utilities fall into this category. It’s crucial to sort these costs correctly to prevent errors.
- Accounting for Non-Operating Items: Don’t forget items like interest and taxes. For instance, $18,177 for interest and $257,642 for taxes significantly affect your net income.
- Calculating Net Income: Subtract all your costs from the gross profit to find your net income. This is your income statement's bottom line.
For a deeper dive into these steps, check out this helpful article.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Although it may look simple, there are traps you need to dodge:
- Misclassification of Expenses: Mistaking fixed costs for variable ones can mess up your gross profit.
- Inadequate Expense Tracking: Not keeping detailed records can lead to wrong expense figures and affect your financial health.
- Ignoring Indirect Costs: Forgetting costs like depreciation can significantly impact your operating income.
To succeed in preparing an income statement, you must be careful and know the common mistakes that can harm your financial statements.
Common Uses of Traditional Income Statements
Traditional income statements are key in financial reporting. They show a company's financial health over time. They help in business cash management and internal management. They are also useful for external parties. These parties look at them for investment clues through investor insights.
Internal Management Review
These statements give a full view of a company's success and stability. They break down revenue, costs, and expenses. This helps in evaluating how well the company manages costs.
From this, managers can make decisions on budgets, planning, and prices. They are key in internal management. This kind of detailed review helps in making smart decisions. This supports a business's growth and its ability to grow bigger.
External Investor Insights
Investors use these statements to check a company's financial health. They see the company's profit and how efficiently it operates. This is key for investors doing thorough checks. It shapes their view on risk and possible returns.
They pay close attention to operating and comprehensive income. These show how well the company's core operations are doing. They also show its financial environment. Investors use them to predict future performance. This helps in deciding whether to invest in or finance the company.
In conclusion, internal management and external stakeholders find these statements very useful. They guide company strategies and investment choices. These documents shape future business moves and relationships with investors. They are crucial for detailed financial analysis and business cash management.
Best Practices for Analyzing Traditional Income Statements
Analyzing traditional income statements needs strategic know-how. Financial ratios and trend analysis are key. They help us get valuable insights from these financial documents.
Financial Ratios
To understand a company's health and efficiency, using financial ratios is key. The gross margin ratio, operating margin ratio, and net profit margin are crucial. They show financial stability and profitability. For example, Company B's operating income was $765,227,000 on September 28, 2019. We can calculate these ratios to compare with others or past performance.
Trend Analysis
Trend analysis looks at financial statements over time. It shows how a company's financial health is changing. This helps predict future performance and guide decisions. For Company B, observing the $1,619,386,000 gross profit in 2019 shows if cost strategies are working.
Tools like Reach Reporting make trend analysis easy. They automatically extract data and show it in interactive ways. This saves time and makes complex data easy to understand. It helps stakeholders make informed decisions.
Limitations of Traditional Income Statements
Traditional income statements provide valuable insights into a company's profitability and operations. However, they have some big limitations. These shortcomings mean they don't fully show a company's financial health. So, professionals often need more information to get the full picture.
Omission of Cash Flow Data
Income statements miss out on showing cash flows. But knowing about cash flows is key to understanding a business’s liquidity and cash position. Since these statements rely on accrual accounting, they record transactions as they happen. This does not reflect the actual exchange of cash. Therefore, a company might look profitable on paper but still struggle with not having enough cash. This can lead to liquidity issues.
Non-Operating Income Considerations
Non-operating income gets included in traditional income statements too. This includes money not made from the main business activities, like investment income or gains from selling assets. These additions can make a company seem more profitable than it really is in its core operations. This can mislead people about the company's true financial health. Especially if this non-operating income has a big effect on the bottom line.
| Financial Statement | Includes Cash Flows | Includes Non-Operating Income |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Income Statement | No | Yes |
| Comprehensive Income Statement | No | Yes, with broader context |
| Cash Flow Statement | Yes | No |
In conclusion, traditional income statements are good for a basic look at profitability. But they don't show everything about cash flows and non-operating income. For a true view of a company's financial health, one must look beyond these statements. Stakeholders should keep these limits in mind when making financial decisions.
Conclusion: The Role of Traditional Income Statements in Business
This article shows how important traditional income statements are. These statements are needed for reports in most fields. They form a basic part of analyzing a business's finances.
They show a company's income and expenses. This gives everyone a clear picture of how the company did before. And they help guess the company's future money situation. The traditional income statement is key in telling a company's money story.
Recap of Importance
Traditional income statements are vital for making big company decisions. They help leaders choose where to take the company, based on solid facts. These statements clearly show where money comes from and goes, for both regular and extra activities.
In farming, they match the yearly crop cycle to show accurate finances. They account for all costs and profits over time. This shows their reliability and attention to detail.
Future Considerations in Financial Reporting
Financial reporting is changing, and traditional income statements will too. They will get updates to handle more complex, data-focused work. This means they will continue to be very important.
Financial experts and businesses want powerful, automatic ways to handle money data. Traditional statements will keep adapting. They'll offer deeper insights, helping to understand a company's financial health as the business world changes.
FAQ
What Is a Traditional Income Statement?
A traditional income statement is a report showing a company's financial performance over time. It presents revenues, costs, and expenses to calculate the net income. This follows the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
What Are the Key Components of a Traditional Income Statement Format?
Essential elements include sales and revenue, cost of goods sold, and gross profit. Also included are selling and general administrative expenses, operating income, and net income.
How Is the Structure of a Traditional Income Statement Organized?
It starts with revenue from sales or services. Next, it lists expenses like COGS and SG&A. It ends with the net income, which is what's left after all deductions.
Why Are Traditional Income Statements Important?
They provide a clear view of a company's financial health. This helps leaders make smart decisions. They are key for getting loans, drawing in investors, and handling profitability.
How Do Traditional Income Statements Differ from Multi-Step and Single-Step Statements?
Traditional income statements break down costs and subtotals like gross margin more than single-step ones, which lump all revenues and expenses together. They offer more insight into operating efficiencies than multi-step statements.
What Is Gross Profit?
Gross profit is sales revenue minus the cost of goods sold. It shows how efficiently a company can produce and manage costs directly.
What Does Operating Income Indicate?
Operating income is the gross profit minus SG&A expenses. It reflects the profit from the company's main business activities.
How Do You Prepare a Traditional Income Statement?
First, find the gross profit by subtracting the cost of goods sold from total revenue. Then, subtract SG&A expenses to get operating income. Lastly, subtract interest and taxes to find net income.
What Are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid in Preparing an Income Statement?
Avoid misclassifying expenses and underestimating indirect costs. These errors can skew the financial outcomes.
How Are Traditional Income Statements Used for Internal Management Review?
They're used to monitor performance, manage costs, and set pricing strategies. This maintains and boosts business profitability.
Why Are Traditional Income Statements Valuable to External Investors?
They provide clear information on a company's profitability and financial stability. This helps investors make wise decisions on investment and credit.
Which Financial Ratios Are Useful When Analyzing Traditional Income Statements?
Ratios like gross margin, operating margin, and net profit margin are key. They help assess efficiency and profitability.
How Crucial Is Trend Analysis When Evaluating Traditional Income Statements?
Trend analysis is crucial. It predicts future performance by examining past financial health, aiding in strategic planning.
What Limitations Do Traditional Income Statements Have?
They don't show cash flow, which can hide liquidity issues. Non-operating income effects can also mislead about core operations.
How Might Financial Reporting Evolve in Relation to Traditional Income Statements?
Financial reporting might embrace more dynamic data and tools. This would boost the role of traditional income statements in fiscal planning and analysis.