Understanding the Profit Margin Ratio Definition
The profit margin ratio shows how much of a company's revenue turns into profit. It's a key way to check if a business is doing well financially. For example, a 35% profit margin means the company makes $0.35 for every $1 it sells. This shows how important it is for businesses to understand their profit margins.
Investopedia explains that the profit margin ratio is a key sign of a company's health. It helps see how well a company can handle costs and grow. This ratio is important for both investors and businesses to know a company's financial standing.
Key Takeaways
- The profit margin ratio is a financial metric that assesses a company's profitability.
- The net margin definition is essential in understanding a company's ability to manage costs and sustain growth.
- A high profit margin indicates a company's efficiency in converting revenue into profit.
- Profit margins vary across industries, with some sectors having higher average net profit margins than others.
- Understanding the profit margin ratio is critical for investors and businesses to evaluate a company's financial health and make informed decisions.
- The profit margin ratio is influenced by factors such as business model, growth goals, industry type, size of the business, geographic location, and operating expenses.
- Comparing profit margin ratios between companies in the same industry provides a more accurate assessment of a company's financial performance.
What is the Profit Margin Ratio?
The profit margin ratio is a key performance indicator that shows how profitable a company is. It's the percentage of sales that turns into net income. This ratio is key to understanding a company's financial health.
To find the profit margin ratio, you divide the net income by the net sales. This helps see how well a company turns sales into profit. Lenders look at it to see if a company can pay back loans. Investors check it to see if profits are enough for dividends.
Important things about the profit margin ratio include: * It shows the percentage of sales that turns into net income. * It tells us how much profit is made for each dollar of sales. * It's used for comparing industries and checking a company's past performance. * A higher ratio means more profit from the same amount of sales or less expenses.
Knowing about the profit margin ratio is vital for financial experts, investors, and others who need financial data. By looking at this ratio, companies can spot areas to get better and make smart choices to boost profits.
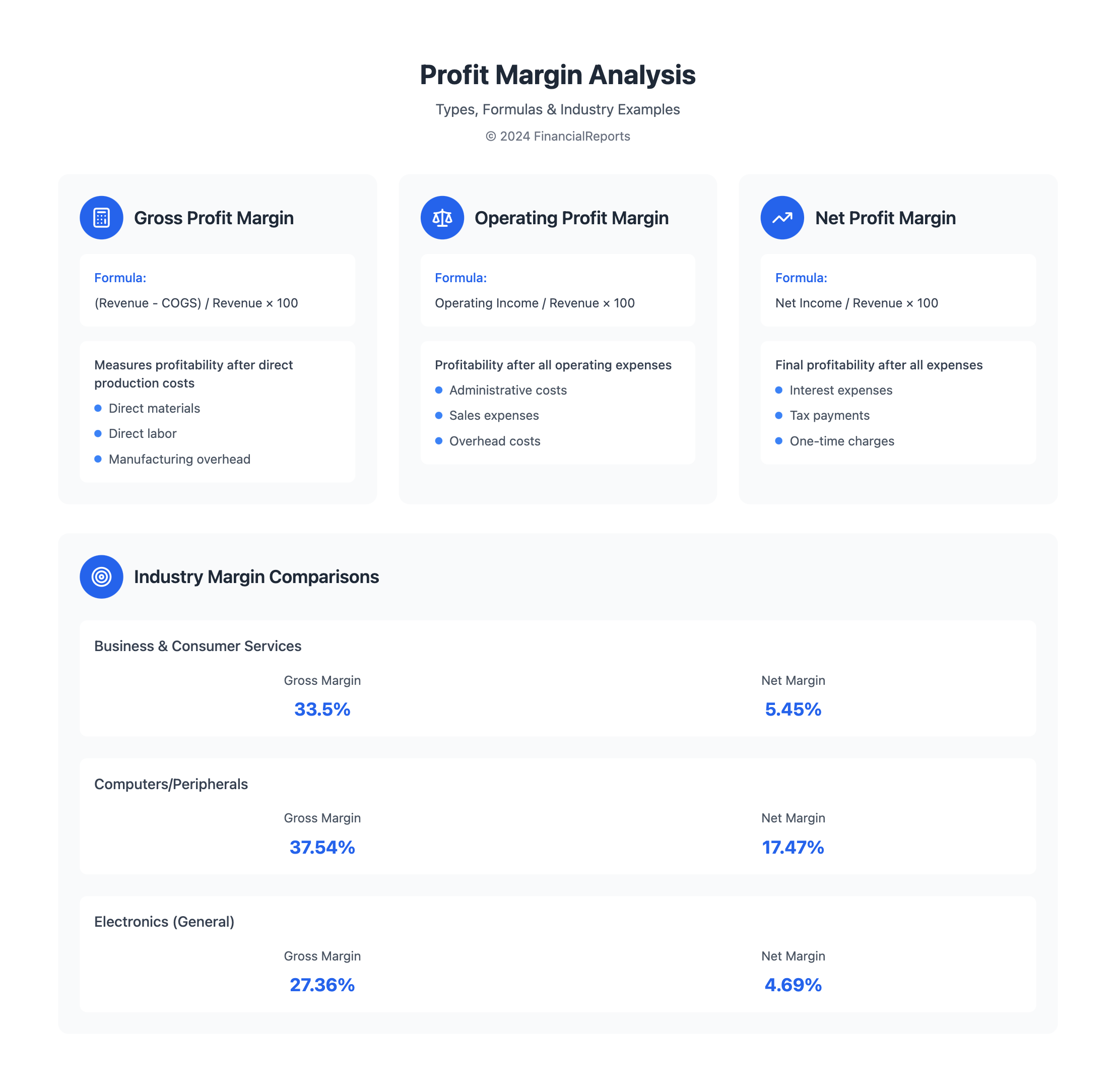
Types of Profit Margin Ratios
When looking at a company's financial health, it's key to check different profit margin ratios. These ratios show how well a company makes money and runs its operations. The Gross Profit Margin is a major one. It compares gross profit to revenue, showing if a company can sell its products for more.
Other important ratios include:
- Operating Profit Margin: shows how much sales are left after operating costs, showing how well a company runs its operations.
- Net Profit Margin: shows how well a company makes money after all costs and taxes, a sign of its financial health.
Knowing these ratios is vital for financial analysis and valuing companies. By comparing a company's ratios to others, its past performance, or industry standards, investors and analysts can understand its financial health. This helps them see how it stacks up against its peers.
| Profit Margin Ratio | Formula | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Profit Margin | Gross Profit / Revenue | Measures a company's ability to charge a premium for its products |
| Operating Profit Margin | Operating Profit / Revenue | Indicates how efficiently a company manages its operations |
| Net Profit Margin | Net Profit / Revenue | Reflects a company's ability to generate earnings after accounting for all expenses and taxes |
How to Calculate Profit Margin Ratio
Understanding a company's financial health is key. The Basic Formula for profit margin ratio is: (Net Sales - Cost of Goods Sold) / Net Sales. This formula shows how profitable a company is.
To find the profit margin ratio, just follow these steps:
- First, find the net sales (revenue) of the company.
- Then, calculate the cost of goods sold.
- Next, subtract the cost of goods sold from net sales to get the gross profit.
- Lastly, divide the gross profit by net sales to find the gross profit margin.
Let's look at Apple's 2023 numbers: Net Sales = $383,285 million, Gross Profit = $169,148 million. Using the Basic Formula, we find the gross profit margin: ($169,148 million / $383,285 million) = 44.1%. This shows Apple did well financially.
| Company | Net Sales | Gross Profit | Gross Profit Margin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | $383,285 million | $169,148 million | 44.1% |
By applying the Basic Formula and following these steps, companies can figure out their profit margin ratio. This helps them make better financial decisions.
Why Profit Margin Matters
Profit margin is a key Indicator of Financial Health that shapes business strategy. It shows how much profit a company keeps after paying expenses. A high margin means more profit and efficiency, while a low one points to areas needing work.
Profit margins vary by industry, usually between 5% and 10%. Companies aim for high margins to show they're doing well financially. Investors look at these margins to judge a company's health and how well it's run.
Ways to boost profit margins include:
- Reducing operating expenses
- Increasing prices without raising costs
- Improving productivity
- Increasing average order value from existing customers
The net profit margin is net income divided by total revenue, multiplied by 100. It shows how much profit is left after all expenses are paid. Net income is found by subtracting COGS, OpEx, interest, and taxes from total revenue. This margin helps evaluate company health, make investment choices, and track profitability over time.
| Industry | Average Net Profit Margin |
|---|---|
| Construction | 5-10% |
| Retail | 2-5% |
| Technology | 10-20% |
Factors Affecting Profit Margins
Profit margins are shaped by many things, like industry standards, costs, and market conditions. The net profit margin shows how well a company is doing financially. It's found by dividing net income by sales.
Things like net profits, sales, and costs of goods sold greatly influence profit margins. Qualitative factors, like market share and how well ads work, also matter a lot. For example, a company with a big market share and good ads can keep higher profit margins than others.
Other things that can change profit margins include taxes and how sales change with the seasons.
Some important factors that affect profit margins are:
- Net profits and sales earnings
- Merchandise costs and sales prices
- Inventory numbers and management
- Market share and competitive strength
- Advertising effectiveness and consumer preferences
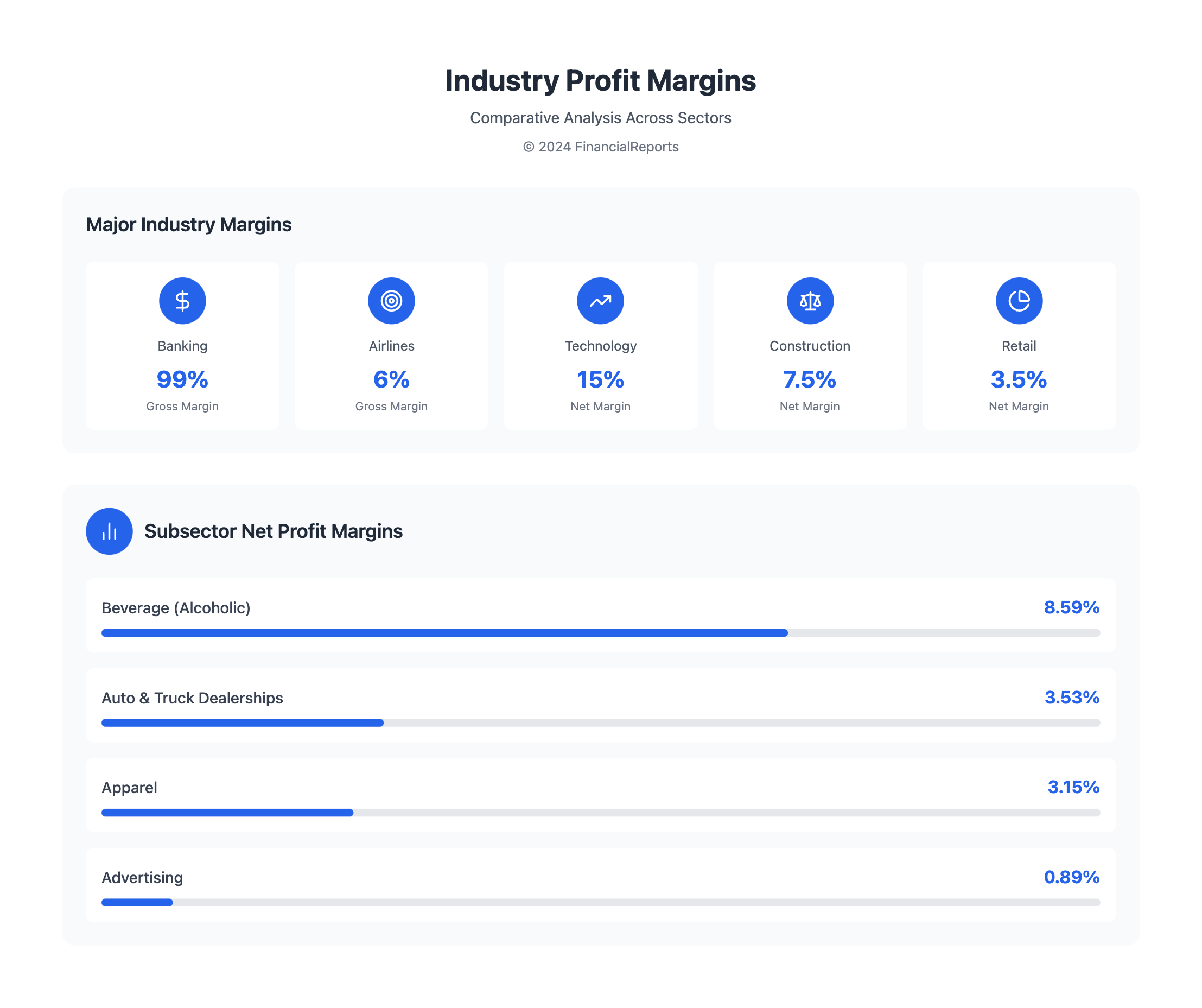
The net profit margin varies a lot between industries. It can go from -16.35% in Real Estate (Development) to 27.52% in Tobacco. Knowing these factors and industry standards helps companies boost their profit margins and compete better.
| Industry | Average Net Profit Margin |
|---|---|
| Advertising | 0.89% |
| Apparel | 3.15% |
| Auto & Truck Dealerships | 3.53% |
| Beverage (Alcoholic) | 8.59% |
By looking at these factors and industry standards, companies can make plans to increase their profit margins. They might try to sell more, change prices, or find ways to cut costs.
Comparing Profit Margin Ratios
When looking at a company's financial health, it's key to compare its profit margins to Industry Benchmarks. This helps see how the company stacks up against its rivals and the overall industry. A higher profit margin means the company is doing better financially.
To compare profit margins, use the formula: Profit Margin = (Net Income / Net Sales) x 100. For example, a company with $500,000 in net sales and $25,000 in net income has a 5% profit margin. This can be compared to Industry Benchmarks to see if the company is doing well or not.
Some industries have unique profit margins. For example, banks have a gross profit margin of about 99%. Airlines, on the other hand, have a gross profit margin of around 6%. By comparing profit margins to these Industry Benchmarks, companies can spot areas to improve and boost their financial health.
- Banking industry: 99% gross profit margin
- Airline industry: 6% gross profit margin
By analyzing and comparing profit margins to Industry Benchmarks, companies can learn a lot about their financial health. This knowledge helps them make smart choices to grow and increase profits.
Common Mistakes in Profit Margin Analysis
When we analyze profit margins, we can make big mistakes. Not counting all expenses can lead to wrong profit numbers. It's key to know what net margin is. It shows how much profit is left after all costs are subtracted from sales.
To steer clear of these errors, we need to think about a few things:
- Gross Profit Margin: This shows how much profit we make after subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS)
- Operating Profit Margin: This tells us how much profit we have after we subtract operating costs from gross profit
- Net Profit Margin: This is the percentage of revenue that stays as profit after all expenses are taken out
For more details on profit margin analysis, check out profit margin analysis. It explains how to figure out and boost your business's profit. By avoiding Misinterpretation of Data and looking at these points, businesses can make smart choices to better their finances.
| Industry | Gross Margin | Net Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Business & Consumer Services | 33.50% | 5.45% |
| Computers/Peripherals | 37.54% | 17.47% |
| Electronics (General) | 27.36% | 4.69% |
By knowing the usual mistakes in profit margin analysis and using the right formulas, businesses can make choices based on data. This helps them improve their profit and stay ahead in their field.
Enhancing Profit Margins
Effective Cost Management Strategies are key to boosting profit margins. By cutting down on expenses and using smart pricing, businesses can see big financial gains. For example, a company can tweak its prices to make more money without spending more, which boosts profits.
Some fields make more money than others. Tech giants like Microsoft and Alphabet often see high profits. On the other hand, big retailers like Walmart and Target usually have lower margins. Cost Management Strategies can help these businesses run better and make more money.
To boost profits, businesses can try a few things:
- Improving supply chain management to save costs
- Using technology to make processes more efficient
- Creating smart pricing plans to earn more
- Reducing waste and using resources better
By using these Cost Management Strategies, companies can do better financially. They can also stay competitive and grow steadily. As the business world keeps changing, it's vital for companies to focus on making more money to stay on top.
Real-World Applications of Profit Margin Ratios
Profit margin ratios are key in Case Studies of Successful Companies. They help businesses spot where they can do better and make smart choices to boost profits. For example, a company can check how profitable its products or services are using the gross profit margin formula. The formula is: [(Total Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold) / Total Revenue] X 100.
A Successful Company like Apple uses this formula to see its gross profit margin. Let's say Apple's total revenue is $100 million and its cost of goods sold is $40 million. Its gross profit margin would be 60%. This helps Apple see how it stacks up against others in the industry and find ways to get better. Case Studies of companies like Apple offer great lessons on using profit margin ratios in real life.
Some important lessons from Case Studies of Successful Companies are:
- Using profit margin ratios to find areas to improve
- Coming up with plans to make more money, like cutting costs or boosting sales
- Looking at profit margin ratios against industry standards to find growth chances
Tools for Monitoring Profit Margin Ratios
Financial experts use Financial Software Solutions to keep an eye on profit margin ratios. These ratios are key for smart investment choices. With these tools, investors can figure out important metrics like gross profit margin, net profit margin, and operating profit margin.
To find these ratios, they use specific formulas:
- Gross Profit Margin: (Revenue - Cost of Sales) / Revenue * 100
- Net Profit Margin: Net Profit / Revenue * 100
These ratios give deep insights into a company's success and efficiency. For more on profit margin analysis, check outinvestopedia. It explains the different profit margins and how to figure them out.
Tools like financial statement analysis software, accounting software, and business intelligence platforms are used. They help users follow and analyze financial data. This lets them spot trends and make choices based on data.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Financial Statement Analysis Software | Enables users to analyze financial statements and calculate profit margin ratios |
| Accounting Software | Provides a detailed look at a company's financial dealings and helps track profit margins |
| Business Intelligence Platforms | Offers advanced analytics and data visualization to spot trends and make smart decisions |
Conclusion and Takeaways
The profit margin ratio is key for checking a company's financial health. It shows how well a business makes money. By looking at different profit margins, like gross and net, companies can see how they manage costs and set prices.
Looking at profit margin trends helps spot areas to get better. It lets businesses compare themselves to others in their field. This helps make smart choices to boost profits.
Keeping an eye on profit margins is important. It's part of a bigger picture that includes other financial health checks. This way, companies can see if they're doing well for the long run.
A high net profit margin means a company is doing well. It shows they're good at managing costs and making more money. By improving operations and controlling costs, businesses can keep their profit margins high. This helps meet their goals and makes shareholders happy.
FAQ
What is the profit margin ratio?
The profit margin ratio shows how much profit a company makes from each dollar of sales. It's a key financial metric that calculates the percentage of revenue turned into net profit.
Why is the profit margin ratio important?
It's a key sign of a company's health and how well it runs. It helps see if a business can manage costs, set good prices, and grow. Investors and analysts use it to judge a company's success and compare it to others.
What are the different types of profit margin ratios?
There are several types: - Gross profit margin shows what's left after costs of goods sold. - Operating profit margin shows revenue after operating expenses. - Net profit margin shows the percentage of revenue that turns into net income.
How is the profit margin ratio calculated?
To calculate, use the formula: Profit Margin Ratio = Net Income / Total Revenue x 100 This formula can be tweaked for different profit margins, like gross, operating, and net.
What factors can affect a company's profit margins?
Many things can change profit margins. These include the industry, costs, pricing, efficiency, and the economy. Companies in certain industries might have lower margins than others.
How can companies improve their profit margins?
To boost margins, companies can: - Cut operating costs - Use smart pricing - Work more efficiently - Offer more products or enter new markets - Use technology to improve processes
How can profit margin ratios be used to compare companies?
These ratios help compare companies in the same or different industries. They show who's doing well and who's not. But, be careful when comparing across industries because norms can vary a lot.
What are some common mistakes in interpreting profit margin data?
Some common errors include: - Ignoring one-time items - Not considering industry factors - Comparing without adjusting for accounting differences - Focusing too much on margins without looking at other financials