Understanding the Operating Margin Formula
The operating margin formula is key in financial analysis. It shows how well a company makes profits from its main business activities. It's found by dividing operating income by net sales, giving the operating margin. This metric helps investors and analysts see how efficient a company is and make smart choices.
Using the operating margin formula, investors can check how well a company controls its costs and stays profitable. The formula is also useful for comparing a company's profit over time and with its competitors. For example, Apple's 30.2% operating margin in 2021 shows its strong core business. On the other hand, the S&P 500 Index's 11% average in 2017 shows the need to look at industry standards and growth rates.
Key Takeaways
- The operating margin formula is a key metric in financial analysis, providing insight into a company's operational efficiency.
- It is calculated by dividing a company's operating income by its net sales, resulting in the operating margin.
- The operating margin formula offers a consistent measure of a company's profitability compared to net profit margin.
- Investors can use the operating profit margin formula to evaluate a company's ability to manage its operating expenses and maintain profitability.
- Operating margin is essential for comparing a company's profitability over different periods and against competitors in the same industry.
- Industry norms and growth rates should be considered when evaluating a company's operating margin.

What is Operating Margin?
Operating margin is a key financial metric. It shows how well a company makes money from its main activities. It's a percentage that comes from dividing operating profit by total revenue. This number changes based on the industry and is used to compare companies within it.
A company's operating margin shows its ability to make profit from its main activities. For example, a 15% margin means it makes $0.15 in profit for every $1 in revenue. This is important for checking how well a company is doing, like in a leveraged buyout.
Definition of Operating Margin
The operating margin is found by using this formula: (Operating Profit / Net Sales) x 100. It shows how well a company makes money from its main activities. A higher margin means better cost control and pricing. A lower margin might mean trouble with keeping costs down.
Importance in Business Analysis
The operating margin is key in business analysis. It helps check a company's financial health and make better decisions. It's good to look at other profit metrics too, like gross and net profit margins. Here are some things to think about when looking at operating margin:
- Operating profit margin only looks at a company's operational profit, not interest or taxes.
- How a company depreciates its assets can affect its profit margin, making it hard to compare with others.
- It's best to compare operating margins with companies of similar size and in the same industry.
Understanding operating margin is important for business analysis. It helps companies see how they're doing financially. This way, they can make better decisions to boost their profits and efficiency.
The Operating Margin Formula
To find the operating margin, we use the operating profit formula. This is a key part of financial analysis. The formula is: Operating Margin = (Operating Income/Net Sales Revenue) x 100. It shows how much of a company's revenue is left after paying for variable production costs.
Calculating operating margin means using the operating income margin formula. This formula looks at operating earnings, or EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes). It's important for seeing if a company can make profit from its main activities.
Breakdown of the Formula
The operating margin formula breaks down into several parts. These include revenue, cost of goods sold, and operating expenses. First, we find operating earnings by subtracting cost of goods sold and operating expenses from revenue. Then, we use the operating profit formula to find the operating margin, which is a percentage.
Components Explained
The main parts of the operating margin formula are:
- Operating Income: This is the earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). It's found by subtracting cost of goods sold and operating expenses from revenue.
- Net Sales Revenue: This is the total revenue from a company's main activities.
Using the operating income margin formula helps us find the operating margin. This gives us insights into a company's financial health and profitability.
| Company | Operating Margin |
|---|---|
| Coca-Cola | 23.1% |
| David's Drinks | 18.75% |
How to Calculate Operating Margin
To find the operating margin, start by looking at the income statement. You'll need the revenue, cost of goods sold (COGS), and operating expenses. Next, subtract COGS and operating expenses from the revenue to get the operating income (EBIT).
Then, divide the operating income by the revenue. Multiply this by 100 to turn it into a percentage. This shows how profitable a company is.
The formula for the operating margin is: Operating Margin = Operating Income / Total Revenue x 100%. For instance, if a company makes $2,000,000 in revenue, spends $1,500,000 on expenses, and has $500,000 in operating income, its margin is 25%.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Find revenue, COGS, and operating expenses from the income statement.
- Calculate operating income (EBIT) by subtracting COGS and operating expenses from revenue.
- Divide operating income by revenue and multiply by 100 to get the percentage.
A higher operating margin means a company makes more profit from its operations. It keeps costs low. The operating margin is different from the gross margin. It includes all operating expenses, like SG&A, R&D, and depreciation.
| Company | Total Revenue | Operating Expenses | Operating Income | Operating Margin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Inc. | $2,000,000 | $1,500,000 | $500,000 | 25% |
Importance of Operating Margin in Finance
Operating margin is key in finance, showing how well a company makes money from its main activities. To grasp its importance, it's vital to learn how to calculate operating profit margin. This means dividing operating income by revenue. The operating margin definition shows the profit a business makes for each dollar of revenue.
A drop in operating margin warns of a company's falling efficiency. It's critical for investors and analysts to watch this metric. By comparing margins with others in the industry, businesses can spot areas to get better and make smart choices. The margin is shown as a percentage, clearly showing a company's profit level.
Some important things to think about when looking at operating margin include:
- Operating margin is a percentage showing how much profit a business makes for every dollar of revenue.
- Comparing operating margins with industry peers gives valuable insights for business decisions.
- A higher operating margin means a company is well-run, efficiently turning revenue into profit.
Understanding the operating margin definition and how to calculate operating profit margin helps businesses make better choices. A decrease in operating margin is a red flag, urging companies to review their plans and adjust to stay ahead.
Factors Influencing Operating Margin
Operating margin is a key metric for checking a company's profit. It's found by subtracting operating expenses from revenue. This shows how well a company manages costs and makes profits.
Industry standards greatly affect a company's operating margin. Some industries, like tech and luxury goods, have higher margins. Others, like retail and manufacturing, have lower margins. A company's cost structure and pricing also play a big role.
Industry Standards and Cost Structure
When looking at a company's operating margin, it's important to consider industry standards and cost structure. The operating profit calculation should include revenue, operating expenses, and non-operating items. Understanding these factors helps companies improve their profitability and stay competitive.
Some key factors that influence operating margin include:
- Pricing strategy: A company's pricing can greatly affect its operating margin. Higher prices can mean more revenue but also lower sales.
- Cost of goods sold (COGS): COGS is a big part of operating expenses. Companies with high COGS may have lower margins than those with low COGS.
- Operating expenses: Expenses like salaries, rent, and marketing can also impact a company's operating margin.
High vs. Low Operating Margin
The operating margin is key when checking a company's health. A high margin shows a company is good at making profits from sales. But, a low margin might mean the company is facing big challenges.
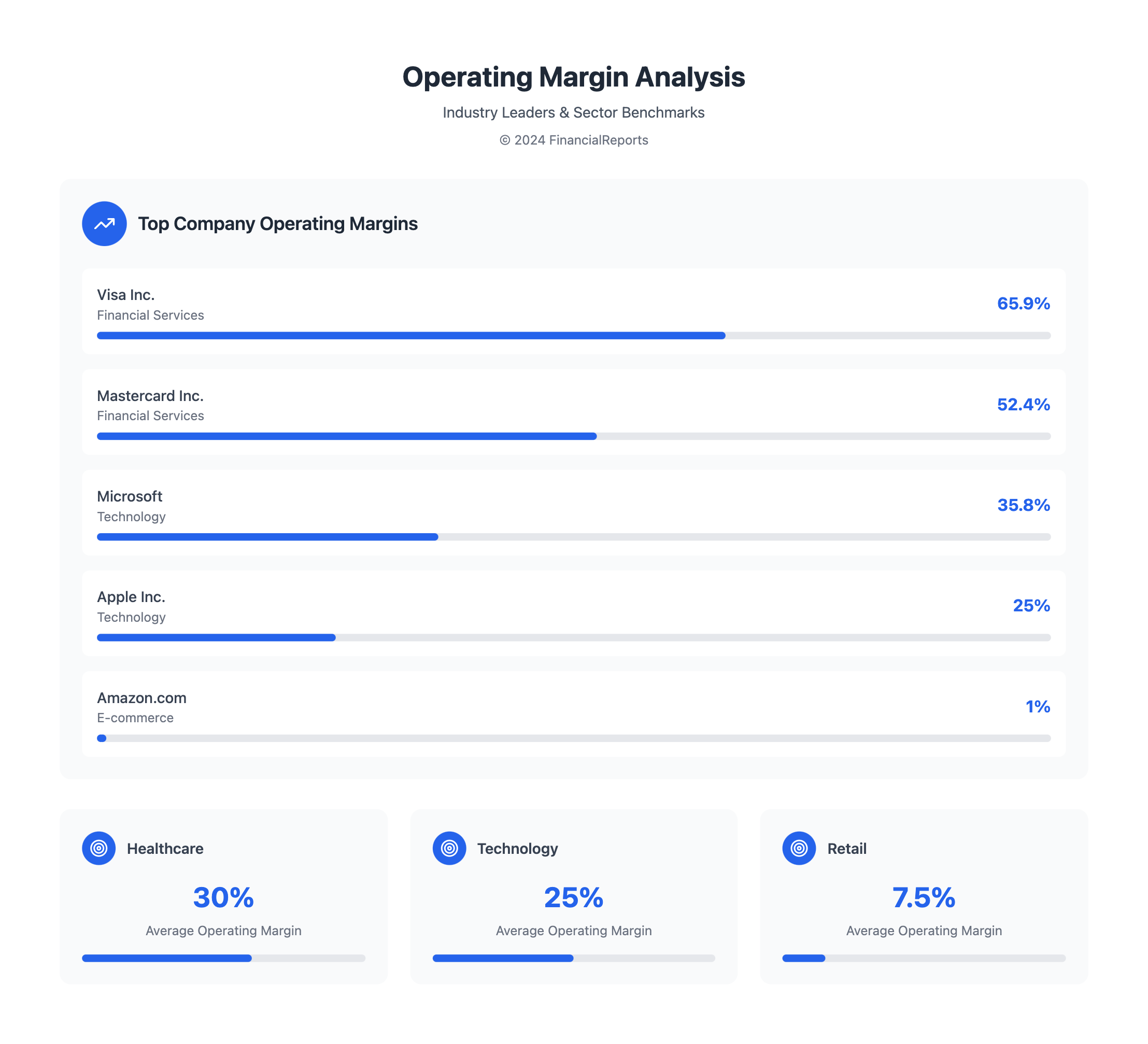
For example, Apple and Microsoft have high margins, at 25.0% and 35.8% respectively in Q4 2021. Amazon, on the other hand, has a much lower margin, at 1.0% in Q4 2021. Here's a table showing margins for different companies:
| Company | Operating Margin Ratio |
|---|---|
| Apple Inc. | 25.0% |
| Microsoft Corporation | 35.8% |
| Amazon.com, Inc. | 1.0% |
| Visa Inc. | 65.9% |
| Mastercard Incorporated | 52.4% |
A company's margin affects its financial health and growth plans. So, investors watch these margins closely. They help predict a company's future success.
Analyzing Operating Margin Trends
To understand a company's success, it's key to look at its operating margin trends. The operating margin equation shows how well a company runs by dividing operating income by net sales. Knowing what operating profit is helps us get the most from this equation. By checking past data, we can spot trends that show if a company is growing or not.
Many things can change a company's operating margin. For example, economic shifts, industry changes, and management choices can all play a part. A drop in operating margin might mean more competition, higher costs, or not running things well. But, if the margin goes up, it could mean better cost control, smart marketing, and more sales.
Historical Performance Analysis
Looking back at a company's operating margin trends can tell us a lot. By studying the operating margin equation over time, we can see where a company might need to get better. For instance, if the margin keeps going down, it might show the company can't keep up with the market or competition.
Impact of Economic Changes
Changes in the economy can really affect a company's operating margin. Knowing the operating margin equation and its parts is important to handle these changes. By looking at operating margin trends, we can see how well a company deals with economic ups and downs. This helps us make smarter choices when investing.
| Industry | Average Operating Margin |
|---|---|
| Technology | 25% |
| Retail | 5-10% |
| Healthcare | 30% |
By studying operating margin trends and understanding the operating profit equation, we can really get to know a company's financial health. This knowledge helps us make better investment choices.
Using Operating Margin for Financial Forecasting
Operating margin is key in financial forecasting. It shows how profitable and efficient a company is. By looking at past margins and future plans, analysts can forecast a company's financial future. The formula for operating profit is vital for these predictions.
To guess how profitable a company will be, analysts look at the operating margin ratio. This ratio shows how much earnings come from core operations. It's calculated by subtracting costs and expenses from total revenue, then multiplying by 100. Comparing this ratio to others and past trends helps analysts spot areas for growth.
It's also important to assess business risks in forecasting. The operating margin ratio helps see how a company reacts to market changes and competition. By thinking about these factors, analysts can predict a company's financial future more accurately. This helps investors and stakeholders make better decisions.
| Company | Operating Profit Margin | Industry Average |
|---|---|---|
| Example Company | 22.8% | 20% |
In summary, the operating margin is a critical tool for financial forecasting. It offers insights into a company's profitability and efficiency. By using the operating profit formula and analyzing the margin ratio, analysts can make informed decisions. This leads to accurate predictions about a company's financial future.
Operating Margin and Investment Decisions
When looking at investments, operating margin is very important. It shows how well a company can turn sales into profit. Knowing how to work out operating profit and how to get operating profit margins helps investors see a company's health.
Companies with high or rising operating margins are often more appealing. They show they can make good money from their main activities. For example, a company with a high margin is seen as efficient, making it a better choice for investors.
To find operating margin, use the formula: Operating Margin = Operating Earnings / Revenue. This tells us how well a company makes money from its main work. Financial experts say it's key to knowing a company's health and growth chances.
Attractiveness to Investors
Investors compare operating margins to see which companies are more appealing. A higher margin means a company is more efficient and likely to make more money. Important things to look at include:
- Revenue growth
- Expense management
- Industry benchmarks
Implications for Valuation
Operating margin also affects how much a company is worth. A higher margin can mean higher stock prices and easier funding. Investors should think about these when looking at a company's margin:
| Company | Operating Margin | Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Apple (AAPL) | 24.6% | $260,174 |
| DT Clinton Manufacturing | 36% | $125 million |
Understanding how to find operating margin helps investors make smarter choices. This can lead to better returns on their investments.
Common Mistakes in Operating Margin Calculation
Understanding a company's financial health starts with calculating the operating margin. Yet, many businesses make errors in this process. These mistakes can lead to wrong conclusions. The right use of the operating margin formula is key.
One common error is mixing up costs. For example, adding non-operating expenses to the mix. This can skew the operating margin, affecting business decisions.
Another mistake is overlooking non-recurring items or changes in accounting policies. These can greatly influence the operating margin. Not accounting for them can result in wrong calculations. The operating profit margin formula is also critical, as it includes operating income and net sales.
By avoiding these mistakes and using the correct formula, businesses can make better decisions. This leads to growth.
- Misclassifying costs, such as including non-operating expenses
- Neglecting to consider the impact of non-recurring items or changes in accounting policies
- Using incorrect accounting methods or formulas
Improving Operating Margin Strategies
Boosting a company's operating margin is key to better profits and staying ahead. Businesses can use many strategies to cut costs and boost sales.
Cost Reduction Techniques
Companies can make their operations more efficient to save money. This means making production smoother, using technology to do tasks automatically, and getting better deals from suppliers. It's important to manage both fixed and variable costs well.
Revenue Enhancement Approaches
On the sales side, businesses can try different pricing methods. This includes dynamic pricing, targeting specific markets, and selling high-margin items. Also, entering new markets or adding more products can help increase margins. It's vital to study customer data and market trends to find the best opportunities.
For lasting improvement, a mix of cost cutting and revenue growth is best. By using these strategies, companies can improve their finances and succeed in the long run.
FAQ
What is the operating margin formula?
The operating margin formula is simple. It's the operating profit (EBIT) divided by total revenue. This is shown as a percentage.
What is operating margin?
Operating margin shows how well a company runs its business. It's the profit left after paying for goods sold and operating costs. It's a key number for measuring success.
What are the components of the operating margin formula?
The formula has two main parts. The numerator is the operating earnings (EBIT). This is the profit from the main business activities. The denominator is the total revenue. This shows how much money comes in.
How do you calculate operating margin?
To find the operating margin, you need some numbers from the income statement. You'll need the operating earnings (EBIT) and the total revenue. The formula is: Operating Margin = Operating Earnings (EBIT) / Total Revenue.
Why is operating margin important in financial analysis?
It's a key sign of a company's health. It shows how well a company makes money from its main activities. It's also used to compare companies in the same field.
What factors can influence a company's operating margin?
Many things can change a company's operating margin. Industry norms, cost types, and pricing strategies are big ones. Companies with high margins often have strong brands or unique positions.
How do high and low operating margins differ?
High margins mean a company controls costs well and has strong pricing. Low margins make a company more sensitive to market changes. They have less room to move financially.
How can you analyze operating margin trends over time?
Looking at past operating margins can reveal a lot. It shows how a company's performance has changed. This can help spot trends or changes in profitability.
How is operating margin used in financial forecasting and risk assessment?
Analysts use operating margin to predict future profits. They look at trends and company specifics. This helps spot risks or opportunities in the market.
What are the implications of operating margin for investment decisions and company valuation?
A high operating margin can attract investors. It can lead to higher stock prices and easier funding. It's also a key part of valuing a company.
What are common mistakes in calculating and interpreting operating margin?
Mistakes include misclassifying costs or ignoring one-time items. It's important to be consistent when comparing margins. This ensures fair comparisons.
How can companies improve their operating margins?
Companies can cut costs or boost revenue. Cutting costs means making operations more efficient. Boosting revenue means finding new ways to make money.