Understanding Profit Rate Fall Tendencies
The concept of the tendency of the rate of profit to fall (TRPF) is a big deal in economics. It's about whether capitalism's growth will hurt its own chances of success over time. This idea says that profits will keep going down because of how capital grows and productivity increases.
The falling rate of profit is when profits don't keep up with the money put into businesses. It's a big part of understanding how capitalist economies work. Karl Marx talked about this in Chapter 13 of Capital, Volume III. His thoughts have really shaped the discussion around this topic.
Other famous economists like Adam Smith and David Ricardo also talked about the TRPF. They saw it as a real thing happening in economies. The TRPF is a tough topic, and experts are not all agreed on what it means for capitalist systems. As profits go down, it can affect investments, growth, and jobs. This makes it very important for those in finance and investing to understand.
Key Takeaways
- The tendency of the rate of profit to fall (TRPF) is a critical issue in economics, with significant debates on its implications for capitalist economies.
- The falling rate of profit is defined as the ratio of profit to the amount of invested capital, and it is considered a key factor in understanding the dynamics of capitalist economies.
- Karl Marx's ideas on the TRPF, as discussed in Chapter 13 of Capital, Volume III, have been influential in shaping the debate on this topic.
- The TRPF is a complex issue, and its implications for capitalist economies are not fully understood by scholars today.
- Understanding the tendency of the rate of profit to fall is important for financial experts and investors trying to make sense of capitalist systems.
- The falling rate of profit can have big effects on investments, growth, and jobs, making it a key area of study for those interested in capitalist economies.
Introduction to the Rate of Profit and Economic Theories
The rate of profit is key to understanding capitalism. Marxist theory says the profit rate falls as capitalism grows. This is because of more competition and more capital.
Economists like Adam Smith, David Ricardo, and Karl Marx have studied profit rates. Marx's idea of the profit rate falling is important. It shows the problems in the capitalist system.
Key Economic Theorists on Profit
Many economists have looked into profit rates. These include:
- Adam Smith, who talked about profit rates in "The Wealth of Nations"
- David Ricardo, who looked at how profit rates and capital accumulation relate
- Karl Marx, who wrote about the profit rate falling in "Capital"
The falling profit rate is a big issue in capitalism. It shows the challenges businesses face in a competitive market. By looking at these ideas, we can understand capitalism better.
| Theorist | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Adam Smith | Discussed the concept of the profit rate in "The Wealth of Nations" |
| David Ricardo | Examined the relationship between the profit rate and the accumulation of capital |
| Karl Marx | Developed the theory of the tendency of the rate of profit to fall in "Capital" |
Defining the Tendency of the Rate of Profit to Fall
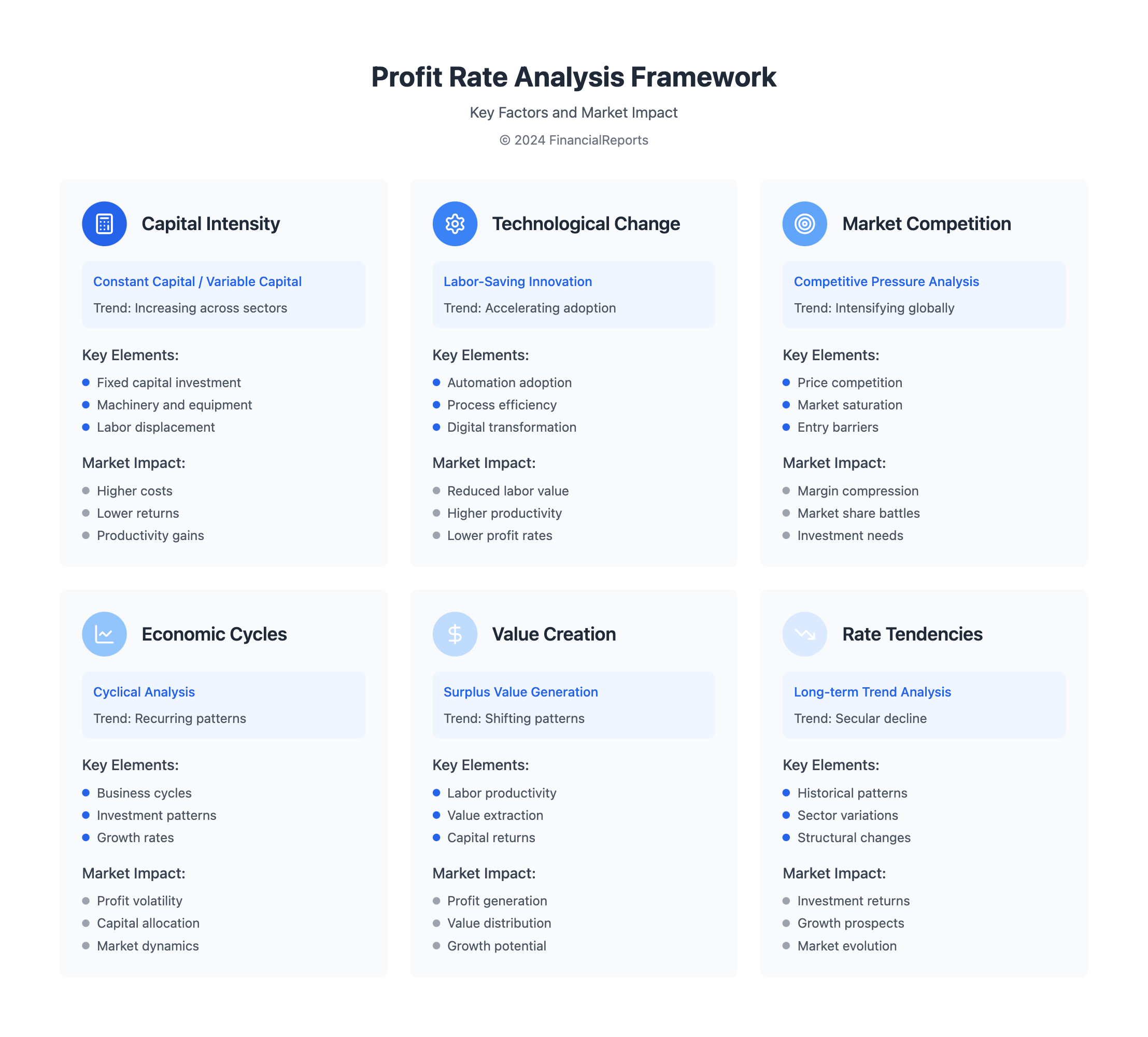
The concept of the rate of profit falling is key to understanding capitalism. It's about how constant capital and variable capital interact. Marx said the rate of profit is found by dividing surplus-value by total capital.
When constant capital grows, the rate of profit drops. For example, if constant capital goes from 50 to 400 and variable capital stays at 100, the profit rate falls from 66⅔% to 20%.
Economic Context and Terminology
In capitalism, the falling rate of profit is important for understanding profitability over time. The law of falling profit rates is linked to labor's productivity growth. More constant capital means more productivity but lower profit rates.
Relationship to Capital Accumulation
Capital accumulation is complex and tied to the falling profit rate. More capital can mean more productivity and growth. But, it also means less profit because constant capital grows faster than variable capital.
Contrasting Stable and Declining Profit Rates
It's important to compare stable and falling profit rates. Stable rates mean constant and variable capital are balanced. Falling rates happen when constant capital grows too fast, leading to lower profits.
Factors Contributing to Profit Rate Declines
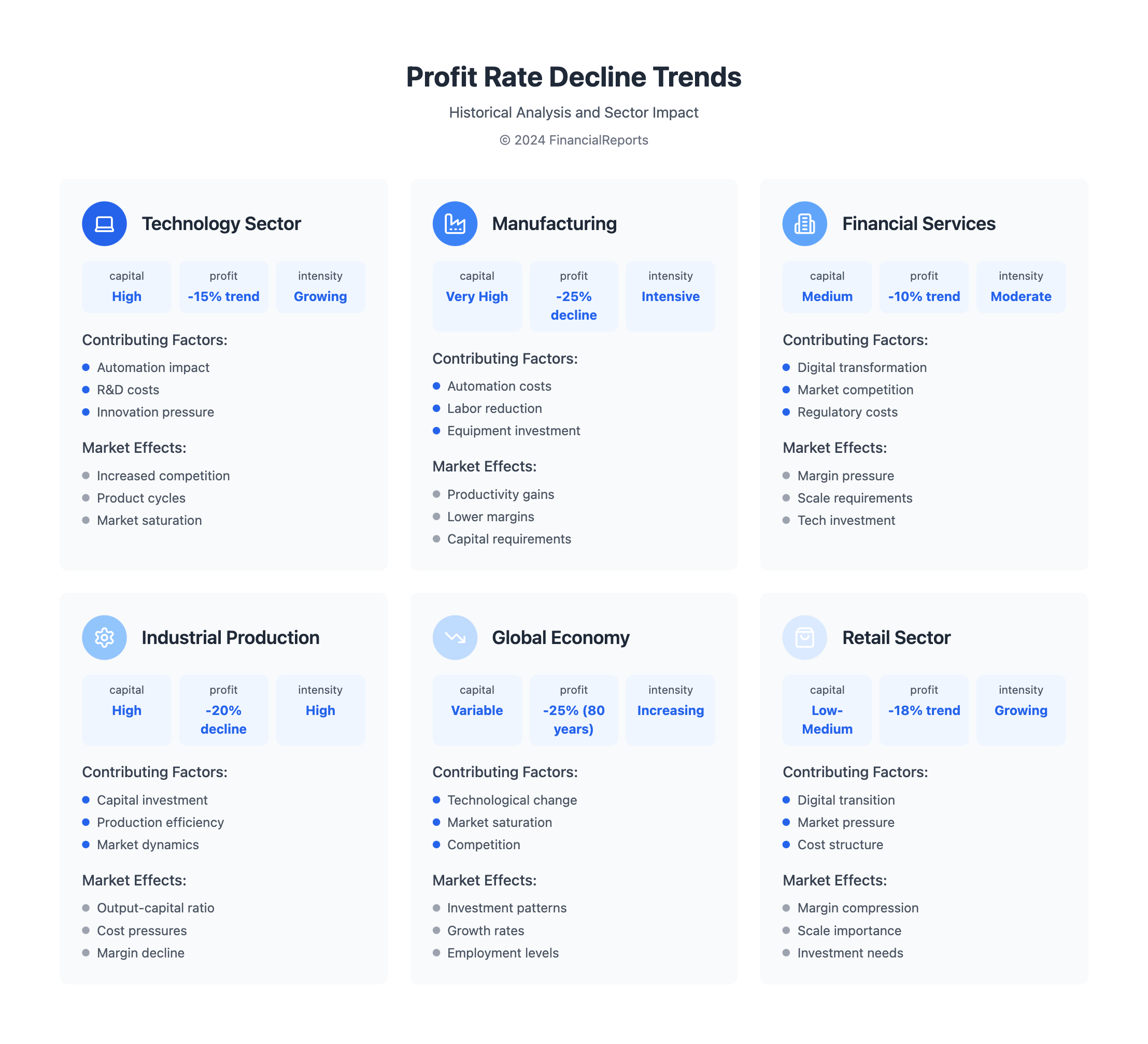
Economists have been talking about the falling profit rate for a while. New technologies that save labor are a big part of this. Studies show the world profit rate has dropped by -25% in 80 years.
Several factors are behind this decline:
- Technological advancements boost productivity but lower the output-capital ratio
- Market saturation leads to less demand and lower prices
- Changes in labor costs affect surplus value and total capital
Impact of Technological Advancements
New technologies can lower the profit rate. This happens because the cost of capital goes up, and the output-capital ratio goes down. From 2000 to 2014, the decline in the output-capital ratio was a big factor in the profit rate drop.
Market Saturation and Labor Costs
Market saturation and changes in labor costs also affect profit rates. When markets get full, demand falls, leading to lower prices and smaller profits. Changes in labor costs can also reduce surplus value and total capital, adding to the profit rate decline.
| Year | World Profit Rate | Output-Capital Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 1960-1980 | -25% | Decline |
| 1980-2019 | -15% | Slow decline |
| 2000-2014 | -10% | Linear trend decline |
The Role of Capital Intensity
The rate of profit tends to fall with more capital investment. This is because more machinery and automation mean higher costs. It's seen in many industries, where new tech boosts efficiency but cuts profit margins.
Measuring Capital Intensity in Industries
Capital intensity grows as capital to labor ratios rise. This is clear in the last 30 years, with big tech and automation investments. Key factors include:
- Investment in labor-saving technology
- Introduction of new production methods and processes
- Increased use of automation and machinery
How Capital Intensity Affects Profit Margins
More capital in industries means higher costs and lower profits. This is because the cost of capital goes up, and returns drop. Michael Roberts points out that the USA's profit rate has fallen steadily, with some ups and downs. This decline affects businesses and the economy, leading to less investment and more competition for profit.
The Influence of Competitive Markets
As thetendency of the rateof profit to has been widely discussed by economists. A key factor influencing this trend is the role of competitive markets. In a capitalist economy, increased competition among firms can lead to a general equalization of profit rates across industries.
Competitive pressures often force companies to engage in "price wars" to maintain market share. This can stabilize or even depress profit margins industry-wide. This aligns with the theory that the declining rate of profit is an inherent tendency within capitalist systems.
Strategies for optimal pricing and market positioning become critical for firms. They seek to maintain healthy profit levels in the face of these competitive dynamics. Financial professionals must carefully navigate these competitive landscapes to identify opportunities for sustainable profitability in their industries.
FAQ
What is the tendency of the rate of profit to fall (TRPF)?
TRPF is a theory that says profit rates in capitalist economies tend to fall over time. It points out that as we get more efficient, the value created by labor goes down. This leads to a drop in profit rates.
How has the concept of the profit rate evolved in economic theory?
The idea of profit rates started with Adam Smith and David Ricardo. But Karl Marx really dug into it in "Capital." Marx's work shows how profit rates can signal economic troubles under capitalism.
What is the economic context behind the tendency of the rate of profit to fall?
TRPF is about how constant capital (like machines) and variable capital (labor) interact. When we invest more in machines, the value created by labor gets less. This makes profit rates drop over time.
What are the key factors contributing to the declining rate of profit?
Several things can lead to lower profit rates. These include new technology that saves labor, market oversaturation, and rising labor costs. These issues often come with economic ups and downs.
How does capital intensity influence profit margins?
More investment in machines and automation can really affect profits. Industries with lots of capital struggle more than those with less. This is because labor's value-making power is overshadowed by technology.
How do competitive market dynamics affect the rate of profit?
Market competition can mess with profit rates. Things like more competition, pricing wars, and big company dominance can make it hard to keep profits up. Businesses need to understand these dynamics to stay competitive.