Understanding Pretax Margin in Business Finance
The pretax margin shows how well a company does before taxes. It tells us how much profit a business makes for each dollar sold. To find it, you divide earnings before taxes (EBT) by sales and then multiply by 100.
This metric helps compare companies in the same field. It shows how good a company is at making profits. A high pretax margin means a company is doing well, while a low one means it's not.
Key Takeaways
- The pretax margin is a ratio used to measure a company's operating efficiency before deducting taxes.
- It is calculated by dividing earnings before taxes (EBT) by sales and multiplying the result by 100.
- Pretax margin is a key indicator for investors and analysts to assess a company's success in balancing sales growth and cost reduction.
- Pretax profit margins can vary significantly by sector and work best when comparing companies within the same industry.
- A good pretax margin indicates how much in earnings before taxes (EBT) is retained by a company per dollar of revenue generated.
- Industry peers can be compared more effectively using the pretax margin as it excludes taxes, considering variations in tax structures and jurisdictions.

What is Pretax Margin?
Pretax margin shows how much profit a company makes before taxes. It helps us see how well a company runs its operations. To find it, we use the pre tax profit margin formula. This involves dividing Earnings Before Taxes (EBT) by sales and then multiplying by 100.
This metric is vital for those who work in finance, investors, and big clients. It gives a clear view of a company's health. By looking at the pretax margin, we can see how well a company does without taxes and other non-operating factors.
Definition and Importance
The pretax margin is the ratio of Earnings Before Taxes (EBT) to sales, shown as a percentage. It's a key sign of a company's success. It helps compare companies in different fields. The pre tax profit margin formula is a standard way to figure this out.
How Pretax Margin is Calculated
To find the pretax margin, we follow these steps:
- Earnings Before Taxes (EBT) is found by subtracting operating costs and depreciation from total revenue.
- Then, we divide EBT by sales to get the pretax margin ratio.
- Lastly, we multiply this ratio by 100 to show the pretax margin as a percentage.
For instance, if a company has an EBT of $100,000 and sales of $1,000,000, its pretax margin is 10%. This means it makes 10 cents of profit before taxes for every dollar sold.
| EBT | Sales | Pretax Margin |
|---|---|---|
| $100,000 | $1,000,000 | 10% |
By using the pre tax profit margin formula, companies can check their financial health. They can then make smart choices to boost their profits.
The Role of Pretax Margin in Business Finance
Pretax margin is key in business finance. It shows how well a company does before taxes are taken out. Analysts and investors watch it closely. It helps them see if a company is doing well and if it can grow.
To find the pretax margin, you divide pretax profit by gross revenue. Then, you multiply by 100. This gives a percentage of how much profit is left before taxes.
The pretax margin is important for comparing companies. It lets you see how different companies stack up. It's one of the main ways to check if a company is making money well.
Other important metrics include gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin. Each gives a different view of a company's money-making abilities. Knowing about pretax margin and these other metrics helps investors make smart choices.
- High pretax margins mean a company is doing well financially and is efficient.
- Low pretax margins might mean a company is not running smoothly or has high costs.
- Investors use pretax margin to see how profitable companies in the same field are.
In short, pretax margin is very important in business finance. It gives insights into a company's success and stability. By looking at pretax margin, experts and investors can make better choices about investments and company performance.
Components Influencing Pretax Margin
Pretax margin shows how well a company runs its operations. It's key to know what affects it. The formula for pretax margin is: Pretax Profit Margin = Earnings Before Taxes (EBT) / Revenue x 100%. This tells us how much profit a company makes before taxes.
Revenue Streams
Revenue streams are vital for pretax margin. Companies with many and good revenue streams tend to have better pretax margins. Sales earnings, merchandise costs, and sales prices all play a part in this.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses also shape pretax margin. Keeping costs low is important for a company's financial health. By cutting down on expenses, companies can boost their pretax profit margin.
Tax Considerations
Taxes are important, even though they're not in the pretax margin formula. They affect net income and profit margins. Pretax margin is often used for comparisons because it shows a company's true operating efficiency.
Ways to Improve Pretax Margin
To make a company's finances better, it's key to work on the pre tax profit margin formula. This means finding ways to run operations better, bring in more money, and set prices wisely. When a company keeps its pretax profit margins high, it shows it's doing well and has a strong business model.
Improving pretax margin can be done by cutting costs and making the supply chain more efficient. Growing revenue by adding new products or entering new markets also helps. Smart pricing, like changing prices based on demand, can increase earnings without losing profit.
Strategies for Improvement
- Reduce operating costs by streamlining operations and renegotiating contracts with suppliers
- Evaluate product performance and consider removing underperforming products to optimize revenue
- Adjust pricing strategies to reflect changes in market conditions and customer demand
- Build brand loyalty through effective marketing and customer retention strategies
By using these strategies, companies can boost their pre tax profit margin formula. This leads to a stronger financial standing. It's important to keep an eye on pretax margins and make smart choices to grow the business.
| Industry | Average Net Profit Margin |
|---|---|
| Advertisement | 3.30% |
| Apparel | 5.87% |
| Beverage (soft) | 18.50% |
Pretax Margin vs. Net Margin
When looking at a company's financial health, pretax margin and net margin are key. They show different things about how profitable a company is. Pretax margin shows how efficient a company is before taxes are considered.
A company's pretax margin can be much higher than its net margin because of taxes. For example, a company might have a 15% pretax profit margin but only a 10.5% net margin after paying 30% in taxes. This shows why pretax margin is important for comparing companies or looking at their efficiency without tax worries.
Key Differences Explained
The big difference between pretax and net margin is taxes. Pretax margin shows a company's core operations, without tax effects. Net margin, on the other hand, shows a company's total profitability, including taxes.
When to Use Each Metric
Investors like pretax margin for comparing companies in different tax situations. It helps make fair comparisons. But, net margin is better for seeing a company's overall financial health and profit.
The table below shows how pretax and net margin differ for XYZ Company:
| Metric | 2018 Value |
|---|---|
| Gross Profit Margin | 71.4% |
| Net Profit Margin | 14.3% |
| Pretax Profit Margin | 20% |
Looking at both pretax and net margin helps investors understand a company better. It helps them make smarter choices.
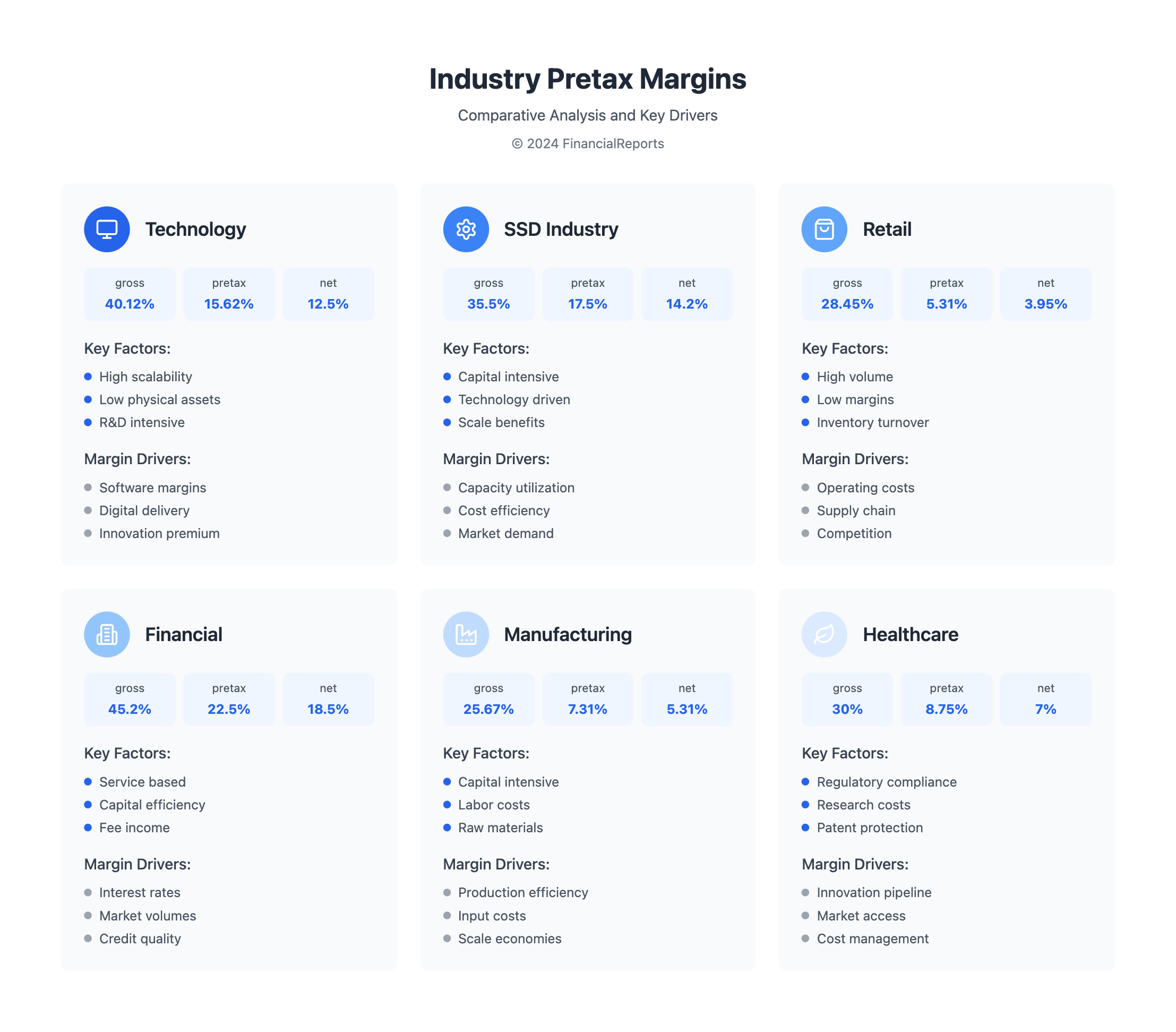
Industries and Their Typical Pretax Margins
Pretax margin varies a lot between industries. It's key to look at specific sectors when checking a company's financial health. The average gross profit margin for all industries is 36.56%. The average net profit margin is 8.54%. But, some industries have higher or lower margins because of things like how much money they need to start, how competitive they are, and special challenges they face.
The tech sector usually has higher pretax margins because it needs less money to start and can charge more. On the other hand, the manufacturing sector might have lower margins because of tough competition and needing a lot of money. The retail sector's margins can change based on how well they manage their stock and their supply chain.
| Industry | Average Gross Profit Margin | Average Net Profit Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | 40.12% | 15.62% |
| Manufacturing | 25.67% | 5.31% |
| Retail | 28.45% | 3.95% |
Knowing these industry-specific pretax margins helps financial experts and investors make better choices. They can better understand company performance and find good investment opportunities.
Analyzing Trends in Pretax Margins
To understand a company's health, investors should look at pretax profit margins along with other metrics. The pre tax profit margin formula is key for evaluating a company's financial performance. By examining a company's pretax margins over 10 years, trends become clear, focusing on the last five years for recent changes.
Many factors influence margins, such as labor, raw materials, energy, and economic conditions. Marketing, weather, and competition also play a role. It's important to compare margins with industry peers to get a true picture. For instance, the SSD industry has a 5-year average pre-tax profit margin of 17.5%, while other industries average 8.6%.
Companies like Trex and Louisiana-Pacific have shown strong margins over the past five years. Trex's average is 26.0%, and Louisiana-Pacific's is 20.8%. Here's a table that shows how comparing margins can help investors:
| Company | 5-year Pre-tax Profit Margin |
|---|---|
| Trex | 26.0% |
| Louisiana-Pacific | 20.8% |
| SSD Industry Average | 17.5% |
By studying pretax margin trends and using the pre tax profit margin formula, investors can better understand a company's financial health and growth prospects.
Limitations of Pretax Margin
Pretax margin has its downsides. It's not great for comparing companies across different sectors. Each industry has its own set of expenses and sales patterns. For example, the apparel industry had a 51.84% gross profit margin in 2023. But the healthcare products industry had a net profit margin of just 7%.
Another issue is how different accounting practices can skew pretax margin. Accounting practices can vary a lot between companies. This makes it hard to compare pretax margins accurately. Also, industry variability is key, as companies in different sectors face different costs and revenue.
Accounting Practices Affecting Margin
How companies account for things like depreciation and revenue can change pretax margin numbers. For example, a company using straight-line depreciation might look better than one using accelerated depreciation. It's important to look at these accounting choices when comparing pretax margins.
Industry Variability
Industry differences also play a big role in pretax margins. Each industry has its own costs and revenue streams. For instance, tech companies might spend a lot on R&D, while retail companies might spend more on marketing. Here's a table showing profit margins for different industries:
| Industry | Average Gross Profit Margin | Average Net Profit Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Apparel | 51.84% | 10% |
| Healthcare Products | 30% | 7% |
| Consumer Electronics | 20% | 11.11% |
In summary, pretax margin is useful but has its limits. Knowing about accounting practices and industry differences helps investors and financial experts make better choices.
Using Pretax Margin for Investment Decisions
Investors often use the pre tax profit margin formula to check a company's health. This formula shows how much profit a company makes before taxes. It helps investors see how well a company is doing financially.
The formula is simple: pre tax income divided by total revenue, shown as a percentage. This number is key for investors. It shows how well a company makes money, helping investors decide if it's a good investment.
Some important things to think about when using pretax margin include:
- Evaluating the company's financial performance and operational efficiency
- Assessing the company's ability to manage operational expenses and generate profits from core activities
- Comparing the company's pretax profit margin to industry peers and benchmarks
Using the pre tax profit margin formula helps investors make better choices. It gives a clear picture of a company's financial health. This allows investors to see if the company is growing, its market position, and its overall health.
Case Studies on Pretax Margin Applications
Pretax margin is key in checking how well a company does financially. A high pretax margin means a company is very profitable. But, a low ratio shows it's not doing as well.
Let's look at some real examples to see how pretax margin works. Companies like Apple and Microsoft have used it to boost their profits. For example, Apple keeps its profit margins high, even with tough competition in tech.
But, some companies have made mistakes with pretax margin. A company with a low pretax margin might rely too much on low taxes. This makes it risky if tax laws change.
| Company | Pretax Margin | Net Profit Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Apple | 25% | 20% |
| Microsoft | 30% | 25% |
Looking at pretax margin and other numbers helps investors and experts understand a company's health. As shown, pretax margin is very important. It can really affect a company's success.
Tools for Measuring Pretax Margin
Businesses can use financial software and platforms to find the pre tax profit margin. These tools make calculations easy and offer detailed analysis. For example, a profit margin calculator helps set the right selling price to increase profits.
The pre-tax profit margin shows how well a company runs before taxes. It's found by dividing earnings before taxes (EBT) by sales and then multiplying by 100. A higher margin means better profits and efficient operations. This helps companies see how they're doing and where they can get better.
Financial software and platforms have important features for measuring pretax margin. These include:
- Automated calculations and data analysis
- Customizable reports and dashboards
- Integration with other financial metrics for a complete view of company performance
By using these tools and understanding the pre tax profit margin formula, businesses can learn a lot about their profits. This knowledge helps them make smart decisions to grow and succeed.
Conclusion: The Importance of Monitoring Pretax Margin
In this guide, we've seen how pretax margin is key to understanding a company's health and profits. It's important for financial experts, investors, and business leaders to keep a close eye on it.
Pretax margin shows how well a company runs and makes money before taxes. By looking at pretax margin trends and other important numbers, businesses can see their financial health. They can spot areas to get better and make smart choices for growth.
Checking pretax margin often, knowing what affects it, and comparing it to others in the industry helps businesses. It lets them set better prices, cut costs, and stay strong financially. This way, companies can adapt quickly to market changes and succeed in the long run.
FAQ
What is pretax margin?
Pretax margin shows how well a company does before taxes. It's the profit left after subtracting costs but before taxes. It's a key way to see if a company is doing well.
How is pretax margin calculated?
To find pretax margin, you use this formula: Pretax Margin = Pretax Profit / Total Revenue x 100. Pretax profit is what's earned before taxes. Total revenue is all the money made by the business.
Why is pretax margin important in business finance?
Pretax margin is key for seeing how a company runs and makes money. It shows how well a business controls costs and makes profits, without worrying about taxes. It helps experts, investors, and clients make smart choices.
How does pretax margin differ from net margin?
Pretax margin doesn't count taxes, while net margin does. Pretax margin shows how a company does on its own, useful for comparing across different places or tax policies.
What factors influence a company's pretax margin?
Many things can change a company's pretax margin. This includes how much money it makes, its costs, and taxes. Better cost control, smart pricing, and more revenue sources can help.
How can companies improve their pretax margin?
To boost pretax margin, companies can cut costs, grow revenue, and set smart prices. By improving operations, selling more without spending more, and pricing right, they can make more money.
What are the typical pretax margins in different industries?
Pretax margins differ by industry. This is because of things like how much money is needed, competition, and special challenges. For example, tech often has higher margins than retail or manufacturing.
How can pretax margin analysis be used for investment decisions?
Pretax margin helps investors understand a company's health and make better choices. By looking at trends, comparing to others, and seeing how it affects finances, investors can make smarter decisions.