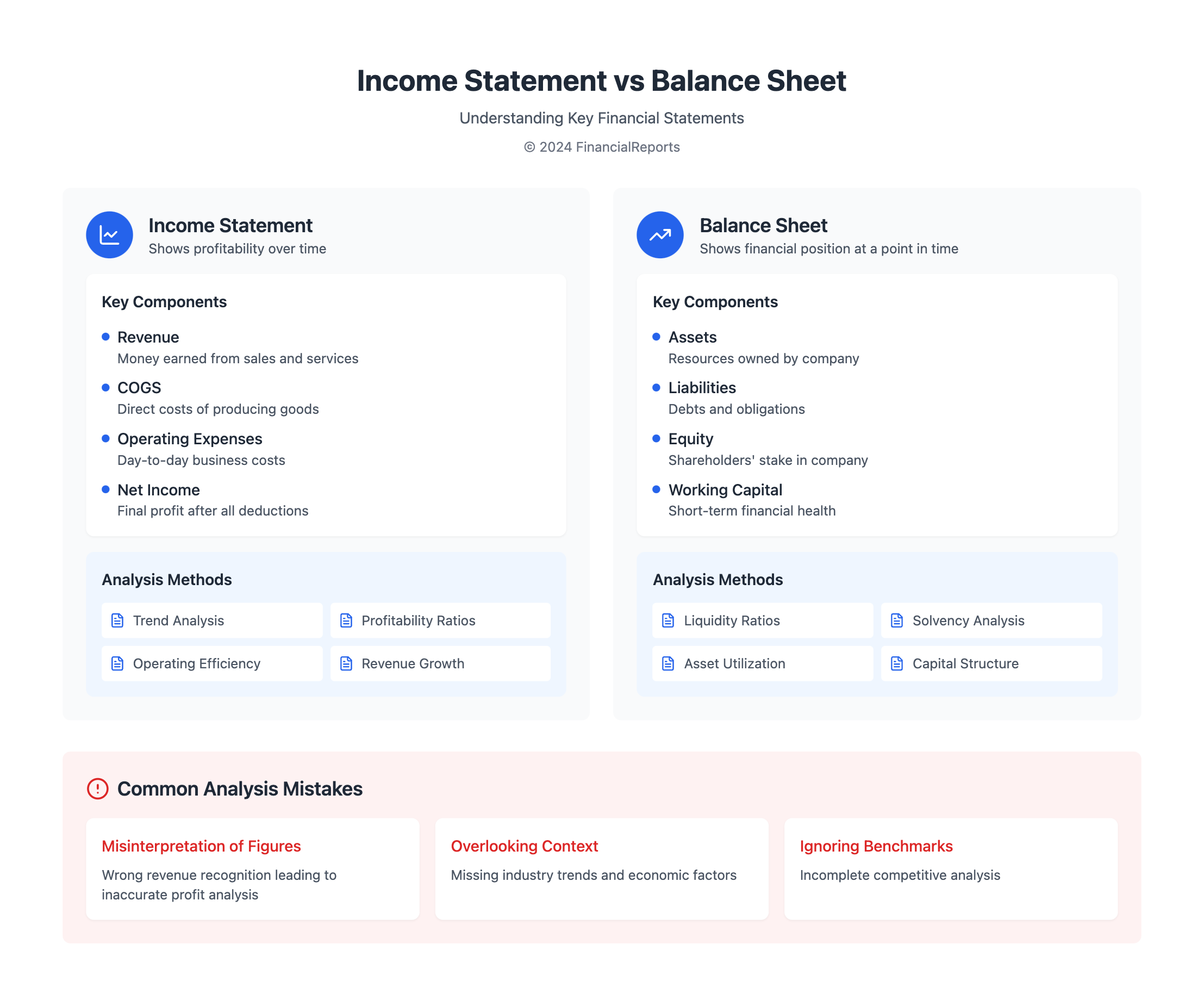
Understanding Income and Balance Sheet Analysis
In the world of finance, income and balance sheet records are key. They're more than just papers; they are the foundation of financial clarity. These documents help make crucial business choices. An income statement shows how well a business is doing over time. It tells us about profits and losses. A balance sheet, on the other hand, shows a company's financial status at a certain moment. It lists what the company owns and what it owes.
Looking closely at the income statement vs balance sheet tells a story of financial wellness. Take Apple Inc., for example. It had total assets worth $375.3 billion at the end of 2017. This number shows its strong financial standing. Then, look at J.C. Penney. Their financial reports show both a gain and a loss of $116 million in the same year. This shows the complex nature of financial health.
Key Takeaways
- Income statements and balance sheets are critical for understanding a company's financial path over time and at a specific moment.
- Apple Inc.'s accurate asset figures underline the value of detailed financial records for investors.
- J.C. Penney's financial results show the differences between operational income and net loss in the same year.
- Financial ratios like the current ratio (3.27) and the quick ratio (2.18) give insights into a company's liquidity and financial condition.
- The debt to equity ratio (0.4 as an example) reveals the mix of debt financing and owner's equity. It's key for evaluating risk and stability.
- Detailed analysis of a balance sheet is crucial to understand not only liabilities but also the equitable strength, as Apple Inc.'s shareholder's equity shows.
Introduction to Income and Balance Sheets
Today, knowing how to read an income statement and a balance sheet is key. These documents help us understand a company's financial health. They are vital for making smart investment choices.
Definition of Income Statement
An income statement shows a company's revenue and expenses over time. It tells us about the company's financial activities and how profitable it is. For example, Sunshine Landscapers LLC had gross revenues of $289,397 in 2010. Their expenses were $195,512, which left them with a net income of $100,885.
Definition of Balance Sheet
The balance sheet, on the other hand, is a snapshot of a company's finances at a specific time. It lists assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity. This helps us see what the company owns and owes. Important metrics like the current ratio, debt-to-equity ratio, and acid-test ratio are used to check a company's financial health.
Importance of Both Reports
The income statement and balance sheet give key insights. They are essential for understanding a company's financial situation. These insights help identify differences between the two reports and provide a full picture of financial health.
Looking at examples of these documents can help with financial planning and making decisions. Studying Sunshine Landscapers LLC's financials, for example, can show us how well they handle money. It reveals their current financial state and their growth potential.
Deep analysis of these reports is crucial for guiding a company to success. In today's data-driven world, being able to analyze financial statements is a must. It's vital for anyone in finance.
Key Components of an Income Statement
Understanding how an income statement works is key to good financial decisions. It shows a company's money flow over time, detailing earnings, costs, and profits. Knowing how to analyze this can give deep insights into a business's health.
Revenue
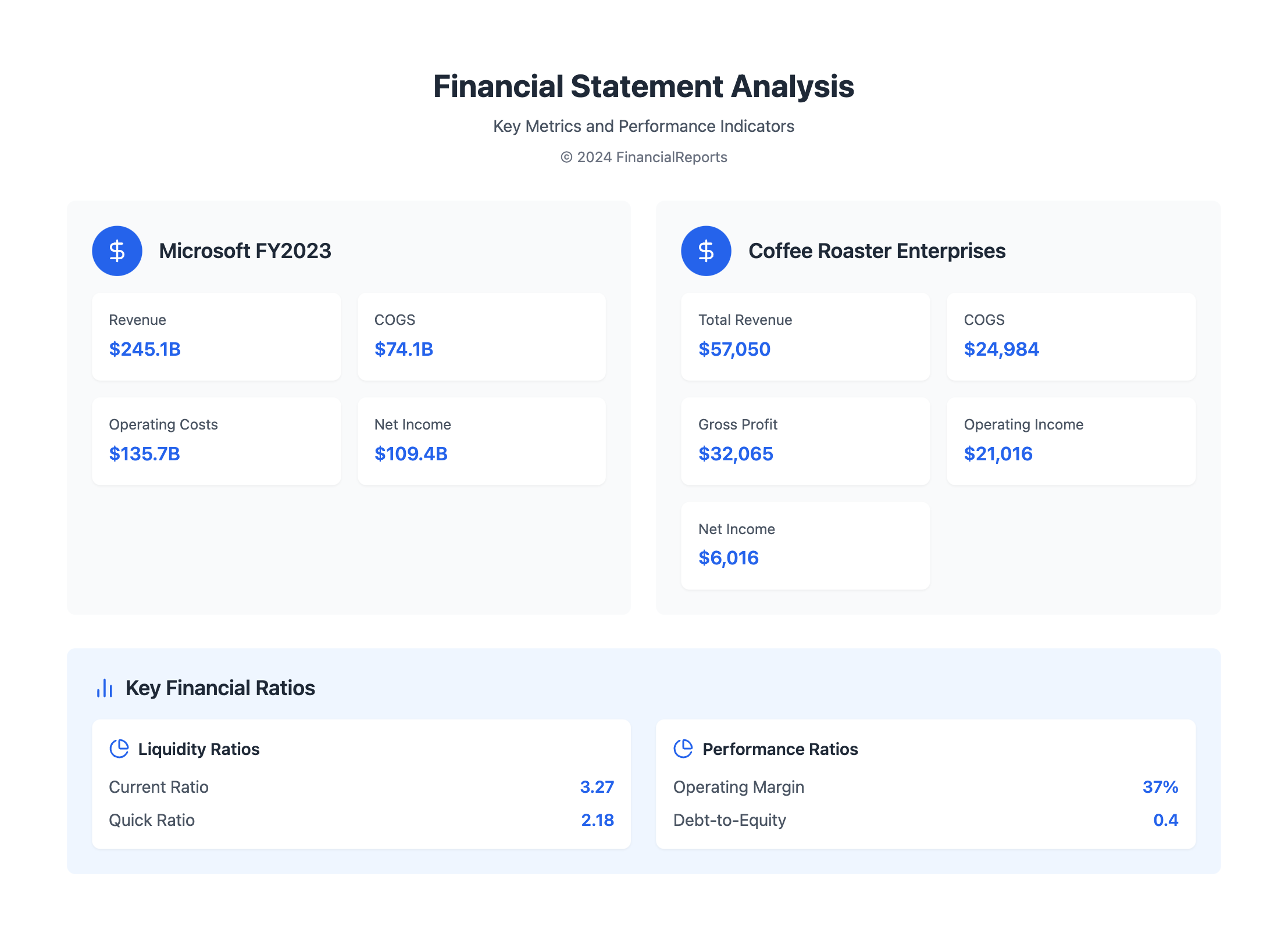
Revenue is the total money made from core business before deducting any costs. For example, Microsoft marked a notable revenue of $245.1 billion in the fiscal year ending June 30, 2023. It sets a standard for evaluating market performance and operational size.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS sits right below revenue, showing direct costs to make or sell products. It helps in understanding how well costs are managed. Microsoft’s COGS for the same period was $74.1 billion. This is taken from the total income to figure out the gross margin.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses are the costs needed to run day-to-day business activities. This includes things like R&D, marketing, and office management. Microsoft's operating costs were high at $135.7 billion. This reflects its big investment in key areas to maintain operations and market position.
Net Income
The net income shows how much money a company keeps after covering all expenses. It's a clear sign of profit over the time reported. For Microsoft, net income was a strong $109.4 billion after all deductions. This shows their high profitability and efficient operations.
Analyzing an income statement in detail helps stakeholders understand it better. It makes it easier to make smart financial and investment choices.
Key Components of a Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is key for showing a company's financial state at a certain moment. It clearly shows assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity. This helps everyone understand the company's financial stability and power.
Assets
Assets are split into current assets and non-current assets. This includes cash, inventory, and property. These are critical for knowing the company's operational resources and revenue-making ability.
Liabilities
Liabilities are current liabilities or long-term liabilities. They cover debts and future payments. Important liabilities include accounts payable and long-term debt. By knowing these, people can understand the company's financial duties.
Equity
The equity part shows retained earnings, common stock, and extra capital. It's what remains for shareholders after clearing liabilities. The balance sheet structure cleanly separates stockholder contributions from retained earnings.
It's vital to examine these parts for a deep understanding. This insight influences decisions whether you're looking at a common stock balance sheet or income statement. For deeper analysis, check this resource on financial statement vs balance sheet analysis.
Analyzing the balance sheet helps assess a company's present and future financial health. It reveals financial readiness and risk levels. This analysis is key for strategic planning and managing risk.
Purpose of Income Statements
An income statement gives a simple, clear look at how a company is doing financially over time. This is key for smart management and making the right strategic moves. It points out important numbers like sales, costs, and profits. These help in figuring out if a business is doing well and how it's running day-to-day. Let's dive deeper into why they are so important.
Assessing Profitability
The income statement is crucial for seeing if a company is making money. It lists all money made and spent, ending with the net income. This shows how financially healthy the company is during a certain time. This is not just useful for the people running the company but also for investors deciding where to put their money. It's about understanding expenses and analyzing financial reports carefully.
Evaluating Operational Performance
Income statements tell us how well a company is managed daily. By looking at costs of goods sold and other expenses against income, we can see how efficient operations are. For example, if costs go up but sales don't, it might mean problems in production or rising costs for materials. Tracking these can help make changes to improve profits.
Strategic Decision-Making
Income statements are vital for big business decisions. They provide a foundation for entering new markets, tweaking prices, or changing how things are done. By looking at past data, companies can predict future trends and plan accordingly. This info guides important choices about where to use resources, aiming for better financial results later.
| Financial Indicator | FY 2022 | FY 2021 | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Net Income | $50M | $75M | -33.33% |
| COGS | $30M | $20M | 50% |
| Earnings per Share (EPS) | $2 | $3 | -33.33% |
| Dividends per Share | $0.045 | $0.050 | -10% |
This table shows key financial data from a company's income statements over two years. It clearly outlines how their financial situation has changed, helping in making informed decisions. By closely managing these aspects, a company can grow shareholder value and achieve steady growth.
Purpose of Balance Sheets
Understanding a balance sheet is crucial for checking a company's financial health. Balance sheets give a clear picture regularly. They are central for both internal reviews and analyzing company's finances by outsiders. We will look at how they fit in corporate finance, highlight income and balance sheet dynamics, balance sheet importance, and how to analyze balance sheets.
Understanding Financial Position
A balance sheet shows what a company owns and owes at any moment. It lists assets, like cash and investments, and shows how they are funded. This helps everyone understand a company's financial health, checking if assets and finances are balanced.
Assessing Liquidity
The balance sheet also shows if a company can pay its short-term debts. It uses metrics like the quick ratio and current assets. This helps investors know if a company can quickly turn assets into cash, showing the investment's risk level.
Evaluating Capital Structure
Analyzing a company's capital structure is another key use of balance sheets. They reveal the mix of debt and equity financing. Looking at the debt-to-equity ratio helps investors understand a company's financial health and strategy. This helps decide if a company has too much debt or enough equity for its needs.
| Financial Metric | Formula | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Debt-to-Equity Ratio | Total Liabilities / Shareholders' Equity | Indicates financial leverage, assessing risk in financing. |
| Quick Ratio | (Cash + Marketable Securities + Accounts Receivable) / Current Liabilities | Measures ability to meet short-term obligations without selling inventory. |
| Asset to Equity Ratio | Total Assets / Shareholders' Equity | Gauges how much of a company's assets are financed by owner funds. |
In short, balance sheets outline a company's financial status and help in making strategic choices. They are key for checking liquidity and understanding capital structure. This makes them vital for keeping businesses on track and transparent about their finances.
How to Analyze Income Statements
An income statement shows a company's financial health and future potential. To fully understand it, we use trend analysis, ratio analysis, and benchmarking. Each method offers unique insights about financial trends and how efficiently a company operates.
Trend Analysis
Looking at financial trends over time helps analysts find patterns of growth or decline. For instance, tracking the net income of Coffee Roaster Enterprises Inc. shows if earnings are stable or not. Steady growth in net income means the company is growing. Meanwhile, big changes may suggest operational issues or changing market conditions.
Ratio Analysis
Ratio analysis uses financial ratios to quantitatively measure performance. Key ratios, like Gross Profit Margin and Operating Profit Margin, tell us about profitability and efficiency. For example, Coffee Roaster Enterprises Inc.'s Operating Profit Margin is calculated by dividing Operating Income by Total Revenue, resulting in about 37%. This shows how well management can control costs and make profits.
Benchmarking
Benchmarking against others in the industry helps see where a company stands. Comparing figures like gross profit margins or net incomes pinpoints where improvements are needed. This helps a company stay competitive and guides strategic decisions.
Below is a table outlining key figures from Coffee Roaster Enterprises Inc.'s income statement:
| Financial Metric | Amount ($) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Total Revenue | 57,050.68 | Total income from sales. |
| COGS | 24,984.79 | Costs tied directly to goods sold. |
| Gross Profit | 32,065.89 | Revenue after subtracting COGS. |
| Operating Income | 21,016.34 | Gross profit minus various expenses. |
| Net Income | 6,016.34 | Earnings after all expenses, including taxes and interest. |
Understanding income statements requires looking beyond the numbers. It's about seeing what they mean for operational efficiency and competitiveness. This deep analysis is crucial for sound financial decisions. It shows why combining financial strategies is important for a thorough view of financial health.
How to Analyze Balance Sheets
Looking into a balance sheet analysis is key to understanding a company's financial stability. It reveals a company's financial position. It also shows how stable it is by using liquidity and solvency ratios.
This analysis uses detailed comparisons, financial ratios, and other metrics. It's to dig deep into the business's financial state.
Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis checks financial statements over time to spot trends or odd things. It compares balance sheets from various times. Analysts see if assets, liabilities, and equity go up or down.
For example, more liabilities might mean solvency troubles. More assets could point to growth. Walmart's 2024 balance sheet with $14.8 billion in cash and over $81.3 billion in equity shows great financial resources.
Financial Ratios
Liquidity and solvency ratios help understand if a company can pay off its debts. The debt-to-equity ratio, like Walmart's 1.84 in 2022, tells us about financial leverage and risk. A high ratio suggests more risk.
Other ratios like the current ratio and return on assets (ROA) show operational efficiency and asset management. ROA's formula is Net Income divided by Average Total Assets. It's vital for seeing how well a company uses its assets.
Vertical and Horizontal Analysis
Vertical analysis looks at balance sheet parts as percentages of total assets. This helps understand each element's role in the financial structure. Horizontal analysis compares financial data across periods. It shows growth or issues over time.
These methods reveal how operations, like Walmart’s inventory management, affect financial health.
| Key Financial Metric | Walmart FY2024 | Industry Average |
|---|---|---|
| Debt-to-Equity Ratio | 1.84 | 1.90 |
| Return on Assets | Calculable from net income and assets | Frequently varies |
| Cash Conversion Cycle | Computation from DIO + DSO - DPO | Variable by industry |
Using these methods to analyze a balance sheet offers a full picture of a company’s financial health. For investors and financial pros, this information is critical. It helps them make smart investment choices and gauge financial strength.
Common Mistakes in Financial Analysis
Financial analysis is key for guiding business decisions. It helps maintain a company's market trust. But it's easy to fall into traps that skew a company's financial status. Balance sheet and income statement difference is vital in doing accurate financial analysis. We will look at these errors, focusing on industry-specific terms and how they affect different sectors.
Misinterpretation of Figures
Misreading numbers is a big issue. It comes from not getting the basic accounting rules. Like, getting revenue recognition wrong is a common mistake. It confuses analysts about when and how to record revenue.
This wrong step can mess up profit analysis and tax calculations. And that can lead to poor business choices.
Overlooking Context
Missing the bigger picture is another mistake. Not checking against industry standards or missing economic trends affects how a company's success is seen. Small mistakes, like skipping little account reconciliations, add up. They cause big mistakes in financial reports.
This shows why a broad, detailed approach to financial reports is needed.
Ignoring Industry Benchmarks
Not using industry benchmarks hurts in sectors where comparing performance is key. Not analyzing financial ratios or giving out incomplete reports blocks a true look at a company's health. Missing out on industry terms and measures means missing key insights on competition and operations.
| Error Type | Common Causes | Impact on Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Inaccurate Revenue Recognition | Misapplication of accounting principles | Overstatement of profits and tax liabilities |
| Misclassifying Expenses | Lack of understanding in capital vs. expense categorization | Distorted financial picture affecting profitability |
| Ignoring Economic Context | Overlooking industry cycles and benchmarks | Misguided assessment of financial health and competitive position |
| Late Financial Reporting | Systemic inefficiencies, irregular accounting practices | Hindered cash flow forecasting and management decision-making |
| Bad Inventory Accounting | Neglected physical counts, inadequate ERP setups | Overstated assets leading to incorrect financial assessment |
To avoid these errors, you need a solid grasp of balance sheet and income statement differences. And you must approach accurate financial analysis with discipline. Correct categorization, prompt account reconciliation, and following the latest accounting standards help dodge these pitfalls. Financial experts should be alert to these issues. This ensures reliable financial reports and wise business decisions.
Tools for Analyzing Income and Balance Sheets
In today's fast-paced finance world, using the right tools to check financial documents is key. This enhances both the speed and correct understanding of financial reviews. Below, we delve into the various tools available for finance experts. These insights cover their uses and benefits.
Financial Software Solutions
For reading complex financial statements accurately, financial data solutions are essential. Financial analysis now benefits greatly from software. Cloud-based and Business Intelligence (BI) tools are very important. They offer real-time reporting, analytical tools, and customizable dashboards. This is vital for in-depth income and balance sheet reviews. They process big data quickly and provide key insights faster than old methods.
Spreadsheet Applications
Even with automated tools becoming popular, spreadsheet applications like Microsoft Excel are still very needed. They are valued for their ability to adapt to many financial tasks. Spreadsheets can handle everything from basic sums to complex financial models. This includes Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA), among others. They let users manually input and adjust data, making them a great option for tailored financial analysis.
Professional Financial Services
If a company needs special expertise, professional financial services provide custom solutions. These services use their own models along with standard tools for deep dives into financial statements. They combine knowledge specific to the industry with financial analytical skills. With their help, institutions can make sense of complicated financial data. This ensures they follow regulations and make smart financial plans.
| Financial Metric | Value ($) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Total Net Sales | 4,358,100,000 | Gross sales in the financial year |
| Cost of Sales | 2,738,714,000 | Total cost directly tied to production |
| Gross Profit | 1,619,386,000 | Net sales minus cost of sales |
| Operating Income | 765,227,000 | Profit earned from primary operations |
| Net Income | 483,232,000 | Total earnings after all expenses |
By blending automated platform solutions with professional services, financial experts can work more accurately and efficiently. This combination leverages both tech and human wisdom. It guarantees a thorough way to manage and make sense of financial data.
Best Practices for Financial Reporting
Understanding the difference between a balance sheet and an income statement is key. It helps financial pros show how honest and accurate their reports are. They stick to GAAP rules to make sure financial statements are true and clear.
To keep financial data accessible worldwide, sticking to the best practices is crucial. This ensures the financial reports are honest. Companies should update and review their data often. This keeps the information up to date and relevant.
Accuracy and the 4 C's (correctness, currency, completeness, and consistency) are very important. Technology helps to keep data organized. Making data easy to read and professional is essential. It shows the brand’s commitment to innovation and sharing knowledge.
Ensuring Accuracy and Clarity
Companies need strict checks to keep their financial reports clear and accurate. This includes reviewing finances regularly. For example, they look at how much money they make and check their stock.
Aligning numbers right and using consistent lines helps make reports easy to understand. This makes the financial statements accurate.
Regular Updates and Reviews
Financial reporting is ongoing. It needs constant updates and checks. Important reports go out monthly, quarterly, and yearly. This tells stakeholders that the business keeps an eye on its money all the time.
Transparency with Stakeholders
Being open and honest in financial reporting is vital. It builds trust and helps people make smart decisions. Financial pros don't just share numbers. They give context and insights. This makes financial reporting more valuable for everyone.
FAQ
How do income statements and balance sheets differ?
Income statements and balance sheets are different. Income statements show revenues and expenses over time. They show if a company made or lost money. The balance sheet shows assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific time. It tells us about a company's financial health.
What are the key components of an income statement?
The key parts of an income statement are revenue, cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, and net income. They together show how well a company is doing financially.
Where do expenses go on a balance sheet?
Expenses aren’t listed on a balance sheet. They're on the income statement. But expenses affect the balance sheet in assets or liabilities, like reducing cash or creating payables.
What is the importance of the balance sheet's equity section?
The equity section shows the value left for shareholders after liabilities are paid. It includes things like common stock and retained earnings. This shows the company's net worth.
Can you evaluate a company's profitability using the balance sheet?
A: The balance sheet shows financial status, not profit. However, looking at retained earnings can give clues about past profits or losses.
How do you conduct ratio analysis on an income statement?
To analyze an income statement, we calculate ratios. Gross profit margin, operating margin, and net profit margin are examples. These ratios help understand profitability and efficiency.
What is the purpose of benchmarking when analyzing financial statements?
Benchmarking is comparing your company's financials to industry norms or rivals. It shows where you stand, what you’re good at, and where to improve. It's key for strategic planning.
Is common stock listed on the balance sheet or income statement?
Common stock appears on the balance sheet in the shareholders' equity section. It shows the ownership stake of common shareholders in the company.
What tools are used for analyzing income statements and balance sheets?
For financial analysis, people use software, Excel, and financial services. These tools allow for in-depth and efficient examination of finances.
What are the best practices for financial reporting?
Top practices include being accurate, clear, and consistent. Follow accounting principles, update regularly, review, and be transparent. This helps stakeholders make informed decisions.