Understanding Formula for Profit Economics
Economic profit is a key financial metric that looks beyond just numbers. It uses the formula for profit economics to give a clearer picture. Unlike accounting profit, which only looks at direct costs, economic profit also considers indirect costs. This gives a more detailed view of a company's real profit.
The formula for profit economics is vital for those in finance and investing. It helps them make better choices. By understanding this formula, businesses can spot where they can improve and make smarter investments.
The way to figure out economic profit is by subtracting both direct and indirect costs from revenue. This gives a deeper look at a business's real profit. It helps managers see if their decisions are working well and find areas to get better.
By knowing the formula for profit economics, businesses can make smarter choices. They can pick investments that give the best returns, considering all costs.
Introduction to Profit Economics
The idea of economic profit is key in finance and making decisions. It shows a company's true financial health better than other measures. The formula for profit economics is used for internal checks and isn't needed for public disclosure.
This lets businesses look at missed chances and see if they're using resources well. It helps them make better choices and find ways to improve.
Key Takeaways
- Economic profit looks at both direct and indirect costs, giving a fuller picture of profit.
- The formula for profit economics is key for finance pros and investors to make smart choices.
- Economic profit is for internal checks and doesn't need to be shared publicly.
- Knowing the difference between economic and accounting profit is important for a business's long-term success.
- The formula for profit economics helps managers see if their decisions are working and find areas to improve.
- Economic profit gives a deeper look at a business's real profit, helping make better decisions for long-term success.
Introduction to Profit Economics
Understanding profit economics is key for businesses to make smart choices and use resources well. To figure out profit, you need to look at total opportunity costs. This shows the real profit of a business.
Economic profit is about the difference between what you get from your investments and what it costs to keep them. It's found by multiplying this difference by the amount invested. This formula helps businesses see how well they're doing financially and plan for the future.
Definition of Profit Economics
Profit economics is about finding the best way to use resources to make value. It looks at how much money comes in, how much goes out, and what's invested. Knowing profit economics helps businesses spot chances to grow their profit and make smart choices about spending.
Importance of Understanding Profit
Knowing about profit is vital for businesses to check how they're doing and plan ahead. It helps them find ways to work better and use resources wisely. By figuring out their economic profit, businesses can see if they're making enough money for their investors.
Key Concepts in Profit Economics
Important ideas in profit economics include opportunity costs, hidden costs, and economic value. Opportunity costs are what you give up to choose something else. Hidden costs are not directly linked to making a product or service. Economic value is when what's left after costs is more than what investors expect. These ideas help businesses make better choices about where to invest and how to use resources.
The Basic Formula for Profit
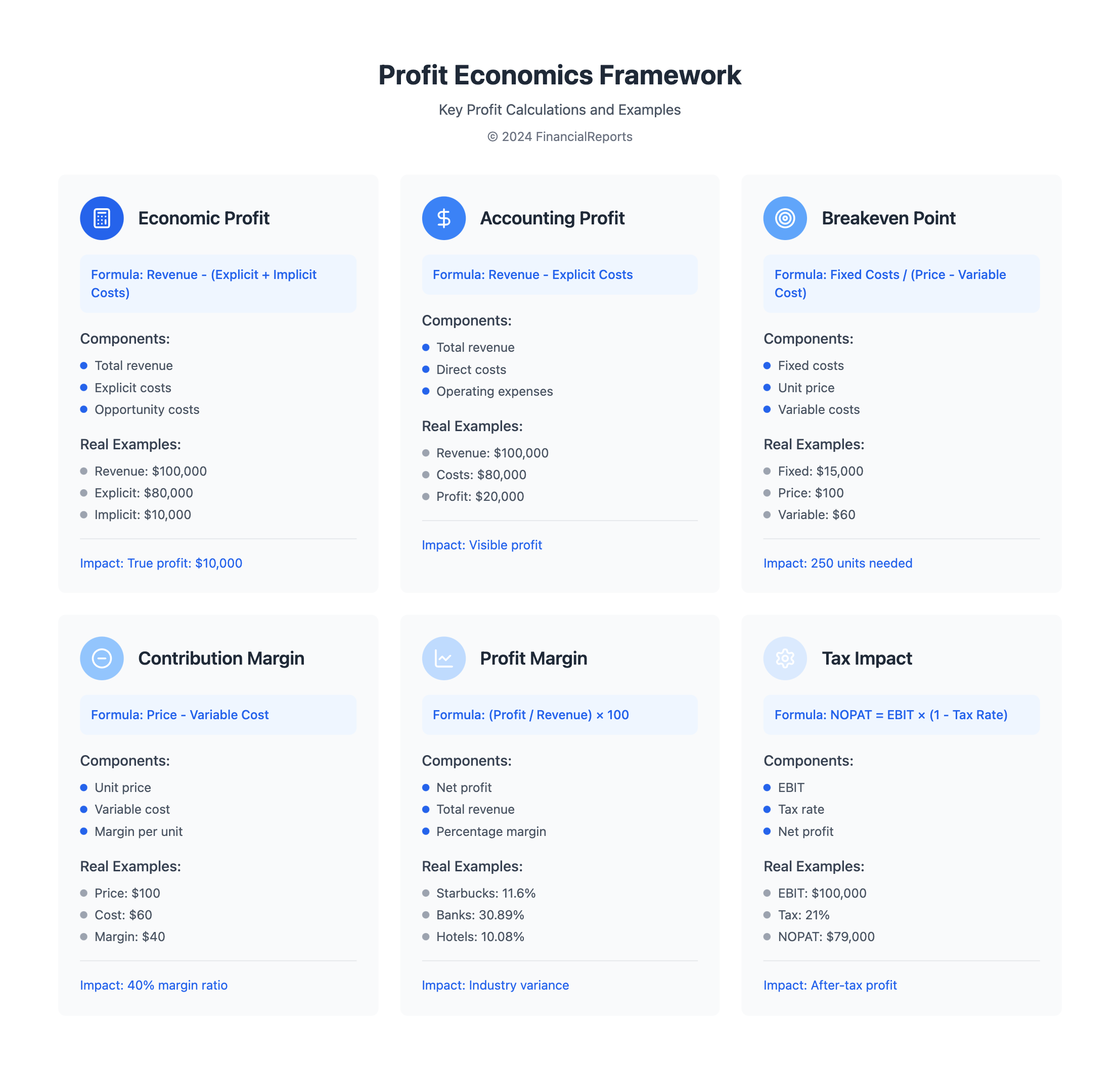
The formula for profit economics is key to understanding a business's financial health. It calculates economic profit by subtracting total costs from total revenue. This includes both explicit and implicit costs. The formula is simple: Economic Profit = Total Revenue - Total Costs.
To use this formula, you need to know its parts. Total revenue is the money made from sales. Total costs are all expenses, like labor and materials. Don't forget implicit costs, like what you could have earned elsewhere.
Profit Equation Explained
The profit equation has a few main parts:
- Total Revenue: The money made from sales
- Total Costs: All money spent on expenses
- Economic Profit: The difference between revenue and costs
Components of the Profit Formula
Understanding the profit formula's parts is vital. It helps businesses see where they can improve. This way, they can make better decisions to increase their profit.
Example of Profit Calculation
Let's say a business made $100,000 and spent $80,000. This includes all costs, explicit and implicit. Their economic profit is $20,000. This shows how well the business is doing financially and guides future decisions.
| Component | Amount |
|---|---|
| Total Revenue | $100,000 |
| Total Costs | $80,000 |
| Economic Profit | $20,000 |
Types of Profit
To understand profit in economics, knowing the different types is key. Accounting profit is the simplest, found by subtracting explicit costs from total revenue. For instance, a coffee company with $20,000 in revenue and $10,000 in costs has a profit of $10,000.
There are several profit types, including:
- Gross Profit: calculated as Total Sales – COGs (Cost of Goods Sold)
- Operating Profit: calculated as Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
- Net Profit: calculated as Operating Profit – (Taxes and Interest)
These profits offer insights into a company's financial health. They help in making smart business decisions.
Knowing these profit types is vital for financial experts, investors, and clients. By examining these metrics, companies can spot areas to grow and boost profits.
| Profit Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Profit | Total Sales – COGs | $20,000 - $10,000 = $10,000 |
| Operating Profit | Gross Profit – Operating Expenses | $10,000 - $5,000 = $5,000 |
| Net Profit | Operating Profit – (Taxes and Interest) | $5,000 - $1,000 = $4,000 |
Factors Affecting Profit
Knowing what affects profit is key for businesses to make smart choices. The profit formula is important here. It helps companies see their real profit. This leads to better investment and resource use.
Profit is influenced by several things. These include making money, controlling costs, and market conditions. Making money is vital. It directly affects a company's profit. Keeping costs low is also important. It helps businesses make more money. Market conditions, like what customers want and who they're competing with, also play a big role.
Revenue Generation
Revenue is a big part of profit. Businesses can make more money by selling more, raising prices, or entering new markets. Here are some ways to boost revenue:
- Developing effective pricing strategies
- Enhancing product offerings to meet changing consumer demands
- Expanding into new markets or geographies
Cost Management
Managing costs is also key to profit. Businesses can cut costs by spending less, working more efficiently, or getting better deals from suppliers. Here are some ways to manage costs:
- Implementing cost-cutting measures, such as reducing energy consumption or streamlining operations
- Renegotiating contracts with suppliers to secure better prices
- Investing in technology to improve operational efficiency
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Revenue Generation | Boosting sales, increasing product prices, or expanding into new markets |
| Cost Management | Reducing expenses, improving operational efficiency, or renegotiating contracts with suppliers |
| Market Conditions | Consumer sentiment, competition, and market trends |
By understanding these factors and using them in the profit formula, businesses can make better choices. This leads to growth and more profit.
The Role of Pricing in Profit
To grasp how pricing impacts profit, it's key to look at the pricing strategies businesses employ. Pricing is vital in calculating profit in economics. It affects both revenue and costs. The price a product sells for depends on what customers are willing to pay, the seller's price acceptance, and what competitors charge.
Businesses use many pricing strategies, like competitor-based pricing and cost-plus pricing. Others include value-based pricing, dynamic pricing, penetration pricing, price skimming, and target costing. Each strategy has its own benefits and drawbacks. Businesses must weigh these carefully when setting their prices. For instance, the freemium model offers a free version to encourage upgrades to paid versions. Tiered pricing gives customers different cost options based on their needs.
Some key pricing strategies include:
- Competitor-based pricing: setting prices based on what competitors are charging
- Cost-plus pricing: adding a percentage of profit to costs
- Value-based pricing: setting prices based on the perceived value of the product
Understanding profit calculation in economics is essential for businesses. It helps them make smart pricing decisions. By exploring different pricing strategies and their effects on revenue and costs, businesses can boost their profits.
| Pricing Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Competitor-based pricing | Setting prices based on what competitors are charging |
| Cost-plus pricing | Adding a percentage of profit to costs |
| Value-based pricing | Setting prices based on the perceived value of the product |
Cost Analysis in Profit Economics
To use the formula for profit economics well, businesses need to do a detailed cost analysis. They must identify and sort costs into fixed and variable expenses. Fixed costs stay the same, no matter how much is produced. Variable costs change with how much is made.
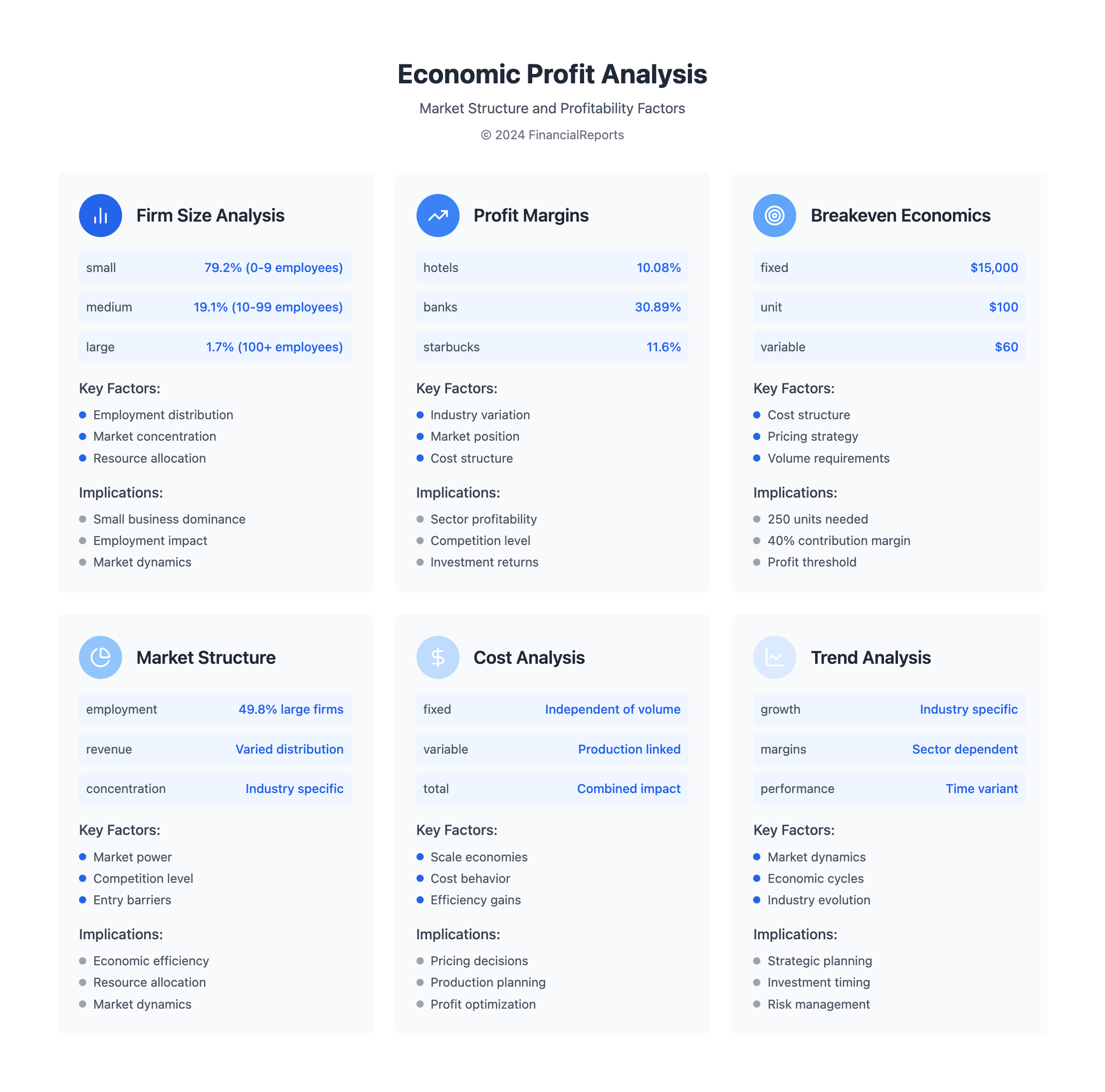
Understanding the contribution margin is key. It's the sales price minus variable costs. This helps find the breakeven point, where revenue equals costs. For example, a company with $100,000 in fixed costs and a 40% contribution margin needs $250,000 in sales to break even.
Some important stats in cost analysis include:
- Contribution margin ratio: found by dividing the contribution margin by total sales
- Unit contribution margin: calculated as the unit sales price minus the unit variable cost
- Breakeven sales volume: determined by dividing fixed costs by the contribution margin ratio
By grasping these concepts and using the profit economics formula, businesses can improve their costs and profit. With 5.7 million firms in the U.S., most with fewer than 10 employees, detailed cost analyses are vital for success.
| Company Size | Number of Firms | Percentage of Total Employment |
|---|---|---|
| 0-9 employees | 79.2% | 11.0% |
| 10-19 employees | 10.8% | 7.4% |
| 20-99 employees | 8.3% | 16.6% |
| 100-499 employees | 1.4% | 14.2% |
| 500 or more employees | 0.30% | 49.8% |
Breakeven Analysis
Understanding breakeven analysis is key to figuring out profit in economics. It finds the point where total costs and total revenue are the same. The formula is Break-Even Quantity = Fixed Costs / (Sales Price per Unit – Variable Cost Per Unit).
For example, if a company has fixed costs of $15,000, sells each unit for $100, and each unit costs $60 to make, they need to sell 250 units to break even.
To find the break-even point, use this formula: Break even point (units) = fixed costs / (selling price per unit – variable cost per unit). This helps companies know how many units they must sell to start making profits.
For instance, with fixed costs of $15,000, a selling price of $100, and a variable cost of $60, they need to sell 250 units to break even.
The break-even analysis is vital for understanding how do you calculate profit in economics. It helps companies figure out when they start making profits. Knowing the break-even point lets them make smart choices about pricing, production, and investments.
The table below shows a company's break-even analysis:
| Fixed Costs | Selling Price per Unit | Variable Cost per Unit | Break-Even Point (units) |
|---|---|---|---|
| $15,000 | $100 | $60 | 250 |
By using breakeven analysis, companies can grasp their costs and revenues better. This makes it easier to calculate profit and make smart business choices.
Profit Margin Metrics
Understanding profit margin metrics is key for businesses to check their financial health. The formula for profit economics helps calculate these margins. These margins show how profitable a company is.
Profit margins vary a lot between industries. For example, hotels and gaming had a 10.08% average in January 2024. Banks in the money sector had a 30.89% average. Starbucks had a gross profit margin of 28.9%, an operating margin of 14.1%, and a net margin of 11.6% in 2024.
To boost profit margins, businesses can increase sales or cut costs. A 10% margin is good, while 20% is high. Here's a table showing profit margins of different companies:
| Company | Gross Profit Margin | Operating Profit Margin | Net Profit Margin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starbucks | 28.9% | 14.1% | 11.6% |
| Apple Inc. | N/A | N/A | 26.0% |
By using the profit economics formula and understanding these metrics, businesses can make better decisions. This helps them stay competitive in their markets.
The Impact of Taxes on Profit
Understanding how do you calculate profit in economics means knowing how taxes play a big role. The profit formula includes revenue, costs, and taxes. First, businesses figure out their taxable income. Then, they use it to find out how much tax they owe.
Calculating a company's tax liability is simple: NOPAT = EBIT × (1 – Tax Rate %). This shows why knowing about corporate taxes is key. It also shows how tax rates change profit calculations. For more on taxes and the economy, check out the Tax Policy Center.
To lower taxes, businesses can use tax deductions. For example, investment and production tax credits help a lot, like for green energy companies. They can also cut taxes by managing their debt and interest payments. This affects their Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT). By knowing how taxes affect profit and using smart tax strategies, businesses can boost their earnings and stay ahead.
Profitability Forecasting
Profitability forecasting is key for financial planning and decision-making. It helps businesses set goals that create long-term value. Economic profit, which includes opportunity costs, gives a clearer view of a company's health.
Accurate forecasting is vital for planning and allocating resources. Tools like trend analysis, regression models, and scenario planning help. They let businesses predict revenue and expenses, guiding decisions on investments, pricing, and costs.
Importance of Forecasting
Forecasting helps businesses spot areas for improvement and growth. By looking at past data and trends, companies can predict future profits. This lets them stay competitive and reach their goals.
Tools for Profitability Forecasting
Some common tools for forecasting include:
- Trend analysis: examining historical data to identify patterns and trends
- Regression models: using statistical models to predict future outcomes
- Scenario planning: creating hypothetical scenarios to anticipate possible outcomes
Analyzing Forecast Results
After creating a forecast, it's important to analyze the results. This may involve:
- Reviewing revenue and expense projections
- Identifying areas for cost reduction or optimization
- Adjusting pricing strategies to maximize profitability
| Forecasting Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Trend Analysis | Examines historical data to identify patterns and trends |
| Regression Models | Uses statistical models to predict future outcomes |
| Scenario Planning | Creates hypothetical scenarios to anticipate possible outcomes |
Conclusion and Future Trends in Profit Economics
Understanding the formula for profit economics is key for businesses aiming for growth. The economic profit shows a company's true value by including all costs. It guides decisions and boosts long-term value.
The future of profit economics will focus more on being green and responsible. Companies will look at how their actions affect the planet and society. New tech, changing tastes, and laws will shape profit economics, making it vital to stay flexible.
Knowing profit economics helps experts and leaders make smart choices. By using the profit formula, businesses can succeed and help the economy grow. As profit economics evolves, it will bring both challenges and chances for growth, showing the need for ongoing learning.
FAQ
What is the formula for profit economics?
Profit economics uses a formula that's different from traditional accounting. It includes both explicit and implicit costs. This gives a clearer picture of a company's real profit, important for experts and investors.
Why is understanding profit from an economic perspective important?
Knowing profit from an economic view helps make better decisions. It involves understanding things like opportunity costs and economic value. These are key for smart financial planning.
What are the different types of profit calculations used in financial analysis?
Financial analysis looks at different profits like gross, operating, and net profit. These are different from economic profit. Each gives unique insights to those who analyze finances.
What factors influence profit from an economic perspective?
Economic profit is shaped by how a business makes money, manages costs, and the market. Companies need to think about these to boost their economic profit.
How does pricing impact economic profit?
Pricing is very important for economic profit. Businesses must pick the right prices, think about discounts, and understand demand. This helps them make more money.
What is the importance of cost analysis in profit economics?
Cost analysis is key in profit economics. Companies must know their fixed and variable costs, find hidden costs, and control costs. This improves their economic profit.
How does breakeven analysis relate to economic profit calculations?
Breakeven analysis shows when a business makes no economic profit. It's useful for planning and making decisions. Knowing this point helps decide on new projects.
What is the relationship between profit margin and economic profit?
Profit margins, like gross and net, are linked to economic profit. Improving these margins can increase a business's economic profit.
How does taxation impact economic profit calculations?
Taxes greatly affect economic profit. Companies need to understand taxes, find deductions, and lower their tax bill. This keeps their profit high while being fair.
What is the importance of profitability forecasting in financial planning?
Forecasting profit is vital for planning and using resources well. Accurate forecasts, using trends and models, help businesses make smart choices. This boosts their long-term profit.