Understanding Corporate Earnings: A Basic Guide
Corporate earnings are the heart of a company's financial success. They show how the stock market might react to a company's performance. By looking at financial statements, balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, you get a full picture of a business's health. These documents reveal the money coming in and going out, plus what a company owns versus what it owes. When we zero in on net earnings from the income statement, we get a clear picture of profit over time. This includes everything from what a company owns, like buildings and cash, to what it owes, such as loans. It helps investors and analysts dig deep, beyond basic numbers, to really understand a business's efficiency and prosperity.
Key Takeaways
- Earnings are a direct reflection of a company's financial success and its potential impact on the stock market.
- Financial statements and earnings provide intricate details on a company's assets, such as current assets of $94,000 and non-current assets of $120,000.
- Shareholder equity, reaching $214,000 on the balance sheet, combines with elements like paid-up share capital and contributed surplus to demonstrate financial viability.
- Operating profit and Earnings per Share (EPS), crucial investor ratios featured in the income statement, influence stock valuation alongside metrics such as the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio.
- Earnings reports, including their release patterns during earnings seasons, form the basis for investor and analyst assessments of corporate performance and future prospects.
- Scrutiny of corporate earnings encompasses not only the bottom-line figures but also ethical considerations, ensuring that published data isn't manipulated to influence stock prices falsely.
- Different profitability measures such as EBT, EBIT, and EBITDA offer varied insights into a company's financial performance, with the aim of reinvestment and dividend allocation for shareholders.
What Are Corporate Earnings?
Corporate earnings show how much profit a company makes in a certain time. These figures come from a detailed look at financial reports. They are key for understanding a company's health and how much money it can make. Investors use them to make choices, like buying or selling stocks.
Definition of Corporate Earnings
Basically, corporate earnings are what's left of a company's income after paying off expenses and taxes. This net income shows on financial reports, telling us how well the company is doing. It helps judge the company's financial stability and future growth when reported in the stock market.
Importance in Business
Corporate earnings aren't just numbers. They affect how people see the market, confidence in investing, and company plans. Good earnings can make investors happy, pushing up a company’s stock value. On the other hand, bad earnings might cause doubt and lower stock prices.
How It’s Calculated
To find corporate earnings, companies take their total income and subtract the cost of goods sold, operating costs, and other expenses. This shows the move from gross to net profit, revealing how well the company runs and makes money. These earnings help shape financial decisions and strategies in the stock market.
Types of Corporate Earnings
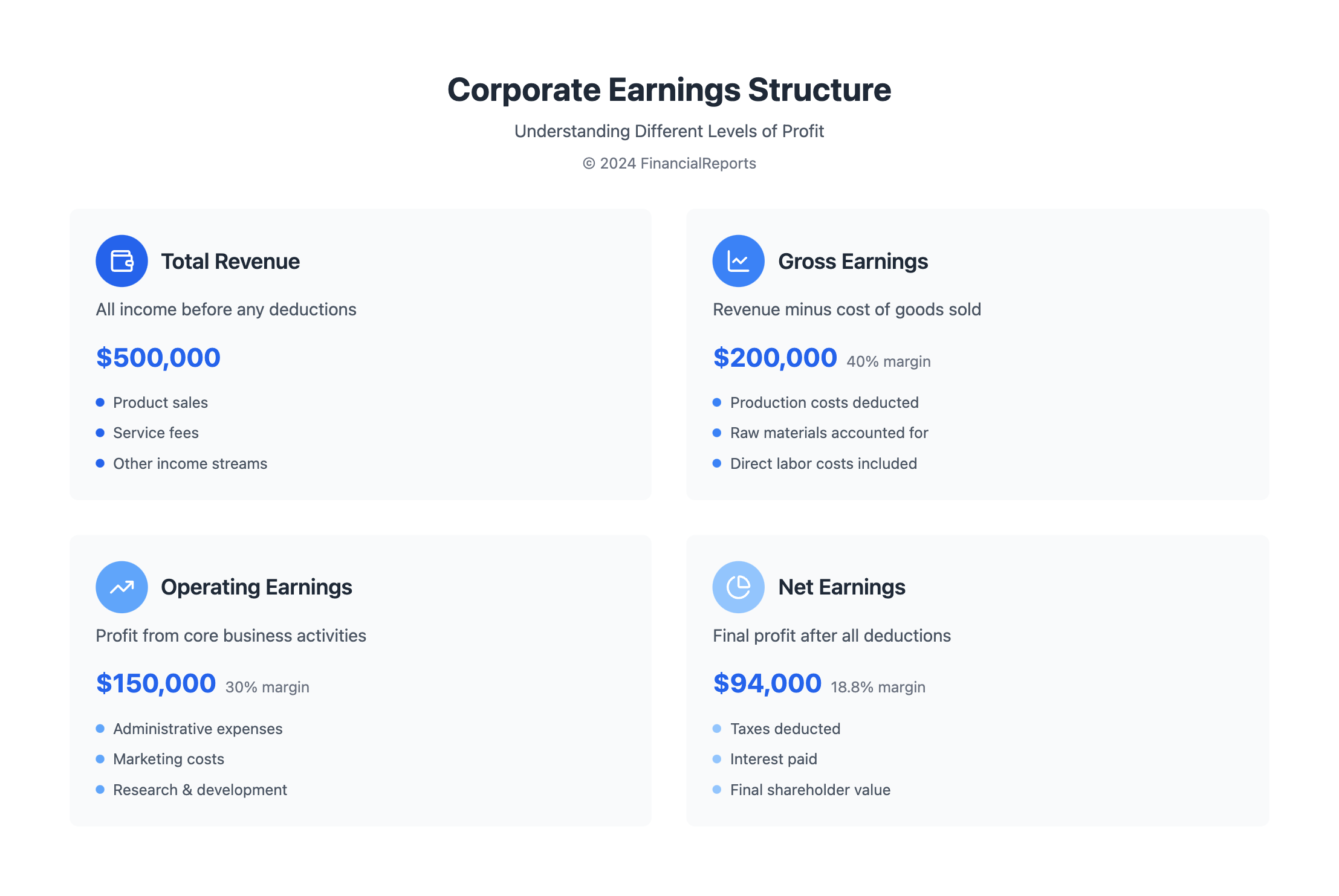
Corporate earnings show how well a company is doing financially. They include gross earnings, operating earnings, and net earnings. Each one offers unique insights into different parts of the company's money-making process. It's important for professionals and investors to understand these types to evaluate a company's performance and stability.
Gross Earnings
Gross profit is a key figure in financial reports. It's the money a company makes after paying for the cost of goods sold (COGS) from its total revenue. The gross profit margin shows how good a company is at producing and selling its main products before paying for overhead or taxes. This number points out how well the main parts of the business are doing.
Operating Earnings
After figuring out the gross profit, operating profit looks deeper into a company's finances. It includes costs like marketing, rent, utilities, and payroll. These are expenses needed to run the company, not including financial costs or taxes. Operating income shows how well a company can make money in its usual business operations, before any unexpected costs.
Net Earnings
Net profit is what remains after paying all operating costs, interest, taxes, and any other expenses. Net income shows the total earnings of a company after everything has been paid. It tells us about a company's final profit level. Net profit is key for reporting to shareholders and for planning the company's future.
Knowing the different types of corporate earnings, from gross profit to net profit through operating income, helps businesses and investors make informed financial decisions. Every level gives a critical view of a company's financial health, which is vital for detailed and smart planning.
The Role of Earnings Reports
Earnings reports are key in the financial world. Investors, analysts, and pros rely on them to judge a company's performance. They are crucial for a full financial check-up and guide due diligence.
What Is an Earnings Report?
An earnings report gives a full picture of a company’s financial results over time. The SEC requires these reports. They include vital numbers like revenues and profits, shown in SEC filings such as Form 10-Q and Form 10-K.
Key Components of an Earnings Report
An earnings report lays out a company's financial health clearly. Main parts include:
- Income Statement: Shows revenue, costs, expenses, and earnings.
- Balance Sheet: Offers a snapshot of assets, liabilities, and equity at the report's time.
- Cash Flow Statement: Highlights cash movements, showcasing how cash is made and spent.
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): Tells how much shareholders would get per share if all profits were given out.
Frequency of Earnings Reports
Companies typically release earnings reports four times a year. This timing fits the fiscal calendar most follow. It provides fresh updates for stakeholders to make smart choices. Earnings season, starting a week or two after a quarter ends, is especially crucial for markets.
| Component | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Income Statement | Reports revenue and expenses over the quarter/year. | Measures operational efficiency and profitability. |
| Balance Sheet | Details assets and liabilities at the end of the period. | Gauges financial stability and capital structure. |
| Cash Flow Statement | Illustrates the cash inflows and outflows. | Assesses liquidity and cash management effectiveness. |
| Earnings Per Share (EPS) | Net income divided by the number of outstanding shares. | Indicates profitability on a per-share basis, critical for stock valuation. |
Earnings reports are vital for financial analysis. They help stakeholders grasp the company's economic state, track its progress, and make investment choices. SEC filings play a role in ensuring a stable financial scene.
How Corporate Earnings Impact Stock Prices
Corporate earnings show how much a company makes and its economic health. These reports greatly influence stock prices. They are key for assessing the value of stocks.
The Connection Between Earnings and Share Value
Earnings reports tell how financially healthy a company is. If a company reports strong earnings, its stock value goes up. But if it misses the mark, its share price can drop quickly.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Impacts
The response to an earnings report can make stock prices jump or fall fast. People watch to see if a company meets their expectations. Over time, a company's financial health shapes its stock value, for better or worse.
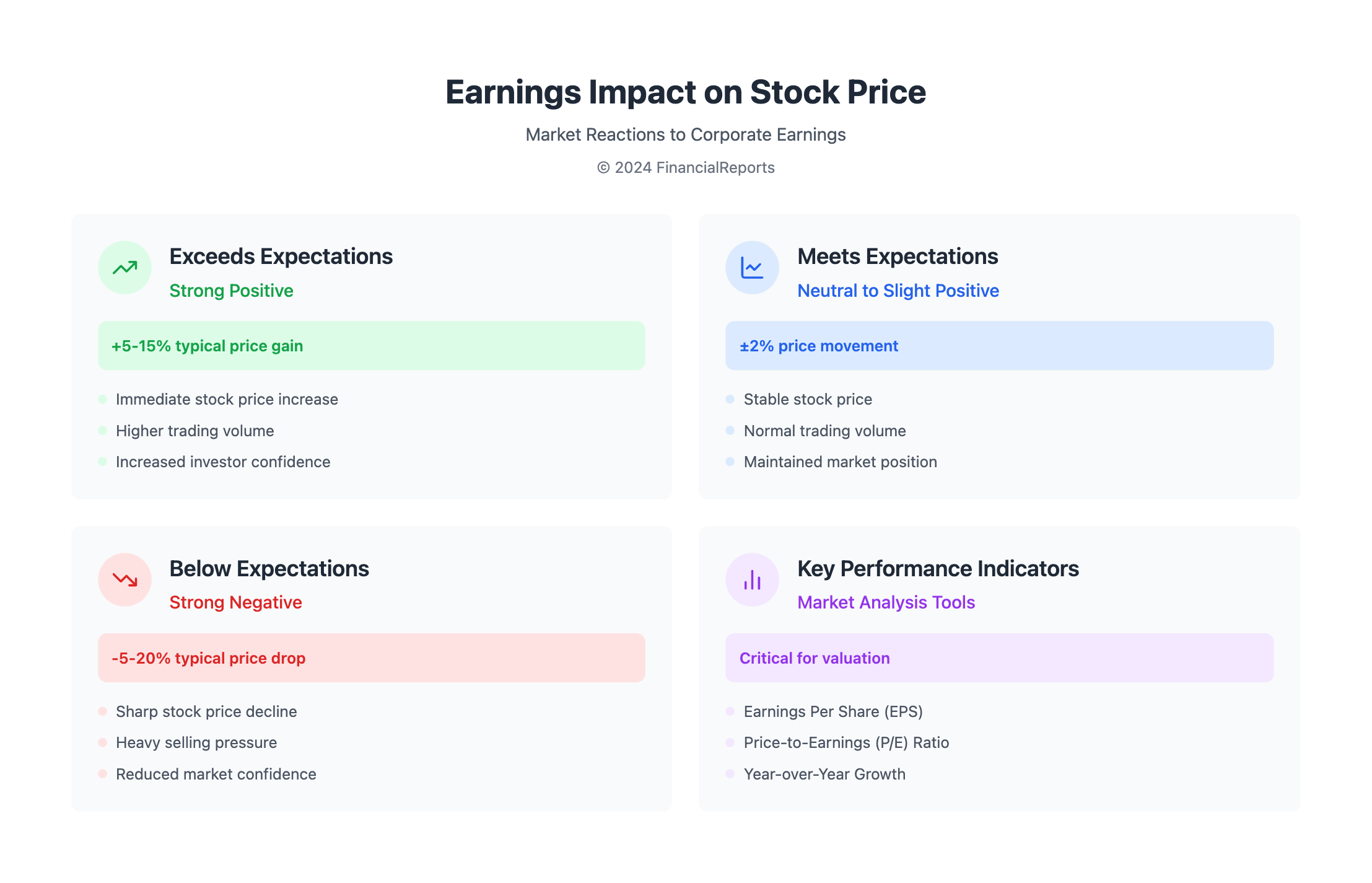
Market Reaction to Earnings Reports
Earnings news can make stock prices swing, especially if it's unexpected. The table below shows how stock prices might react to different earnings outcomes:
| Earnings Scenario | Market Reaction | Typical Effect on Stock Prices |
|---|---|---|
| Earnings exceed expectations | Positive | Rise in stock prices |
| Earnings meet expectations | Neutral/Stable | Marginal changes or stable prices |
| Earnings below expectations | Negative | Fall in stock prices |
| Guidance above expectations | Very positive | Significant rise in stock prices |
| Guidance below expectations | Very negative | Significant drop in stock prices |
Short-term traders and long-term investors need to understand this. Knowing how earnings affect stocks helps them make better choices. They can plan by looking at current results and future potential.
Analyzing Earnings Reports
The practice of earnings analysis is about understanding the key financial signs. These signs show a company's financial health and its growth path. They come from reports given every quarter through SEC filings, like Form 10-K or 10-Q. These reports give investors important insights into how the company is doing and its position in the market.
Key Metrics to Consider
Financial experts look at several key metrics in an earnings report. They focus on revenue, net income, and Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT). Each of these helps tell us more about a company’s financial state and how well it operates. Knowing these is crucial for a detailed financial analysis.
Earnings Per Share (EPS)
EPS shows the profit for each share of common stock. It tells us how profitable a company is and helps investors decide if a share is a good buy. A rising EPS suggests a company is doing well, which attracts more investors.
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
The P/E ratio is key in evaluating stocks. It compares a company’s share price with its earnings per share. This helps figure out if a stock is priced right or not based on its earnings. The P/E ratio also shows what the market expects in terms of a company’s future earnings growth. It's a crucial part of stock valuation.
Understanding these metrics well can lead to smarter investment choices. Thanks to real-time data and advanced analytics, investors can understand market trends better. They can predict how stock prices might move and make more informed decisions quickly.
| Financial Metric | Description | Relevance to Earnings Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue | Total income generated from business operations. | Indicates the company’s scale of operations and market reach. |
| Net Income | Total profits after all expenses have been deducted from revenues. | Shows the actual profitability, excluding non-operating influences. |
| Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) | Profits before the deduction of interest and tax expenses. | Helps assess operational efficiency irrespective of tax and financing factors. |
| Earnings Per Share (EPS) | Profit allocated to each outstanding share of common stock. | A direct measure of corporate profit on a per-share basis. |
| Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio | Market price per share divided by annual earnings per share. | Assesses if the stock is overvalued or undervalued based on earnings. |
Factors Affecting Corporate Earnings
It's important for those involved to understand what affects corporate earnings. We'll look at main factors such as economic conditions, industry trends, and management choices. Each has a big impact on how well a company does.
Economic Conditions
Economic conditions are key in shaping corporate earnings. Things like inflation, interest rates, and economic growth influence spending and investment. For example, high inflation reduces how much people can buy. This decreases company sales. On the other hand, low interest rates might encourage companies to grow, increasing their earnings.
These economic elements create an environment that can either help or hamper company performance. It all depends on the current economic situation.
Industry Trends
What's happening in a specific industry also matters a lot for its financial health. Things like new tech, changing customer likes, new rules, and competition are important. For instance, a tech firm investing in research could lead to new products. These products could capture more market and boost profits.
Another example is the car industry moving towards electric vehicles. This big change is influencing earnings across the global market.
Management Decisions
The choices managers make have a huge effect on earnings. Decisions about merging with other companies, keeping costs down, investing in new tech, and developing new products are crucial. Good leadership and smart planning can improve a company's standing and its earnings.
Choices about pricing, budgeting, exploring new markets, or selling parts of the business also matter a lot. They shape how well a company does financially.
When you put all these pieces together—economic trends, industry shifts, and management decisions—you get a complex picture. It shows how corporate earnings can change a lot. Understanding these parts is essential for foreseeing company success and making smart investment choices.
Earnings Forecasting
Forecasting earnings is key in financial planning. It plays a big role in forming strategies and evaluating businesses. This process helps predict financial well-being and aids in making smart choices. Investors and managers pay close attention to it.
Why Forecast Earnings?
Earnings forecasts are valued by many, from investors to those running companies. They signal a company's future financial health and profit chances. Using advanced models for these forecasts helps with thorough planning and lessens risks.
Techniques for Forecasting
Many methods exist for forecasting, from data-driven models to expert insights. Analysts use past data, trends, and detailed company info. These efforts make future earnings clearer. Reviewing past performance is also crucial for accurate predictions.
Importance of Accurate Forecasts
Good forecasts guide people through ups and downs in the market, building trust with investors. They are key for strategic planning, offering a glimpse into potential business achievements. Thus, they greatly influence how investors see the future and move the market.
| Year | Percentage of Firms Forecasting Earnings | Mean Growth Forecast by Managers (%) | Realized Future Growth Rate (%) | Investor Reaction to News Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993-1996 | 1.2% | 15 | 3 | Underreact to Bad News |
| 1997-2007 | 18% during earnings announcements | 15 | 3 | Overreact to Good News |
| 1994-2006 | <10% in non-earnings periods | 15 | 3 | Mixed reactions |
These statistics show the importance of careful strategic planning in forecasting. With the right approach to earnings projections, companies can improve their market standing and gain investor confidence.
Comparing Corporate Earnings
Effective financial benchmarking and comparative analysis are key in the financial world. They help understand corporate earnings over time and against different benchmarks. This work points out trends and aids in making smart choices.
Year-over-Year Comparisons
Looking at changes from one year to the next is very telling. Microsoft, for example, saw its net income margin jump from 45.6% in 2020 to 52.8% in 2021. This shows its skill in growing profits even with market swings.
Peer Comparisons
- Microsoft stands out with a gross margin ratio of about 68%, showing its strength against the tech sector.
- Its operating profit margin, around 42%, is a mark of how well it's run.
Sector Comparisons
Different industries have unique profit levels, ways of operation, and challenges. For instance, regional banks have a high gross profit margin of 99.75%. In contrast, the auto industry has a much lower margin of 9.04%.
This stark difference in numbers stresses why sector comparisons matter. They show how a company stands within its industry. This understanding helps investors and analysts see beyond mere numbers to gauge a company's true financial health.
By constantly keeping an eye on financial metrics and trends, experts can have a clear view of where a business stands. This is true for both the present and the past. Such detailed analysis leads to better investment choices and business strategies.
The Impact of Non-Operating Income
Non-operating income is crucial for a company's financial strategy and health. It comes from activities outside the main business, like dividends and gains from asset sales. These revenues are key during changing economic times.
Definition of Non-Operating Income
This income isn't from the main business activities. It includes things like interest and dividends. Financial reports use this category, helping investors see the difference between regular and extra earnings.
Examples and Implications
Non-operating income greatly affects a company's finances. For example, selling a business unit can temporarily raise profits. This doesn't reflect the regular business, so investors need to analyze carefully.
| Type of Non-Operating Income | Examples | Impact on Financial Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Income | Profits from interest-bearing accounts | Can offer a steady stream of incidental revenue, enhancing liquidity. |
| Dividend Income | Earnings from stock holdings in other companies | Contributes to overall income, potentially offsetting operational losses. |
| Asset Sale Gains | Income from the sale of business assets or real estate | Often results in a significant but non-recurring boost to earnings. Critical for short-term financial relief and investment in core areas. |
| Rental Income | Revenue from property leasing | Provides a diversification in revenue sources, essential for risk management within a broader financial strategy. |
Knowing both recurring and one-time non-operating income is key for financial modeling and strategy. Analysts and investors assess these incomes to understand a firm's real financial state. This makes sure strategic choices are informed by both operational strength and extra income potential.
Common Misconceptions about Corporate Earnings
It's important for financial experts to really get the ins and outs of corporate earnings. But many fall for earnings misconceptions and financial misunderstandings. When you take a closer look at profit analysis, you'll see the full picture of a company’s finances is often hidden by just looking at the earnings on the surface.
Misinterpreting Earnings
One big mistake is looking at earnings numbers by themselves. High earnings don't always mean a company has cash ready to use. This mix-up comes from accounting methods like accruals, which can make the company's cash flow seem different than it is.
Also, people often forget to consider the investments made to get those earnings. Ignoring this can make a company seem more stable and capable than it really is.
Let’s talk about some common financial strategies and how they affect how earnings look:
| Action | Impact on Earnings Perception | Actual Effect on Cash Flow |
|---|---|---|
| Using Accruals | May inflate earnings | No real cash impact |
| Capital Investment Ignored | Earnings appear higher | Potential future cash outflows |
| Operational Cost Reduction (25% decrease) | Improves earnings outlook | Immediate positive cash impact |
| Energy Efficient Practices (30% savings) | Cost efficiency reflects in earnings | Direct saving, enhancing cash reserves |
| Inventory Management Optimization (20% cost reduction) | Lower operating costs boost earnings | Reduces holding costs, frees up cash |
Avoiding earnings misconceptions is key for accurate financial analysis. By understanding these profit analysis and financial misunderstandings, financial experts can make better investment choices. This leads to better financial strategies and standing in the market.
Regulatory Environment Influencing Corporate Earnings
The world of business earnings is greatly shaped by different rules. These ensure clear and consistent money reports worldwide. In the U.S., the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is key. Worldwide, firms follow the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) to keep global financial honesty.
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Role
The SEC sets strict rules on sharing earnings info. This makes sure companies share right and on-time financial data. This protects investors and keeps the financial markets honest. Through its rules, the SEC makes firms share truthful data about their money health. This helps people make smart choices. The SEC also keeps updating its rules to handle new market problems.
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
Using IFRS is key in making money statements the same worldwide. This lets people understand and analyze reports the same way, no matter the country. Thanks to IFRS, companies can make reports that are clear and match up, beyond borders. This standard brings accounting together globally. It boosts international investment and growth.
This common way of reporting, supported by the SEC and IFRS, is crucial. It keeps financial statements reliable. The teamwork between different rules and the unified plan by IFRS set strict standards. These affect global company reports. It helps create a same global economy.
Future Trends in Corporate Earnings Reporting
In finance, reporting technology is changing fast. It's creating the financial future with AI, cloud computing, and big data. These tools make reports better and let us predict earnings faster and more accurately. This means companies can share news about their earnings quickly and look ahead with confidence.
Technology’s Influence on Earnings Reports
Tech is changing how fast and accurately companies share their earnings. Before, earnings season started two weeks after a quarter ended. It lasted about six weeks. Now, with AI, companies can share their earnings anytime, clearly and quickly. This makes the stock market more dynamic. Leaders like Microsoft and Apple show how good reporting affects the economy and investor decisions.
The Shift Toward Sustainability Metrics
Finance now also focuses on sustainability, important to investors worldwide. Financial reports are starting to include sustainability metrics. Investors want to know a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) efforts. These details are becoming as essential as profits. Reporting now covers both financial success and how a company cares for the future.
FAQ
What are corporate earnings and why are they important to a business?
Corporate earnings show a company's profitability over time, based on the income statement. They're key for assessing a business's health, guiding investors, and affecting stock prices.
How are corporate earnings calculated?
To find corporate earnings, add up all revenues and subtract business expenses. This includes costs of goods sold and operational costs. The result, net income, measures business performance.
What distinguishes gross earnings from operating and net earnings?
Gross earnings are what a company makes from its main activities before expenses. Operating earnings consider costs directly from operations. Net earnings are the total profits after all costs and revenues.
What is the significance of earnings reports for stakeholders?
Earnings reports detail a company's financial status, featuring revenues, expenses, and profits. Stakeholders use them to judge management, check the business's health, and decide on investments.
How do corporate earnings impact stock prices?
Corporate earnings influence stock prices by affecting how investors feel. If earnings are good, stock prices usually go up. Bad earnings can lower stock prices. Their long-term trends show a company's value.
Which key metrics should be analyzed in earnings reports?
Look at Earnings Per Share (EPS) and the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio in earnings reports. EPS shows profit per share, while P/E Ratio compares stock price to EPS. These help understand a company's financial health.
What factors can affect corporate earnings?
Corporate earnings can be influenced by economic conditions, industry trends, and managerial decisions. This includes inflation, consumer spending, technology changes, and mergers.
Why is earnings forecasting crucial for businesses and investors?
Earnings forecasting helps plan strategies, inform investments, and predict growth. Accurate forecasts are crucial. They impact stock prices and show if management meets expectations.
How is comparative analysis used in evaluating corporate earnings?
Comparative analysis looks at corporate earnings over time, against competitors, and within the industry. It helps understand financial health and market position.
What constitutes non-operating income and how does it impact a company?
Non-operating income comes from things not part of everyday business, like interest or asset sales. Though not from the core business, it's important for a full financial view.
What are some common misconceptions about corporate earnings?
A big myth is linking high earnings with lots of cash. Also, assessing earnings without considering capital investments is misleading. Thorough financial analysis is needed.
How does the regulatory environment affect corporate earnings reporting?
The SEC and other bodies require companies to share financial data. This ensures transparency and adherence to standards like the IFRS, making earnings comparable globally.
What trends are shaping the future of earnings reporting?
Technology is making earnings reporting clearer and forecasts more accurate. Including ESG factors shows a commitment to broader corporate responsibility and performance.