Understanding Company Profit Definition | Essential Guide
Profit is key for any business. Knowing what profit means is vital for those in finance, investors, and clients. Profit is when a business makes more money than it spends, after taxes.
This idea helps measure how well a business is doing. It's important for those who invest in companies. Understanding profit helps make smart choices and grow a business.
Profit is linked to revenue. Revenue is all the money a business makes. Profit is what's left after paying for things and taxes. Knowing about different profits, like gross and net, helps see how well a company is doing.
The tax rate on profits also affects profit. In the U.S., it's now 21%, down from 35% after the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the company profit definition is essential for financial professionals, investors, and institutional clients.
- Profit is the financial benefit realized when revenue exceeds expenses, costs, and taxes.
- The company profit definition is closely tied to the concept of revenue and is influenced by the corporate tax rate on profits.
- There are various types of profit, including gross profit, operating profit, and net profit, each providing insights into a company's performance.
- A clear understanding of the company profit definition is necessary to make informed decisions and drive business growth.
- Define profit and understand what does profit mean to make informed decisions and drive business growth.
- Company profit definition is critical in evaluating a company's performance and serves as a key indicator for investors and stakeholders.
What is Company Profit?
Understanding profit is key to knowing a company's financial health. Profit in business is more than just making money. It shows how well a company runs its operations.
Definition and Importance
A profit is what's left after all expenses are subtracted from total income. It shows how well a company uses its resources to make money. For investors and stakeholders, profit is a key way to see how a company is doing and if it can keep going.
Key Components of Profit
Several things make up what profit is:
- Revenue: The total money made from sales before any costs are taken out.
- Expenses: The costs of making that revenue, like operating costs, taxes, and interest.
- Financial Metrics: Tools like gross profit, operating profit, and net profit that give more insight into how profitable a company is.
By looking at these parts, businesses can find areas to get better and make smart choices to boost their profits. Knowing what profit means helps in planning for the future and growing.
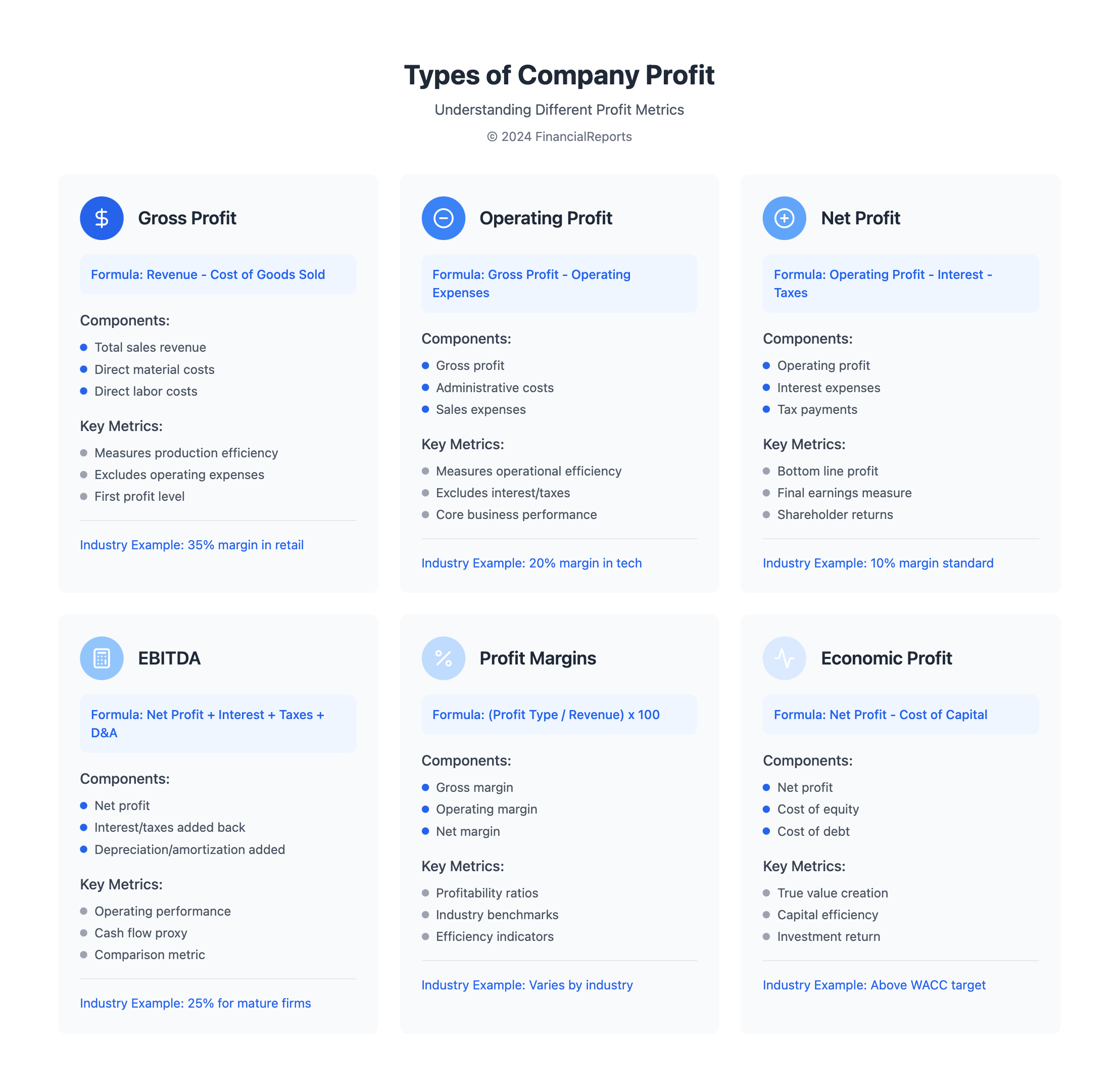
Types of Company Profit
It's key to know the different profits in accounting to understand a company's health. Each profit type gives special insights into how well a business is doing.
Gross Profit
Gross profit is what's left after subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from revenue. It shows how well a company makes and sells its products.
- Calculation: Gross Profit = Revenues - COGS
- Significance: Shows the profit before other costs are added.
Operating Profit
Operating profit is what's left after subtracting operating expenses from gross profit. It shows how well a company runs its main activities.
- Calculation: Operating Profit = Revenue - COGS - Operating Expenses - Depreciation
- Significance: Shows how well a business operates.
Net Profit
Net profit is the final number, showing total revenue minus all costs, including taxes and interest. It gives a full view of how profitable a company is.
- Calculation: Net Profit = EBIT - Interest Expense - Taxes
- Significance: Crucial for seeing if a company can stay financially stable.
Other Profit Types
There are more profit types like EBITDA and adjusted net income. EBITDA ignores non-operating costs. Adjusted net income removes one-time items to show real ongoing profit.
How to Calculate Company Profit
To understand what is the best definition of profit, we need to explore how it's measured. Knowing how to calculate profit is key to seeing how well a company is doing financially. It helps guide the company's future plans.
Basic Profit Calculation Formula
The basic way to figure out a company's profit is: Profit = Revenue - Expenses. This simple formula is the base of the profit definition business. But, to really understand profit, we need to look at different types of profit.
- Gross Profit: This is found by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total revenue.
- Operating Profit: It's the gross profit minus operating expenses, depreciation, and amortization.
- Net Profit: This is the profit left after all expenses, including taxes and interest, are subtracted from revenue.
Adjustments for Accurate Figures
To get a true picture of a company's profit, we need to make some adjustments. These adjustments help us see how well the company is doing without misleading information.
- Non-cash Expenses: Things like depreciation and amortization are subtracted from gross profit but don't use cash.
- One-time Charges: Unique expenses, like legal settlements or restructuring costs, should be left out to keep profit analysis clear.
- Industry-specific Factors: Some industries need special adjustments, like how to value inventory or costs for following rules.
The Role of Revenue in Profit
Revenue, or sales, is the base for profit. To grasp profit, we must look at revenue and how it affects a business's health.
Revenue vs. Profit
Revenue is the total income from selling goods or services before expenses. For example, Amazon.com made $514.0 billion in net revenue in 2022. Yet, it had a net loss of $2.7 billion. This shows that high sales don't always mean high profits.
This example stresses the need to control costs to make profit from revenue.
Importance of Revenue Management
Good revenue management is key to making more profit. It includes strategies to boost income from business activities. Some important strategies are:
- Pricing Strategies: Changing prices to meet demand and increase revenue.
- Sales Forecasting: Predicting sales to guide financial choices.
- Revenue Diversification: Adding new products or services to increase income.
Using these strategies helps companies improve their profit margins. It's not just about selling more. It's about managing and improving revenue for lasting financial success.
Understanding Profit Margins
Profit margins are key to understanding a company's financial health. They show how much profit a business makes from its sales after paying for costs. This helps stakeholders see how well a business is doing financially.
Gross Profit Margin
The gross profit margin shows the profit left after selling goods minus the cost of making them. It's found by:
Gross Profit Margin % = (Gross Profit / Revenue) x 100
This margin tells us how well a company makes its products. For example, a 35% margin means it makes $0.35 for every dollar sold.
Operating Profit Margin
The operating profit margin shows profit after paying for running the business. It doesn't include taxes or interest. The formula is:
Operating Profit Margin % = (Operating Profit / Revenue) x 100
This shows how well a company manages its costs.
Net Profit Margin
The net profit margin shows the profit after all costs, including taxes and interest, are subtracted. It's calculated as:
Net Profit Margin % = (Net Profit / Revenue) x 100
This gives a full picture of a company's profitability.
| Profit Margin Type | Formula | Example Percentage | Industry Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gross Profit Margin | Gross Profit / Revenue x 100 | 35% | Retail, Manufacturing |
| Operating Profit Margin | Operating Profit / Revenue x 100 | 20% | Technology, Consulting |
| Net Profit Margin | Net Profit / Revenue x 100 | 10% | Restaurants, Automotive |
Knowing these profit margins helps financial experts and investors compare and improve. Accurate and smart use of profit margins is vital for making good business decisions and keeping a company strong over time.
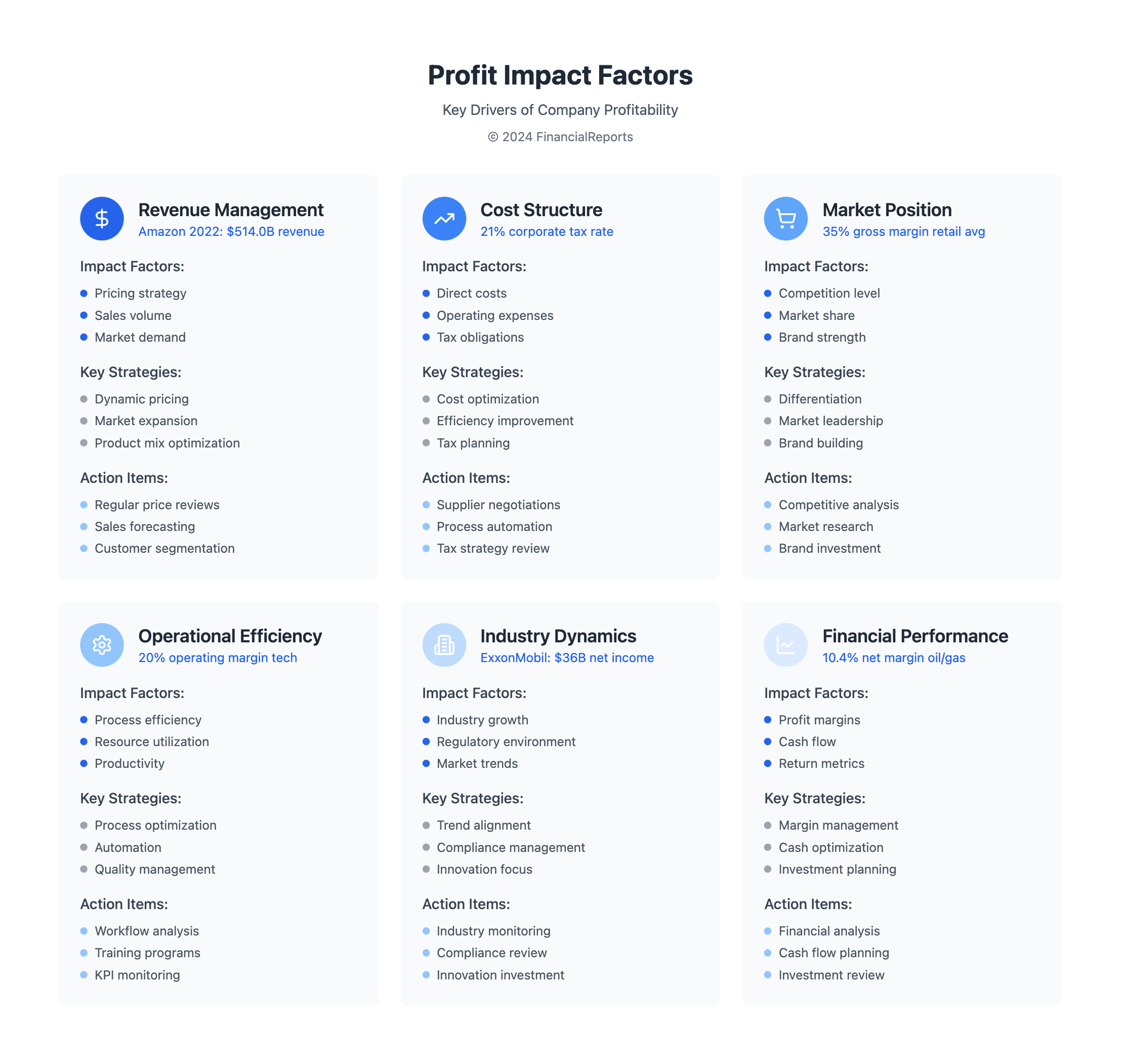
Factors Affecting Company Profit
Knowing the company profit definition is key for businesses to make smart choices. To define profit, we must look at both inside and outside factors that affect a company's earnings. One big factor is how well a company runs its operations. This means making processes better, using resources wisely, and boosting productivity.
By making operations more efficient, businesses can cut costs and earn more. This leads to higher profits.
Another important factor is the market itself. This includes competition, the state of the economy, and trends in the industry. Companies need to keep up with these changes and adjust their plans as needed. Good cost management is also key. It helps companies keep their profit margins healthy.
By understanding whats it mean to make profit, businesses can work on selling more, spending less, and setting better prices. This helps them make more money.
Some key things that affect profit margins include:
- Net or gross profit
- Sale prices
- Consumer sentiment
- Inventory levels
By managing these factors well and keeping up with market trends, businesses can boost their profit margins. This helps them stay strong in the long run.
The Impact of Costs on Profit
Understanding how costs affect profit is key for businesses. Profit is the money left after all costs are subtracted from sales. The profit a company makes varies based on different cost types.
Accounting has various profits, like gross, operating, and net profit. Each profit type considers different costs. For example, gross profit is found by subtracting the cost of goods sold from revenue. Operating profit is found by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit.
Here are some costs that can affect profit:
- Raw materials and labor costs (direct costs)
- Electricity bills and office rent (indirect costs)
- Sales person salaries and commissions (direct costs)
- Insurance and depreciation (indirect costs)
Knowing about different costs and their impact helps businesses cut costs. They can reduce expenses, streamline supply chains, or work more efficiently. This can lead to higher profits.
| Cost Type | Example | Impact on Profit |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Costs | Raw materials, labor | Directly affects gross profit |
| Indirect Costs | Electricity bills, office rent | Affects operating profit |
Financial Statements and Profit
Understanding profit meaning in business starts with financial statements. These documents show a company's financial health and how profitable it is.
Income Statement Overview
The income statement, or profit and loss (P&L) statement, shows a company's income, expenses, and profits over time. For example, Amazon's 2017 income statement shows its profits without a gross income subtotal. ExxonMobil's 2023 income statement reported $344.6 billion in total revenue and $36 billion in net income.
- Total Revenue: The total income from sales.
- Total Costs: Expenses for making goods or services.
- Net Income: Profit after all expenses are subtracted.
How to Analyze Profitability
To analyze profitability, look at key metrics from the income statement. Understanding what is the best definition of profit is key. It usually means net income. Important ratios include:
- Net Profit Margin: Shows profit for every dollar of revenue.
- Gross Profit Margin: Percentage of revenue above cost of goods sold.
- Operating Profit Margin: Percentage of revenue after operating expenses.
Using ExxonMobil's 2023 data, the net profit margin is about 10.4%. This profit definition business metric shows how well a company makes profit from its operations.
Profit and Tax Implications
It's key to know how profit and taxes are linked for any business. The profits you make affect how much tax you owe. This can really shape your company's financial health.
Understanding Tax Obligations
Businesses face different tax rules based on their profits. Here are some important points:
- The U.S. has a flat 21% corporate tax rate, down from 35% after the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.
- State corporate taxes vary, from North Carolina's low rates to New Jersey's higher ones.
- International businesses might face different tax rates. For example, the Bahamas and UAE have no corporate tax. But, Hungary's rate is around 9%.
How Profits Affect Business Taxes
Profits play a big role in how much tax you owe. Here are some key points:
- C corporations are taxed at a flat 21% rate.
- S corporations let profits pass through to owners' personal tax returns, avoiding entity-level taxes.
- Businesses can reduce taxable profits by deducting things like employee salaries, health benefits, and advertising costs.
Good tax planning helps businesses keep more profits while following the law. By understanding what does it mean to make profit and define profit in business, companies can better manage their taxes.
The Importance of Profit in Business Strategy
Profit is key in setting a company's direction. It shows the company's financial health and growth chances. This is what makes profit so important.
Profit as a Growth Indicator
Knowing the types of profit helps see business growth chances. Net profit shows if a company can grow and invest more. Companies with good profit can spend on research, expanding markets, and increasing shareholder value.
Long-term Sustainability and Profit
Profit is vital for lasting success. Using profits for growth and innovation helps a company stay strong. Good profit strategies include:
- Keeping profit margins high to handle unexpected costs.
- Managing costs well to boost profit.
- Building trust with stakeholders through clear finances.
A clear company profit definition helps make smart decisions. It balances making money now with keeping the business strong for the future.
Common Misconceptions About Company Profit
Profit is key to knowing if a company is doing well financially. But, there are many wrong ideas about it. One big mistake is mixing up profit and cash flow. Cash flow shows how money moves in and out of a business. Profit, on the other hand, is an accounting number that counts revenue and expenses differently.
Just because a company makes a lot of money, it doesn't mean it's making a lot of profit. Costs like taxes and other financial duties can cut into profits. Also, people think all profits can be spent right away. But, companies often use their profits to grow, invest in research, or make other smart moves for the future.
Knowing the real deal about profit helps leaders, investors, and financial experts make better choices. It shows how important a company's profits really are.
FAQ
What is the definition of company profit?
Company profit is the money left over after a business pays all its costs. It shows how well a company is doing financially. This is key to knowing if a business is healthy and successful.
What are the key components that contribute to a company's profit?
Profit comes from revenue, expenses, and other financial numbers. Revenue is the money from selling goods or services. Expenses are the costs to make that money, like materials and labor. Profit is what's left after subtracting expenses from revenue.
What are the different types of company profit?
There are several profit types. Gross profit is revenue minus the cost of goods sold. Operating profit is revenue minus operating expenses. Net profit is revenue minus all expenses, including taxes and interest. Other types, like EBITDA, are used for specific financial analysis.
How is company profit calculated?
Profit is calculated as: Profit = Revenue - Expenses. This formula can be used for different profit types. Accurate profit calculation needs all financial data, including adjustments for non-cash expenses.
What is the relationship between revenue and profit?
Revenue is the base for profit. But, high revenue doesn't always mean high profit. Profit is what's left after expenses are deducted. Good revenue management is key to high profits.
How can profit margins help assess a company's profitability?
Profit margins show how profitable a company is. They measure the percentage of revenue that turns into profit. This helps compare to industry standards and find areas for improvement.
What are the internal and external factors that can impact a company's profit?
Profit is affected by internal and external factors. Internal factors include how well a company operates and manages costs. External factors, like market conditions and competition, also play a big role. Managing these factors well is key to success.
How do different types of costs affect a company's profit?
Costs like fixed and variable affect profit differently. Fixed costs, like rent, stay the same. Variable costs, like materials, change with sales. Managing these costs well can boost profit.
How do financial statements, particular the income statement, report and analyze company profit?
The income statement shows a company's revenue, expenses, and profit. It helps understand a company's financial health. This info is vital for making smart financial decisions.
How do a company's profits impact its tax obligations?
Profits affect a company's taxes. Taxes are based on taxable income. Knowing tax rules and strategies helps reduce taxes while keeping profits high.
Why is company profit important for business strategy and long-term success?
Profit shows a company's growth and informs strategy. It guides decisions on expansion and investment. Good profit management is essential for success and staying competitive.
What are some common misconceptions about company profit?
Many think high revenue means high profit. But, profit is revenue minus expenses. Another mistake is mixing profit with cash flow. Understanding these concepts is key to financial health.