Understanding Classified Income Statement Basics
For any financial professional, understanding a company's financial situation is key for making smart business choices. A classified income statement is more than a simple report of profits. It sheds light on a firm's financial health, guiding strategic moves.
This financial report details different types of income. It highlights main income sources, like sales, and other extra income sources. By breaking down earnings and costs, companies can pinpoint how to improve financially.
Look at Microsoft as an example. It made $109.4 billion in operating income from $245.1 billion in revenue, after covering $135.7 billion in operating costs. Such detailed info helps professionals plan better and strengthen their company's stand in the market.
Classified income statements do more than track profit. They are key for deep financial analysis, including EBIT and EBITDA. This makes them crucial for making big business decisions with clarity.
Key Takeaways
- A classified income statement details a company's financial outcomes, showing core and extra income sources.
- It gives a clear financial picture by providing in-depth numbers like operating income and EBITDA.
- These statements help in making informed business choices by offering a clear view of financial health.
- They allow for detailed financial analysis, as seen with Microsoft, aiding in strategy and planning.
- They also help compare financial performance over time, boosting strategic vision.
- By offering detailed financial insights, they highlight a company's operational efficiency and appeal to investors.
What is a Classified Income Statement?
A Classified Income Statement, also known as a profit and loss statement, organizes financial data into distinct categories. This way, it makes the company's financial activities clearer and easier to understand. Knowing how are items classified on the income statement is key for financial reporting. It shows how well a company is doing over a certain time.
Definition and Purpose
The classified income statement breaks down revenue, expenses, gains, and losses. This breakdown offers a detailed look at financial data. Businesses can then pinpoint their strong and weak financial areas accurately. Key totals, like gross margin and operating expenses, are highlighted.
For example, gross profit shows how efficient the company's operations are. While net income tells us the final profit after all costs.
Importance in Financial Reporting
The classified income statement is vital in financial reporting. It helps businesses check their financial health. It's also important for external people like investors and creditors. They use it to see how the company is doing and its potential for growth. The way expenses are detailed helps in making strategic decisions and analyzing finances.
Today, being open about finances is very important. The classified income statement is key in this. It helps stakeholders understand complex financial data. This supports making smart decisions in various industries.
Key Components of a Classified Income Statement
Looking into the income statement of a business shows us its financial condition. A good income statement clearly shows key finance areas, mainly splitting them into revenues, expenses, and net income. These areas are important for people needing clear and right data to make smart choices.
Revenues
When it comes to making money, the income statement separates money made from regular business activities and other sources. Money from sales of goods or services is regular income. Money from investments or rent is other income. It's key to record income accurately to show how well a firm is doing.
Expenses
The costs in an income statement are split into direct and indirect costs. Direct costs come from main business activities, like the cost of making goods or paying employees. Indirect costs might be interest or losses from selling assets. Showing these costs clearly helps understand how well resources are used.
Net Income
To find out a company's profit or loss, we take all the money made and subtract all costs. This final number tells us if the company made money or lost it during a certain time. A positive number means the company is doing well and might get more investment.
| Category | 2020 | 2021 |
|---|---|---|
| Total Revenue | $800,000 | $1,000,000 |
| Gross Profit | $595,000 | $680,000 |
| Operating Expenses | $210,000 | $150,000 |
| Net Income | $64,000 | $181,000 |
| EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) | $385,000 | $530,000 |
| Net Profit | $64,000 | $181,000 |
This table shows how a company grew over two years. It highlights the need for a clear and detailed income statement in making financial decisions.
Difference Between Classified and Unclassified Income Statements
Understanding classified and unclassified income statements is crucial for financial experts. They depend on accurate and detailed financial data. The main difference lies in how they are organized and the detail level provided.
Structure and Format
Classified income statements are organized carefully. They separate business activities into operational and non-operational. This makes financial analysis easier and clearer. Income and expenses are sorted into categories like "Revenues", "Cost of Goods Sold", and "Operating Expenses".
On the other side, unclassified income statements put all financial activities together. They do not break down details, which can hide important financial insights.
Reporting Detail
Classified income statements give a detailed look at a company's finances. They split financial results into main and side operations. This helps track key performance metrics. Unclassified statements provide a broader view. This might work for small companies or inside reviews, but not for detailed investor analysis. Classified statements give a deeper understanding of finances, like knowing different types of debts.
This difference affects how people see and use financial information in making big decisions. Classified statements are crucial for detailed financial checks needed by stakeholders. Unclassified statements might be enough for simple, internal checks.
The decision to use classified or unclassified statements depends on the business's and stakeholders' needs. They must decide based on their need for detail and transparency in financial reports.
Revenue Recognition in Classified Income Statements
In classified income statements, understanding revenue recognition is key. It follows rules that set when and how to record revenue. This makes sure financial reports match what really happens economically. The focus is on recognizing revenue at the right time during an accounting period. This is crucial for accurate revenue reports and financial results.
Timing and Measurement
The timing of revenue recognition is very important. It follows principles that match revenue with the time it is earned. This is true even if payment comes later. According to ASC 606-10-20, revenue is earned when goods or services are provided. This links revenue with the assets gained from these activities. It ensures revenue and costs are reported in the same fiscal period. This helps keep financial statements clear and consistent.
Common Methods
Different methods are used for revenue recognition. The method depends on how the business earns its revenue. For example:
- Sales of goods are recognized once the customer takes control of the items.
- Revenue from services is recorded after the service is done or during the service period. This reflects the ongoing benefits to the client.
- Long-term contracts might use the percentage-of-completion method. Here, revenue is recognized based on how much of the contract is finished.
Using various methods helps ensure revenue is reported accurately across different kinds of transactions.
| Revenue Source | Timing of Recognition | Accounting Method Used |
|---|---|---|
| Sale of Goods | Point of delivery | Immediate recognition |
| Provision of Services | Service completion or over service period | Revenue over time |
| Long-term Contracts | Based on project completion percentage | Percentage-of-completion |
| Tuition and Fees | Academic term | Immediate recognition in fiscal year |
| Grant and Contract Revenue | As expenses are incurred | Accrual basis aligned with budget and performance |
This careful approach to revenue recognition ensures financial reports are accurate and trustworthy. It's vital for stakeholder analysis and decision-making. By following strict accounting methods, companies maintain financial honesty. They also meet regulatory requirements.
Expense Classification in Classified Income Statements
Understanding expense categories in classified income statements is key. It helps analyze financial performance accurately and make strategic decisions. Expenses are split into operating and non-operating. This shows an organization's financial health and how well it operates.
Operating vs Non-operating Expenses
Operating expenses are costs from main business activities. They include things like salaries, rent, and utilities. These are essential for daily operations and directly tied to the company's main activities. Non-operating expenses are costs not related to main business activities. This includes interest expenses and gains or losses from foreign exchange. They help understand the whole financial scene but don't show the main business performance.
Fixed vs Variable Expenses
Fixed expenses don't change with production or sales. Rent and salaries are examples. Variable expenses, like utilities or commissions, change with business activity.
| Expense Type | Category | Amount ($) |
|---|---|---|
| Rent | Fixed Operating Expense | 50,000 |
| Salaries | Fixed Operating Expense | 100,000 |
| Utilities | Variable Operating Expense | 10,000 |
| Interest Expense | Non-operating Expense | 15,000 |
Effective expense categorization is crucial for businesses. It lets them analyze financial performance deeply. They can find areas to cut costs and allocate resources better. This leads to higher profitability and long-term success. A good system for classifying expenses offers strategic benefits for financial planning and operational changes.
How to Prepare a Classified Income Statement
Making a classified income statement takes careful work. It's important to get financial statement accuracy right. Here, we explain how to prepare an income statement and point out mistakes to avoid. These errors can mess up your financial information.
Step-by-Step Process
- Gather Financial Data: First, collect all your financial info. This includes revenues, expenses, and cost of goods sold. Make sure all the figures are correct to keep the income statement accurate.
- Categorize Data: Next, divide your data into operating and non-operating activities. This classification helps separate main activities from side ones.
- Calculate Gross Profit: Subtract the cost of goods sold from net sales. For example, with TechWidget Inc., if sales are $500,000 and costs are $300,000, the gross profit is $200,000.
- Compute Operating Income: You can find operating income by subtracting expenses from gross profit. A classified income statement explains this well.
- Consider Non-Operating Items: Also, calculate any revenues and expenses that aren't from normal operations. This shows their effect on income before taxes.
- Calculate Taxes and Net Income: Determine the income before taxes. Then, apply the tax expense to find net income. This shows the after-tax result of all business activities.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Misclassification of Expenses: Be sure to correctly label expenses as operating or non-operating. Getting this wrong can skew your operating income.
- Inaccurate Revenue Recognition: This mistake affects gross profit and the entire income statement. Always recognize revenues correctly, as they are earned, following matching principles.
| Category | Data from TechWidget Inc. |
|---|---|
| Net Sales | $500,000 |
| Cost of Goods Sold | $300,000 |
| Gross Profit | $200,000 |
| Operating Income | $90,000 |
| Income Before Taxes | $90,000 |
| Income Tax Expense | -$35,000 |
| Net Income | $55,000 |
By avoiding these common errors, financial specialists can improve financial statement accuracy. This leads to better income statement preparation. As a result, it offers reliable insights into a business's financial health.
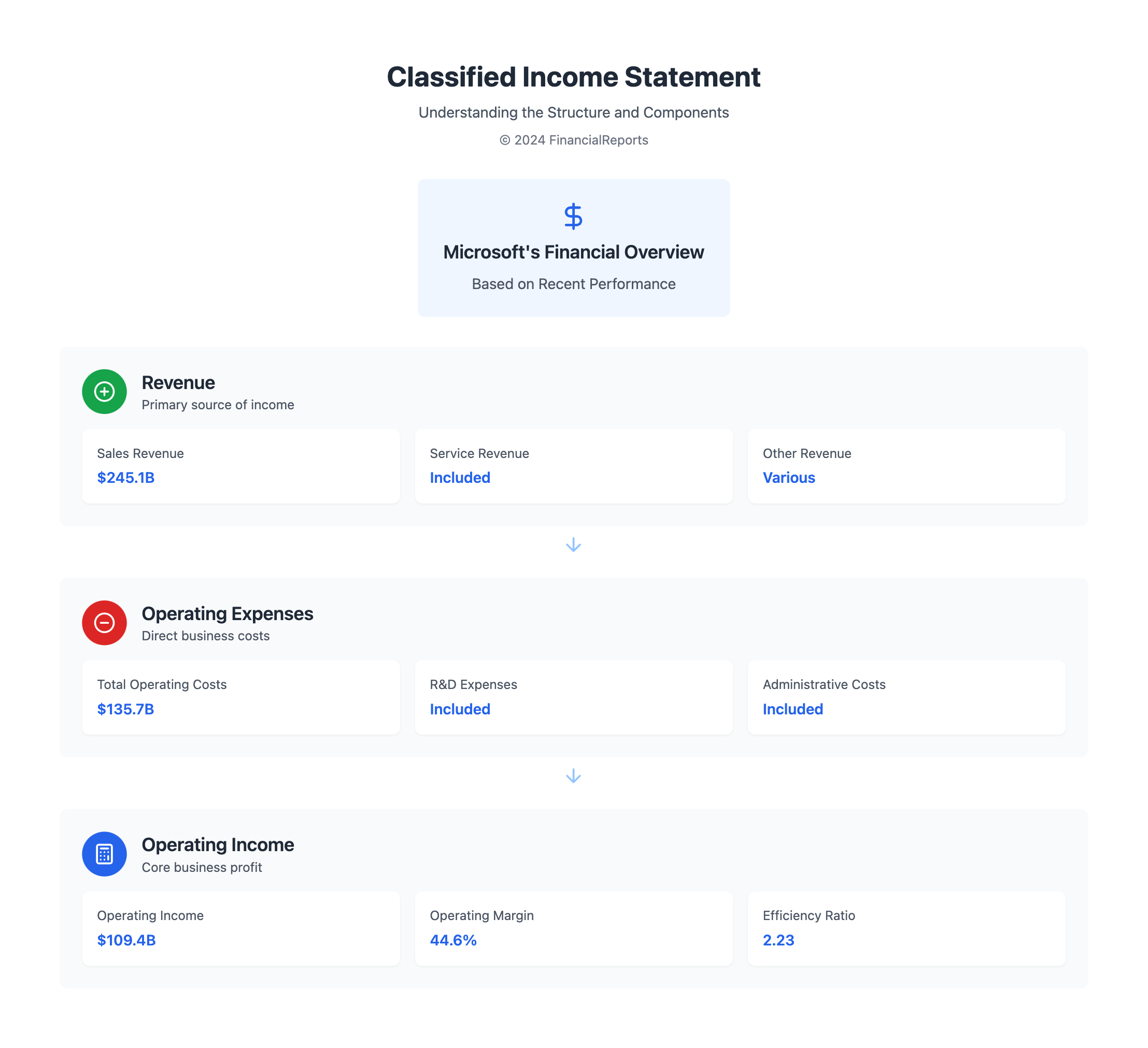
Use of Classified Income Statements for Decision Making
Classified income statements are vital for analyzing a company's performance. They organize revenue, costs, and expenses to show financial health. This helps companies understand how they're doing and plan their next moves.
By looking at these statements, businesses can match their plans with how much money they're making or losing. They help navigate through ups and downs in the market.
Financial Analysis
Analysing financials with these statements means looking closely at numbers that show how well a business is doing. For example, gross profit shows how well the core business is doing. It's found by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the revenue.
Net income takes this a step further by including costs not related to the main business activities. By looking at Income from Operations and Net Income, businesses get valuable insights. This info helps them make smart choices.
Performance Evaluation
Evaluating performance with these statements is about more than just seeing if a business made money. It involves comparing current profits to past ones. This lets businesses see if they're improving.
They look at how much they're spending on things like Sales Salaries Expense and Utilities Expense. This affects their overall income. Understanding how seasons and pricing affect income and expenses gives a full picture of financial health.
By using these details, companies can tweak their strategies to be more profitable and competitive. In short, a classified income statement guides companies towards smarter, data-based decisions.
Impact of Industry Differences on Income Statements
Income statements change a lot between industries. This is because each industry has different needs and rules to follow. These differences change how companies report finances and meet laws. Let's see how this changes the way companies report their finances.
Sector Variations
Industries have their own ways of making money and spending it. Take Amazon, for instance. They make money from selling things and providing services. This includes stuff like shipping, advertising, and making content. This is different from companies that make things, which usually just sell products and focus on production costs. So, companies need to organize their revenues and expenses in ways that match their business types.
Regulatory Considerations
Different industries also have to follow different laws for reporting finances. These laws make sure companies' financial statements are correct and clear for people looking at them. Depending on the rules, how companies report costs like depreciation or restructuring changes.
The way companies choose to report finances monthly or through thirteen-period cycles depends on their needs and internal goals.
| Item | Technology (e.g., Amazon) | Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Main Revenue Streams | Product sales, Services (content, cloud) | Product sales, Contract services |
| Key Expenses | Fulfillment, R&D, Technology, Marketing | COGS, Production overhead, R&D |
| Regulatory Compliance Focus | Data security, International commerce | Environmental regulations, Labor laws |
| Income Statement Presentation | Detailed breakdown of operating and non-operating expenses | Consolidated operating expenses, segmented by function |
| Periodic Financial Reporting | Monthly statements for closer monitoring of tech project expenses | Possibly thirteen-period cycles to monitor long-term production costs |
The table shows that different industries have to approach financial reporting in their own ways. This is because of specific industry needs and legal rules. By adapting financial reporting, companies can be clear and follow the laws, meeting both their goals and regulations.
Common Ratios Derived from Classified Income Statements
Classified income statements offer a lot of data for financial ratio analysis. This analysis is key for looking into a company's financial health, how it performs, and its place in the market.
Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios show how well a company can make money compared to sales, assets, and equity. Important metrics include:
- Gross Margin Ratio: Gross Profit / Net Sales
- Operating Margin Ratio: Operating Income / Net Sales
- Net Profit Margin: Net Income / Total Revenue
- Return on Assets (ROA): Net Income / Total Assets
- Return on Equity (ROE): Net Income / Shareholder’s Equity
These ratios help investors and analysts see how good a company is at turning sales into profits.
Efficiency Ratios
Efficiency ratios check how well a company uses assets and liabilities to make money and handle investments. Important operational efficiency metrics include:
- Asset Turnover Ratio: Net Sales / Average Total Assets
- Inventory Turnover Ratio: Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory
- Receivables Turnover Ratio: Net Credit Sales / Average Accounts Receivable
These stats are vital for seeing how well a company manages its resources to increase output and profits.
To wrap it up, using financial ratio analysis and operational efficiency metrics from classified income statements helps to fully understand a company's financial and operational health. It also shows how well it's doing in competitive markets.
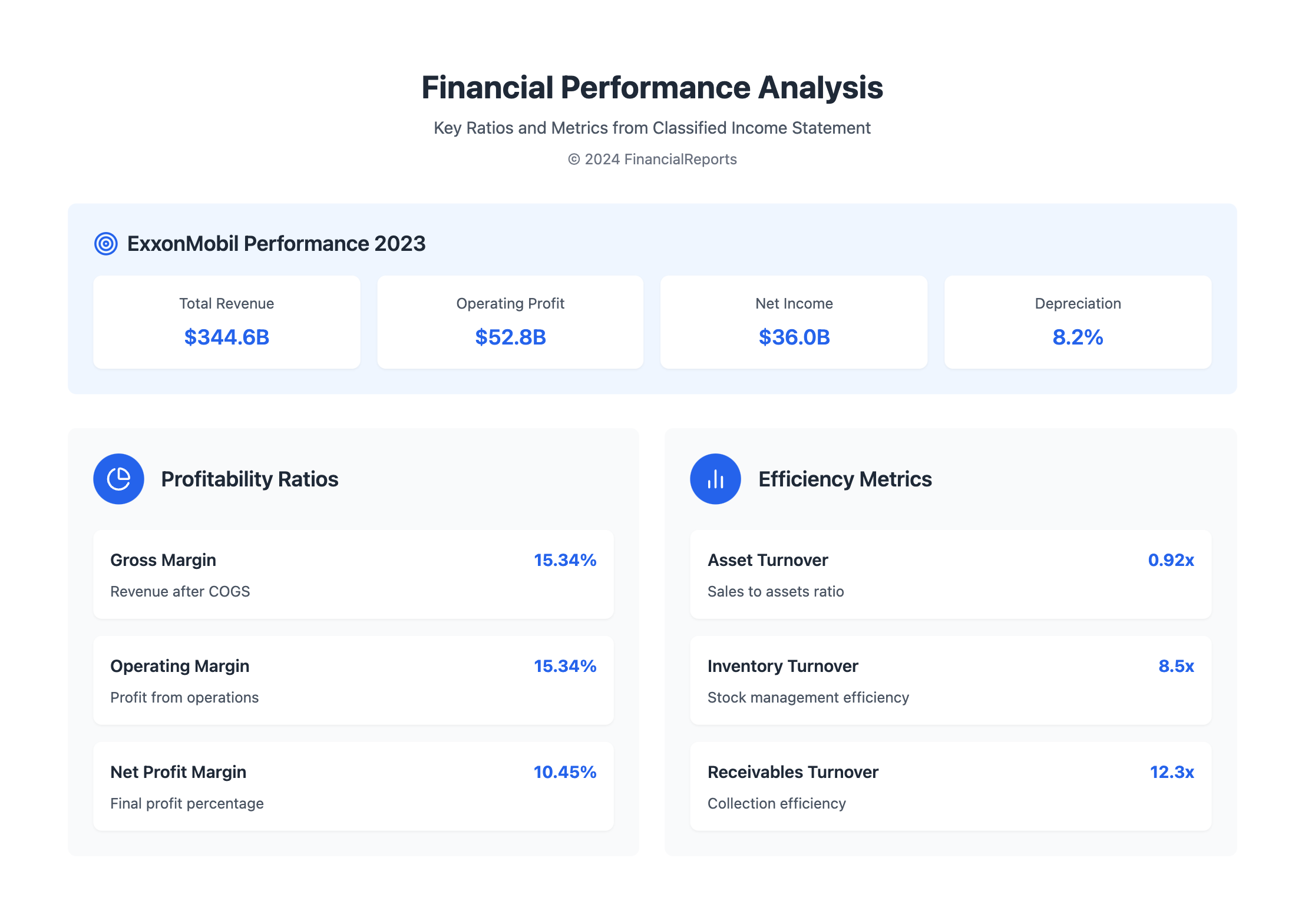
How Investors Use Classified Income Statements
Investors use classified income statements to get a real grasp on a company's financial health. They focus on investment analysis and risk management. These documents distinguish between everyday operations and unusual events. This helps show the company's true performance.
Evaluating Profitability
When checking a company's profitability, investors look at different margins and earnings. Classified income statements list these details clearly. For example, things like operating profit margin and net profit margin are key. They show if the team in charge can make money both in main and side jobs. Let's consider ExxonMobil Corporation's 2023 figures as an example.
| Financial Indicator | Calculation | FY 2023 Data | Result (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gross Profit Margin | Gross Profit / Total Revenue | $52.8B / $344.6B | 15.34 |
| Operating Profit Margin | Operating Profit / Total Revenue | $52.8B / $344.6B | 15.34 |
| Net Profit Margin | Net Profit / Total Revenue | $36B / $344.6B | 10.45 |
Assessing Risk
Risk assessment involves a deep dive into certain income statement areas. It helps spot financial weaknesses or hazards. Investors look at things like depreciation expenses and income taxes. They see how these affect the company’s stability and profit. The table below displays how ExxonMobil's income statement outlines their risk regarding asset management and tax duties.
| Aspect | Percentage of Total | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Depreciation Expenses | 8.2% | Reflects the aging and replacement policy of assets |
| Income Taxes as % of Profit Before Taxes | 15% | Highlights fiscal burden and efficiency |
| Other Income/Expenses | 3% | Indicates non-operational impact |
By closely looking at profitability and risk, with the details from classified income statements, investors and financial pros can do a better job. They can predict how well investments will do in the future. They also can protect their investments from big swings or drops. This is key to how we change the use of financial data around the world.
Auditing Classified Income Statements
The practice of financial auditing is crucial for evaluating income statements. It ensures data integrity. This means making sure financial documents are accurate, complete, and meet reporting standards. These elements build trust in financial information.
Importance of Accuracy
Accuracy in financial reporting is key. Auditors look closely at income statements. They check that money flow matches the correct time periods. This careful check helps show a company's true financial state. It lets people make smart choices based on the financial health of a business. Trust in these documents can affect investments and loan terms.
What Auditors Look For
Auditors examine many things in financial statements. They check if financial data is accurate and if the right accounting standards are used. They also look at how financial information is presented. They review documents and transactions to back up the figures. Auditors search for fraud or mistakes that could mess up the financial statements.
| Financial Statement | Key Auditing Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| Income Statement | Revenues, Expenses, Net Income, Earnings Per Share |
| Balance Sheet | Assets, Liabilities, Stockholders’ Equity |
| Cash Flow Statement | Operating, Investing, and Financing Activities |
| Statement of Retained Earnings | Changes in Equity, Dividends, Profits/Losses |
Auditors work hard to make sure financial statements follow the Generally Accepted Auditing Standards (GAAS). This keeps the data integrity safe from big mistakes. Their work makes financial reports more trusted. It also boosts confidence in how a company is run. The solid methods used in financial auditing keep income statements correct. They help achieve the goal of clear and reliable financial reporting.
Trends and Future of Classified Income Statements
Financial documents, especially classified income statements, are changing fast due to technology and new rules. Looking ahead, we see important trends in accounting and financial reports. Technologies like automation and digital platforms are not just changing how we gather and process financial data. They are also creating new standards for how precise and efficient classified income statements can be.
Technological Advances
Automation is a key focus, aiming to cut down on mistakes and speed up processing. The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning is changing how classified income statements are made. These technologies can sort through lots of data to correctly identify revenues and expenses. This makes the financial data more reliable. They also allow for immediate analysis, giving financial experts the ability to make quick, informed choices. This helps them quickly adjust to changes in the market.
Shifts in Reporting Standards
Changes in reporting standards are keeping pace with technology. They aim to make things more transparent and consistent. Organizations like the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) are updating rules. For example, the Auditing Standards Update (ASU) improves how income statement expenses are shown. This change meets the demand for more specific financial data. These changes help stakeholders understand a company's financial health better. They also make it easier to compare financial performance across different sectors. Stakeholders should stay updated on these changes and provide input. This will help keep financial reporting clear and comparisons straightforward.
FAQ
What is a Classified Income Statement?
A classified income statement is like a report card for a company's money over time. It shows incomes, expenses, and more, broken down into categories. This breakdown helps in making smart business choices.
Why is a Classified Income Statement important in financial reporting?
It's vital because it offers deep insights into how a company makes and spends money. This information helps in comparing performance and making decisions.
What are the key components of a Classified Income Statement?
Important parts include revenues from sales or services, expenses for running the business, and the net income. Net income shows the final profit after all deductions.
How does a Classified Income Statement differ from an Unclassified Income Statement?
A classified income statement provides a detailed look at finances by splitting up different types of activities. An unclassified one gives a broad overview without splitting details.
What are the Revenue Recognition principles in Classified Income Statements?
Revenue is recognized when it's earned, even if payment hasn't been collected yet. This method helps match revenue accurately with the expenses that generated it.
How are expenses classified on an Income Statement?
Expenses are tagged as operating if they are from main business activities, or non-operating for side activities. They're also marked as fixed or variable based on how they change with production levels.
What is the process for preparing a Classified Income Statement?
Creating one requires gathering financial data, accurately recording all transactions, and figuring net income. It's important to classify items correctly to avoid mistakes.
How can Classified Income Statements be used in decision-making?
They provide a clear financial picture, highlighting strengths and areas to improve. This info is key for strategic planning and evaluating performance against competitors.
How do industry differences affect Income Statements?
Unique costs and incomes in different industries mean income statements can look different. Rules and standards may also dictate how these statements must be presented.
What financial ratios can be derived from Classified Income Statements?
They help calculate ratios indicating profitability and operational efficiency. This includes gross margin, net margin, and return on assets among others.
In what ways do investors use Classified Income Statements?
Investors check these statements to understand profit trends, revenue stability, and spend management. They look for signs of healthy finances or potential risks.
Why is auditing Classified Income Statements important?
Auditing ensures the numbers are true and comply with accounting standards. It builds trust in the company's financial reports, affecting investment choices.
What trends are shaping the future of Classified Income Statements?
Tech advances like automation and AI are changing how these statements are made, aiming for better accuracy and speed. Also, reporting standards are evolving for better transparency and comparability across industries.