Service Revenue on Balance Sheet - Financial Reports Guide
Service revenue is a key part of a company's balance sheet in the financial reports guide. It represents the value of services given, even before getting paid. This is shown as accounts receivable. It's crucial for good financial analysis, showing if a company can make money from its main operations. This not only helps understand profitability but is also important for looking at a company’s financial health.
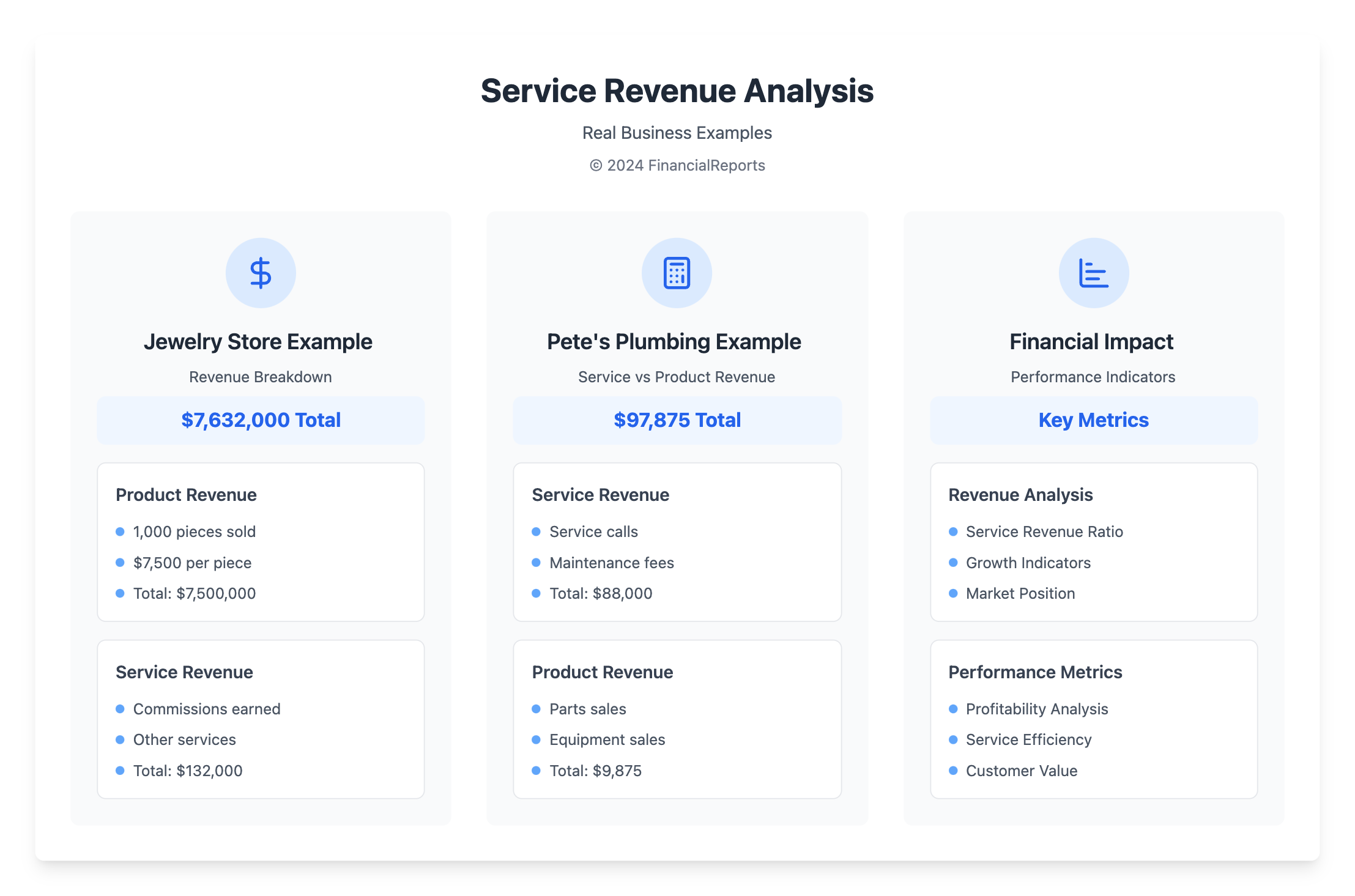
A jewelry store's example shows this well. If it sells 1,000 pieces at $7,500 each, it reports $7,500,000 in sales revenue. But that's not the full story. Add $132,000 from other sources like commissions, and total revenue hits $7,632,000. This total is key for deep financial checks. These numbers help companies plan well and stay ahead in the market.
Looking at service revenue trends gives a clear picture of how a business is doing and its place in the market. Things like accounts receivable show how well a company turns services into cash. This is vital for growth. For a business like Pete’s Plumbing, service revenue can be more important than product sales—$88,000 over $9,875. So, understanding service revenue is a must for navigating today's business world.
Key Takeaways
- Service revenue on a balance sheet reflects potential cash flow and accounts receivable as a current asset.
- Accurate recording of service revenue is critical for maintaining liquidity, profitability, and comprehensive financial reports guide.
- Analyses of service revenue trends grant insights into a company's operational efficacy and market wellness.
- Recording transactions with precision ensures robust accurate financial analysis and data-driven decision-making.
- Service revenue, vital for assessing financial health, must be reported and combined with other income streams for an accurate portrayal of total revenue.
- Recognizing service revenue on income statements rather than as an asset on the balance sheet aligns with proper accounting practices.
- Technology and evolving financial standards continue to shape the future of service revenue reporting.
Understanding Service Revenue in Accounting
The service revenue accounting is vital for modern businesses. In service industries, it's key to know the service revenue accounting definition. This knowledge helps manage businesses effectively and accurately.
Definition of Service Revenue
Service revenue is what a company earns from its main activities, no goods sold. Take Pete's Plumbing as an example. It makes most of its money from service calls. Their financials show: Service Calls: $88,000 and Product Sales: $9,875. This shows what really brings in profits for service-based companies.
Importance in Financial Reporting
The financial reporting importance of service revenue is huge. It shows if a company is doing well and its place in the market. Pete's Plumbing uses a double-entry accounting system. This means every transaction makes the books balance. This keeps their financial reporting accurate.
Also, service revenue details help investors and analysts. They can see where the company's money comes from. This tells them how the company's service model works to bring in steady income.
Knowing and reporting service revenue right is key for many businesses, especially service ones. Detailed service revenue info in reports means more transparency. It helps make smart investment and business choices.
How Service Revenue Affects the Balance Sheet
Service revenue plays a big part in a company's financial health, especially for those offering services. It goes deep into the financial statements. It changes both the current and future money situation of a business.
Positioning in Financial Statements
Service revenue changes the balance sheet by affecting accounts receivable. This means it shows money that clients owe for services. It makes the asset side of the ledger bigger because it's about earned money not yet received.
First, it shows up as more current assets, making the total assets larger. Then, when paid, it increases cash, which is key for daily business and staying flexible financially. Service revenue helps predict cash flow and keeps the company's incomings and outgoings balanced.
Relationship to Assets and Liabilities
Service revenue has a complex but crucial link to assets and liabilities. It raises accounts receivable, which is an asset. This rise in assets needs to be matched by changes in liabilities or equity. This keeps the core accounting equation balanced.
| Balance Sheet Components | Impact by Service Revenue |
|---|---|
| Current Assets | Increase in Accounts Receivable |
| Cash Reserves | Increase upon Payment Collection |
| Current Liabilities | Potential Increase in Customer Prepayments |
| Shareholder Equity | Adjustment in Retained Earnings Post-Revenue Recognition |
The table shows how service revenue directly changes the balance sheet. For example, deferred revenue is an important liability. It represents prepayments for services not yet given. This helps in making financial statements accurate and avoids overstating earnings.
Handling these parts right ensures the company follows accounting rules and makes strong decisions based on correct financial information. It shows why companies need advanced financial reporting tools. Such tools are made for service businesses to accurately track and report service revenue. This helps give a clear and correct view of the company’s finances, which aids in making wise choices.
Recognizing Service Revenue
The revenue recognition principle is key in financial reporting. It says revenue from services is recognized only when certain conditions are met. These conditions are known as performance obligations. This principle helps ensure financial statements honestly show a company's earnings during a specific time.
Revenue Recognition Principle
This principle depends on specific criteria. It's not just about delivering a service. It also must match the contractual terms with customers. Companies must follow a five-step process to meet the standards of the FASB and IASB, especially the new ASC 606. This process starts with identifying the contract and ends with recognizing revenue when obligations are met.
Performance Obligations
Under ASC 606, performance obligations are promises to deliver goods or services. Each must be distinct and accounted for separately. The customer should be able to benefit from the good or service on its own or with other resources. Revenue is recognized only when these obligations are fulfilled, ensuring accurate financial reporting.
| Steps in Revenue Recognition | Description | Impact on Financial Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Identify the Contract | Legal agreement between business and customer | Establishes the basis for enforcements of rights and obligations |
| Identify Contractual Performance Obligations | Specific tasks that must be fulfilled | Clarifies the scope of work and revenue recording timelines |
| Determine the Transaction Price | The amount expected to be received in exchange for fulfilling obligations | Informs valuation and measurement of service exchanges |
| Allocate the Transaction Price | Links transaction price to individual performance obligations | Enhances accuracy in revenue allocation to corresponding tasks |
| Recognize Revenue | Accounting and reporting of revenue post obligation fulfillment | Results in financial statements that mirror economic reality |
By following these steps, companies align with global standards. This builds trust among stakeholders by reducing risks of revenue inflation and misrepresentation in reports.
Accrual vs. Cash Basis Accounting
It's crucial for businesses to pick between accrual and cash basis accounting. This choice affects how they show their financial health and handle money from services. The two methods of accounting change how companies report finances and make decisions.
Key Differences
The main thing setting accrual and cash basis accounting apart is when transactions get recorded. With accrual accounting, incomes and expenses are noted when they happen, no matter when cash changes hands. Big companies need to use this method under GAAP rules. It makes financial reports show everything owed and owed to, giving a full view of finances.
On the other hand, cash basis accounting only records money when it actually moves. Small companies and one-person businesses like this way for its ease. It shows cash flow directly which makes tracking money simple. You don't need to keep an eye on debts or bills this way.
Implications for Recording Revenue
Choosing an accounting method drastically changes how you report money made from services. For instance, cash basis can make a company look richer in times when lots of cash comes in, like holiday sales for retailers. Yet, it might hide real debts, which can be tricky when checking finances.
But accrual accounting gives a more even look at a company's money situation. It matches money made with costs in the same time. This is key for businesses that need to show clear and full money records to people interested, like when getting an audit or seeking investors.
Rules also play a part in which accounting way to use. For example, the IRS says businesses making over $25 million a year must use accrual accounting. Tax law changes, like the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, raised the cash basis limit to $30 million, affecting this choice.
So, deciding between cash and accrual accounting needs thought. Consider your company's size, rules you must follow, and the need for deep financial details.

Common Reporting Issues with Service Revenue
Service revenue is crucial in financial reports, but it faces challenges. Issues like misclassification risks and unearned revenue impacts need careful monitoring. These problems can skew the true financial picture if not handled correctly.
Misclassification Risks
Service revenue misclassification happens between operational and non-operational revenues. This confuses stakeholders about a company's main income sources and financial health. An example is wrongfully categorizing performance obligations under ASC 606, leading to complex reporting and the need for financial statement corrections.
Impact of Unearned Revenue
Unearned revenue, or payments for services not yet provided, is tricky for reporting. It shouldn't be counted as earned revenue until the service is delivered. If mishandled, revenue figures can be misleading, affecting performance indicators. A strong system is crucial to track and correctly recognize unearned revenue to keep financial statements accurate.
| Issue | Impact on Reporting | Suggested Action |
|---|---|---|
| Inaccurate performance obligation identification | May lead to financial statement restatements | Review and adjust recognition policies in line with ASC 606 |
| Currency revaluation discrepancies | Affects KPI and GAAP disclosures | Integrate a CTA report into the GL system for accurate month-end close |
| Complex data collection from unbundled ERP systems | Increases risk of data mishandling and reporting errors | Implement a Finance Data Platform to unify and process data accurately |
| Unearned revenue misreporting | Leads to inflated short-term revenue figures | Enforce rigorous tracking and recognition processes for unearned revenue |
Dealing with reporting issues, especially the unearned revenue impact, is essential. Clear, accurate financial information is crucial for stakeholders. Using advanced technology and better internal controls can help solve these problems. This improves financial report reliability in the service sector.
Service Revenue and Financial Ratios
Understanding how service revenue affects critical financial ratios is key to analyzing a company's financial well-being. These ratios come from the company's financial statements. They show how well it operates, stays liquid, and makes profits. Service revenue is a big part of total revenue, affecting these ratios.
Key Ratios Affected
Service revenue impacts several important financial ratios:
- Liquidity Ratios: Like the current ratio and quick ratio. They show if a company can pay its short-term bills. More service revenue can raise current assets and improve these ratios.
- Profitability Ratios: This includes the gross margin ratio and return on assets. Businesses with more service revenue usually have lower costs of goods sold. So, they can have better margins.
- Efficiency Ratios: Service companies often have different results in inventory and asset turnover ratios. This is because they process fewer physical goods.
- Solvency Ratios: Including the debt to equity ratio and interest coverage ratio. If service revenue increases profitability and cash flow, these ratios may get better.
Analysis for Stakeholders
Doing a detailed analysis with financial ratios has many pluses:
- Comparative Performance: It shows how a company's financial health compares to others in the industry. This is key for external stakeholders deciding where to compete.
- Investment Decisions: It gives insight into if a company's service revenue is making enough profit and cash flow for investing.
- Risk Assessment: It finds possible financial risks and helps forecast future profit and stability.
Stakeholders use these analyses to forecast financial health and make choices about lending, investing, and strategic plans. Performance indicators from service revenue and financial ratios guide these decisions.
Disclosures Related to Service Revenue
In financial reporting, clear revenue disclosures are key for understanding a company’s health. They explain the complex details of service revenue. Entities follow rules to make their disclosures clear and consistent. This practice helps meet legal requirements and boosts investor trust and market stability.
Required Information
ASC 606 requires entities to share detailed disclosures on service revenue. These disclosures include both numbers and explanations. They cover the nature, timing, and amount of revenue from customer contracts. Entities must describe how they recognize revenue and measure progress towards fulfilling contracts. They also explain pricing and how they estimate and allocate variable consideration.
Entities must also share how they make significant decisions on revenue recognition. You can find more about revenue disclosure practices and the judgement involved. This includes potential risks in recognizing revenue.
Best Practices for Transparency
Transparency is more than following rules; it builds trust and improves financial analysis. Best practices include in-depth explanations of revenue sources. They make complex revenue info easy to grasp for readers. And, they show revenue in different ways, like tables, to clarify financial data.
These practices help companies govern their finances well and connect with stakeholders. As reporting gets more detailed, clear revenue disclosures remain crucial. They form the basis of corporate transparency and strategic decision-making.
Service Revenue in Different Industries
Service revenue varies greatly across different industries. It depends on the type of work a company does. This affects the company's finances in unique ways.
Variability Across Sectors
Some sectors see more ups and downs in revenue due to how they bill and deliver services. For example, consulting firms record earnings as they complete work. They might also account for future earnings from ongoing projects. On the other hand, retail stores usually earn service revenue right away, like from warranties or support.
Industry-Specific Considerations
It's crucial to grasp the revenue details of each sector. This knowledge is key for crafting financial strategies and following rules. Industries such as IT and professional services often work on long projects. They need detailed plans for recording earnings over time.
| Industry | Typical Revenue Model | Example: % of Total Revenue from Services | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consulting | Fee for Service, Retainers | 95% | Deferred revenue and client retainers management |
| Information Technology | Managed IT Services, Project-based | 80% | Revenue recognition on long-term projects |
| Retail | Product Sales, Ancillary Services | 20% | Recognition of warranties and support services |
| Professional Services | Hourly Rates, Project Fees | 90% | Accurate tracking of billable hours and job costing |
The differences in how industries handle service revenue show the need for flexible financial tactics. Understanding these unique revenue models is essential. It ensures businesses stay compliant and report their finances accurately. The variety in services underscores the importance of adapting to the specific financial practices of each industry.
Audit and Compliance Considerations
In financial reporting, service revenue disclosure must be precise. This is key for audit integrity and true financial health shows. Considering the many layers of audit requirements and compliance is essential. Different governing bodies demand it.
Importance of Accurate Reporting
Correct reporting is crucial for integrity and trust with investors. The PCAOB sets strict auditing guidelines, such as Release No. 2017-001. These set the auditor's role in keeping financial reports error-free, whether from mistakes or fraud.
This matters even more for organizations like CILs. They must meet high auditing standards to get federal funds. Through detailed audits, they can show compliance and keep their federal support.
Compliance with Accounting Standards
Following standards like GAAP and IFRS helps keep financial reports consistent worldwide. AS 3105 advises on how to handle deviations from standard opinions. This improves auditor reports in quality and clarity.
Following these rules means dealing with complicated aspects, like Critical Audit Matters (CAMs). CAMs are tough or subjective parts of the audit. They've been important for audits since December 15, 2017. They guide auditors in complex parts of reporting, raising audit quality.
Management letters come from these audits and are key for improving an organization. They suggest ways to better processes. They underline the value of detailed audits in making companies more accountable and efficient in reporting.
Auditing and compliance are closely linked parts of financial reporting. They form a solid base for being clear with stakeholders, ensuring their trust, and keeping organizations running for a long time.
Future Trends in Service Revenue Reporting
The world of service revenue reporting is always changing. This is because technology keeps advancing and financial practices are shifting. Financial reporting is getting more complex. Technology plays a big role in this, making it easier to manage finance structures. Automation and better software are making financial reports clearer and more accurate. This helps businesses have better control over their financial stories.
Impact of Technology
Software as a service (SaaS) companies are at the forefront, changing the game. They use things like monthly recurring revenue (MRR) and annual recurring revenue (ARR). Plus, they are bringing in advanced forecasting models that really shake things up. These methods are backed by data science to make really accurate predictions. Technology makes everything more transparent. It improves how we audit, monitor churn rates, and calculate ACV. This all leads to better financial decisions based on real data.
Evolving Standards and Practices
Financial practices are changing, leading to new ways of recognizing and reporting service revenue. We now use accrual-based revenue recognition. This method records income when it's earned, not just when cash is received. It's crucial for clear reporting. Also, we're being more careful about separating bookings from real revenue. This accuracy is essential. SaaS companies are being very transparent in their financial reporting. They use income statements, cash flow analyses, and balance sheets. This not only helps them but also guides the future of financial reporting. It ensures trust among investors, clients, and regulators.
FAQ
What is the definition of service revenue in accounting?
Service revenue is the money a company makes from its services. It doesn't include product sales or investment gains. This revenue is counted when the service is given and billed.
Why is service revenue important in financial reporting?
It shows the main earnings from a company's services. This tells us how profitable and efficient a business is. It's key for correctly evaluating a company's financial success.
Where does service revenue appear on the balance sheet?
It isn't directly listed on the balance sheet. But, it leads to accounts receivable in current assets. This shows money owed to the company after services are billed.
How does service revenue relate to a company's assets and liabilities?
It boosts a company's accounts receivable, an asset. When a service is billed and paid for, cash increases, boosting liquidity. It only becomes a liability if the service is paid for in advance.
What is the revenue recognition principle in accounting?
This principle says revenue is recorded when a service is done, not when paid. It makes sure revenue is shown when it's really earned. This gives a truer financial picture.
How do accrual and cash basis accounting differ when recording service revenue?
Accrual accounting records revenue when a service is done, cash basis when payment is received. The method chosen changes how and when revenue is shown in accounts.
What are some common reporting issues with service revenue?
Issues include misclassifying service revenue and mishandling unearned revenue. These can change financial analysis and falsely show a company's performance.
Which financial ratios are significantly influenced by service revenue?
It affects important ratios like net profit margin and current ratios. Correct service revenue information is essential for accurate ratios and understanding company performance.
What information is required to be disclosed related to service revenue?
Companies must share the type, amount, and timing of service revenue. Financial reports should have detailed notes for clarity and to meet standards.
How does service revenue vary across different industries?
It depends on the industry, such as consulting firms mainly earning from services. Service type and billing practices are key for reporting revenue by industry.
Why is accurate reporting of service revenue crucial for audits and compliance?
Precise reporting ensures financial statements meet standards like GAAP or IFRS. Errors can lead to severe issues like financial restatements or losing trust from stakeholders.
How are advancements in technology affecting service revenue reporting?
Technology like automation improves recording and reporting of service revenue. It boosts analysis quality while meeting changing accounting standards.