Profitability Insight: Revenue Minus Cost Analysis
Profitability analysis is key for checking if a business makes money. It compares what it earns to what it spends. To see how well a company does, we look at revenue minus cost. This shows where to make more money and where to cut costs.
When we talk about gross profit and net profit, we need to know the difference. Gross profit is what's left after selling products minus the cost of making them. Net profit is what's left after all expenses and taxes are subtracted. This tells us how much money a company really makes.
Looking at revenue and costs helps businesses find out how much profit they make from different sources. For example, the Electronics product line made $1,000,000, but it cost $600,000 to make. So, it made $400,000 in profit. This shows why knowing revenue minus cost is so important for a company's success.
Key Takeaways
- Revenue minus cost analysis is essential for evaluating a business's profitability.
- Gross profit vs net profit calculation helps identify profit-maximizing strategies and operational inefficiencies.
- Understanding what does net profit mean is vital for businesses to make smart choices.
- Defining gross profit as the difference between revenue and cost of goods sold is key for financial analysis.
- Regular profitability analysis can help businesses find ways to cut costs and boost revenue.
- Profitability ratios, such as gross profit margin and net profit margin, are used to analyze a company's financial performance.
- Higher profitability ratios show a company is good at turning revenue into profit.
Understanding Revenue and Cost Components
Revenue is all the money a business makes before any costs are subtracted. Costs can be fixed, like rent, or variable, like materials. It's key to know the difference between gross income and gross profit. This involves looking at different types of income and the expenses that go with them.
The difference between gross profit and net profit is in what's subtracted from revenue. Gross profit is what's left after subtracting the cost of goods sold. Net profit is what's left after subtracting all expenses, including taxes and interest. Knowing this helps businesses improve their profitability.
Here are some important points to remember when looking at revenue and costs:
- Revenue types: product sales, service income, recurring revenue, and one-time income
- Cost categories: fixed costs, such as rent and employee salaries, and variable costs, such as raw materials and commission
- Expenses: materials, labor, overheads, and other direct costs
By understanding these, businesses can make better choices about pricing and production. This helps them increase their gross income vs gross profit and profit and net profit.
| Revenue Type | Cost Category | Expense |
|---|---|---|
| Product Sales | Fixed Costs | Materials, Labor, Overheads |
| Service Income | Variable Costs | Commission, Raw Materials |

The Importance of Revenue Minus Cost Calculation
Figuring out revenue minus cost is key to knowing if a business is profitable. It shows the difference between what a company makes and what it spends. This helps businesses see how well they're doing and where they can get better.
For example, Amazon makes a lot of money but can also lose money. In 2022, Amazon made $514.0 billion but spent over $288 billion on goods and $501 billion on operations. This shows how important it is to understand revenue minus cost.
Determining Profitability
To figure out if a business is making money, you need to subtract costs from revenue. This means taking away the cost of goods and expenses from what the company makes. This number tells you how healthy the company is and helps with decisions on pricing and production.
Strategic Financial Decisions
Knowing revenue minus cost is also key for making big financial choices. It helps businesses see how to make more money and spend less. For instance, a company might raise prices to cover costs or invest in new tech to save money.
| Company | Revenue | Cost of Goods Sold | Operating Expenses | Net Income |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $514.0 billion | $288 billion | $501 billion | -$2.7 billion |
By looking at revenue minus cost, businesses can learn a lot about their finances. They can see how changes in pricing or costs affect their bottom line. This calculation is a powerful tool for improving financial health.
Different Methods for Calculating Revenue Minus Cost
It's key to know the difference between gross profit and net profit. Gross profit is found by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total revenue. Net profit is found by subtracting operating expenses, taxes, and other costs from gross revenue. Companies can use direct calculation or a percentage of revenue to figure out revenue minus cost.
Direct Calculation
The direct calculation method is simple. It involves subtracting total costs from revenues. For example, if a company makes $100,000 and spends $70,000, they have $30,000 left. You can find more about revenue at revenue calculation pages.
Percentage of Revenue
The percentage of revenue method splits costs based on percentages. This is helpful when costs change. For example, a company might spend 60% on COGS and 40% on operating expenses. This way, companies can manage costs and make smart choices about pricing and production. Gross profit margin is important for checking how profitable a company is and making strategic plans.
- Gross profit margin is calculated as (Revenue - COGS) / Revenue x 100
- Gross profit focuses on variable costs, excluding fixed costs like rent and administrative expenses
- Gross profit can vary based on whether a company uses absorption or variable costing methods
Analyzing Fixed vs. Variable Costs
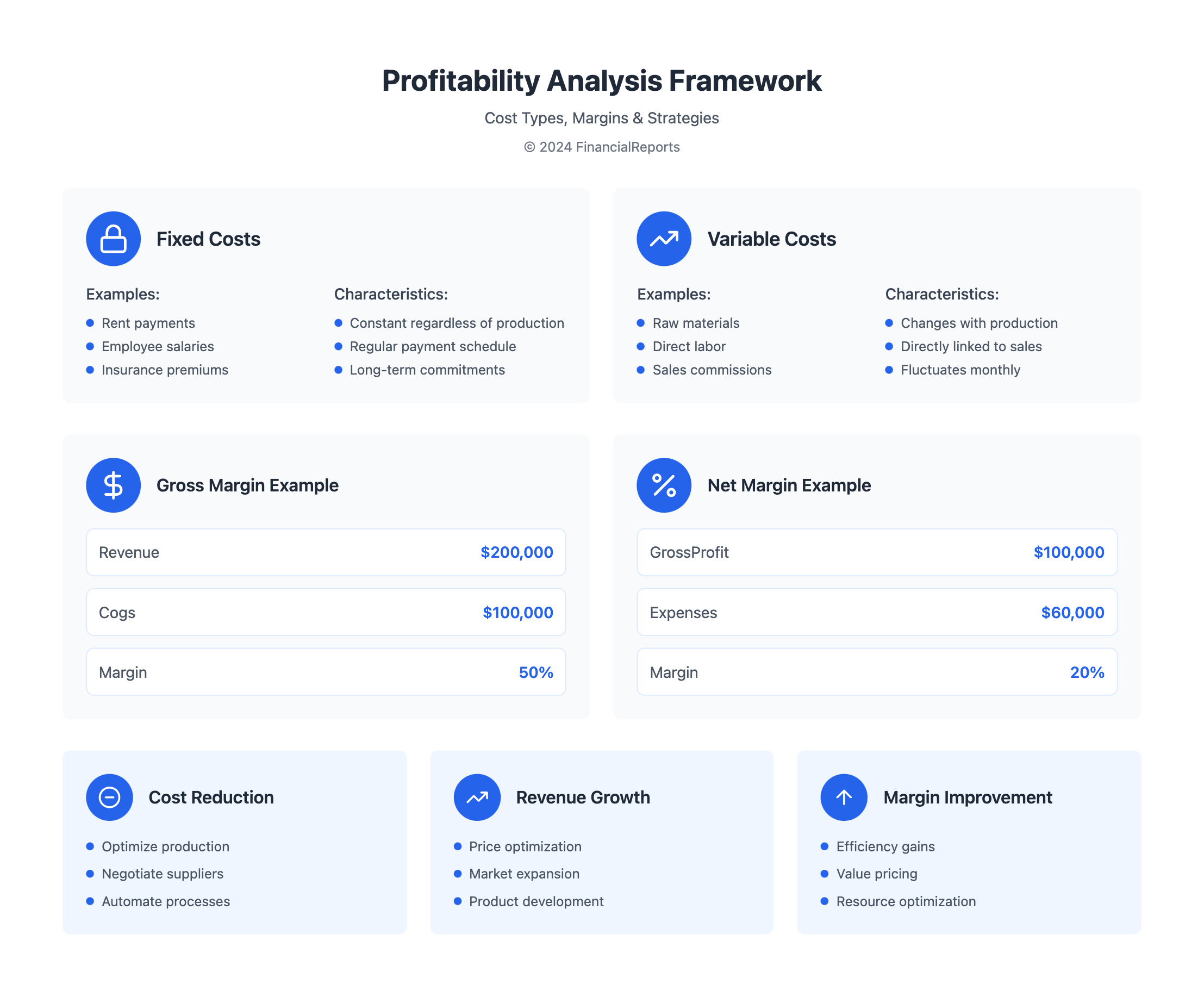
Understanding fixed and variable costs is key when looking at gross and net profit. Gross profit is a key indicator of a company's health. It shows how much profit is made after subtracting the cost of goods sold from revenue.
Fixed costs stay the same, no matter how much is sold. These include things like rent, salaries, and utilities. Variable costs, on the other hand, change with how much is produced. Examples are raw materials, labor, and shipping.
Understanding Fixed Costs
Fixed costs don't change with production levels. They include things like rent, insurance, and salaries for non-variable employees. Knowing these costs helps figure out when a company breaks even.
Understanding Variable Costs
Variable costs change with production levels. They include raw materials, labor, and utilities. Cutting these costs can boost profit margins.
Looking at fixed and variable costs helps companies make smart choices. They can decide on pricing and production better. This way, they can improve profits and reach their goals. Understanding these costs helps manage expenses and increase profits.
The Role of Gross Margin in Revenue Analysis
Gross margin is key in financial analysis. It shows how profitable a company is and how well it makes things. It's the percentage of revenue left after subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS). This tells us about the company's health and growth chances.
What is Gross Margin?
Gross margin is the difference between a company's net sales and its COGS, shown as a percentage of net sales. It shows how much of the revenue the company keeps after paying for direct production costs. This shows if the company can make profits.
Calculating Gross Margin
To find gross margin, use this formula: Gross Margin = (Net Sales - COGS) / Net Sales x 100. For instance, if a company makes $200,000 in net sales and spends $100,000 on COGS, its gross margin is 50%. This is because ($200,000 - $100,000) / $200,000 x 100 = 50.
Looking at gross margin over time helps us understand a company's efficiency, pricing, and financial health. Investors and analysts often check gross margin to judge a company's performance and future.
FAQ
What is the significance of analyzing "Revenue Minus Cost" for profitability?
Understanding "Revenue Minus Cost" is key to seeing how profitable a business is. It shows profits from different sources, spots where things can be improved, and helps use resources better. This way, businesses can work more efficiently and grow steadily.
What is the definition of revenue, and what are the different types of revenue?
Revenue is all the money a business makes before paying taxes or other costs. There are two main types: recurring income (like subscriptions) and one-time payments.
What are the two main categories of costs, and how do they impact profitability?
There are two main cost types: fixed costs (like rent and salaries) and variable costs (like materials and commissions). Changes in these costs can greatly affect a business's finances. Businesses need to manage these costs well to stay profitable.
How is "Revenue Minus Cost" calculated to determine profitability, and what are the strategic financial decisions involved?
"Revenue Minus Cost" is figured out in two ways: direct subtraction or percentage allocation. The best method depends on the data available and important metrics like profit margins. Knowing how to calculate this helps businesses make smart financial choices, improve their market position, and fix weak areas.
What is the difference between fixed and variable costs, and how do they impact profitability analysis?
Fixed costs, like rent and salaries, stay the same no matter how much you sell. Variable costs, like materials and commissions, change with sales. Understanding these costs helps businesses use resources better and boost profits.
What is gross margin, and how does it contribute to revenue analysis?
Gross margin is the profit from selling a product or service. It shows how profitable something is. By looking at gross margin, businesses can see how efficient they are and make better choices about pricing and costs.