Operating Profit vs Net Income: Key Differences
When we look at a company's financial health, two important numbers stand out: operating profit and net income. Operating profit is what's left after all costs are subtracted, except for debt, taxes, and some special items. Net income, on the other hand, is the profit after all costs are taken out of the revenue from sales. Knowing the difference between these two is key for anyone who invests, analyzes, or makes financial decisions.
Understanding the difference between operating profit and net income is critical. Operating profit shows how well a company runs its core business. Net income gives a full picture of the company's financial health. By comparing these two, we can see where a company can get better financially. This helps experts understand a company's profitability and make smart choices.
Key Takeaways
- Operating profit and net income are two distinct metrics used to evaluate a company's financial performance.
- Operating profit is calculated as operating revenue minus cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and depreciation and amortization.
- Net income is the result of all costs, including interest expense, taxes, and any one-off items.
- The comparison of operating profit vs net income is critical for understanding a company's management effectiveness and financial health.
- Both operating profit and net income are essential measurements of profitability, but they provide different insights into a company's financial performance.
- Analysis of profitability metrics like gross profit, operating profit, and net income is necessary to understand a company's overall financial health.
- Operating profit vs net income analysis helps investors and analysts evaluate a company's long-term financial viability and compare profitability across different industries.
Understanding Operating Profit
Operating profit is key to understanding a company's financial health. It shows what's left after all operating costs are subtracted from total income. This measure helps see how well a company runs its main business and makes profits.
When we look at operating vs net income, remember that operating profit doesn't include debt interest or taxes. But net income does.
To find operating profit, you subtract operating costs from gross profit. Gross profit is what's left after subtracting the cost of goods sold from total income. The main parts of operating profit are:
- Sales or revenue
- Cost of goods sold (COGS)
- Selling, general, and administrative (SG&A) expenses
- Depreciation and amortization
Looking at operating profit helps investors see if a company can keep making money over time. It's very important for startups to show they can make profits and keep running.
Exploring Net Income
Net income shows how much money a company makes after all costs are subtracted. It includes things like interest, taxes, and special items. Knowing the difference between operating and net income helps experts and investors see if a company is really making money.
To figure out net income, you need to look at a few things:
- Operating profit, which is what the company makes from its main activities
- Non-operating income, like interest or money from selling assets
- Interest expenses, which are payments for borrowed money
- Taxes, which are what the company pays on its earnings
- Extraordinary items, like one-time gains or losses
The formula for net income is: Net Income = Operating Income + Non-Operating Income - Interest Expense - Taxes. By understanding these parts and how they add up, experts and investors can better understand a company's financial health. This helps them make smart choices.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Operating Income | Profit earned from core operations |
| Non-Operating Income | Income from non-core operations, such as interest income |
| Interest Expense | Interest paid on debt |
| Taxes | Taxes paid on taxable income |
Key Differences Between Operating Profit and Net Income
Understanding the difference between operating profit and net income is key when looking at a company's finances. Operating profit looks at a company's main activities, without interest and taxes. Net income, on the other hand, shows the total profit, including other income.
To find operating profit, you subtract operating costs, depreciation, and amortization from gross profit. Net income is found by subtracting all costs, including interest and taxes, from total revenue. This shows how operating profit vs net income are different.
Profitability vs. Overall Profit
The operating profit margin shows how well a company does in its main activities. Investors compare this to see who's doing better in their field. Net income, though, gives a wider view of a company's success, including income from investments and asset sales.
Impact of Non-Operating Income
Income from investments and asset sales can greatly affect a company's net income. But, these are not part of operating profit. Knowing this helps investors understand a company's true financial health.
The Significance of Operating Profit
Operating profit is a key financial metric. It shows how well a company does from its main business activities. It's found by subtracting operating costs from gross profit. This gives insights into how well a company manages its costs.
The operating profit margin is another important measure. It's found by dividing operating income by total sales. This shows how efficient a company is in its operations.
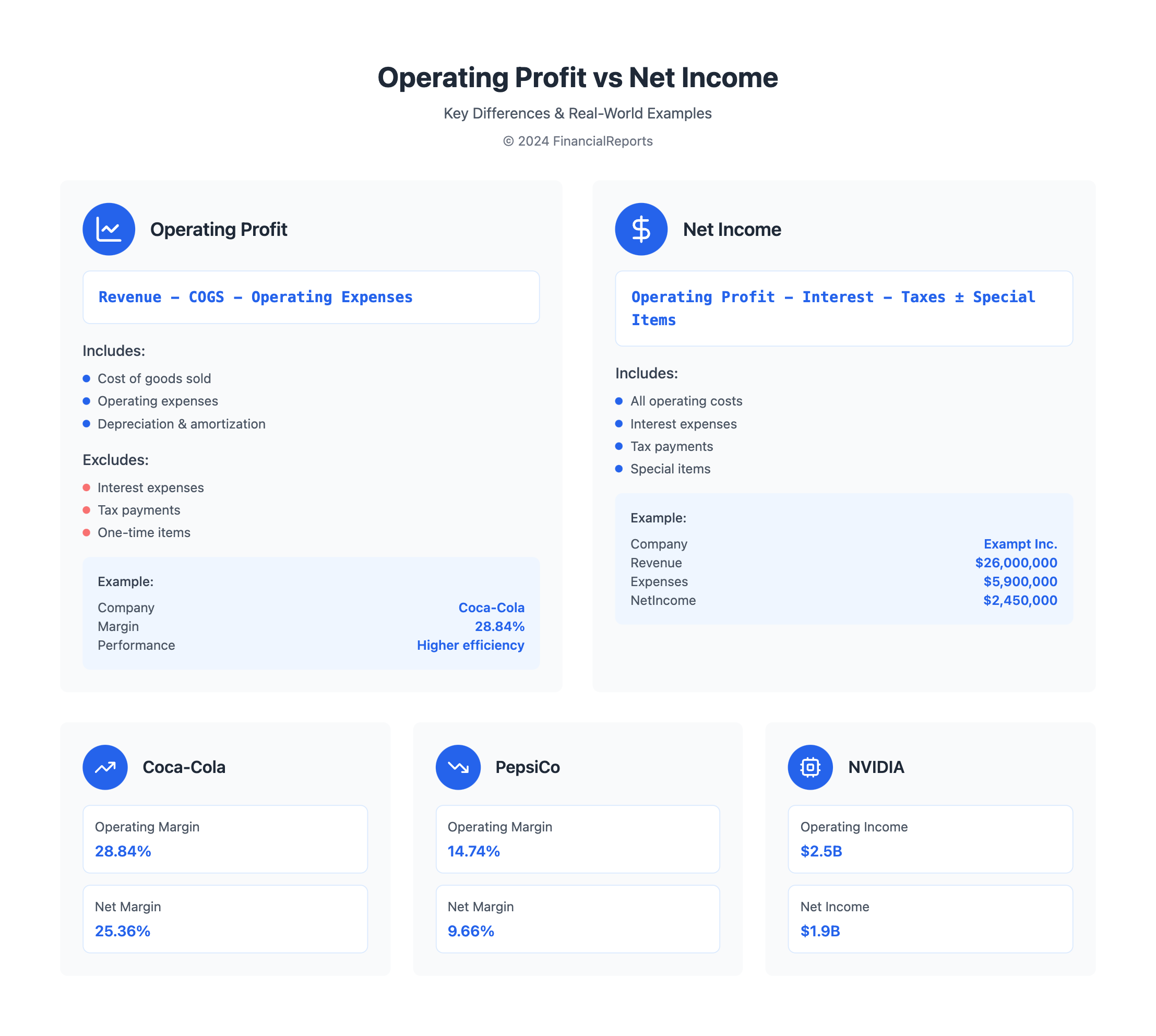
A high operating profit margin means a company is very profitable. This makes investors and financiers happy. For example, Coca-Cola had an operating profit margin of 28.84% in 2021. This was higher than PepsiCo's 14.74% margin.
This shows how important operating profit is. It helps judge a company's financial health and how it stacks up against others in its field.
Operational Efficiency Indicator
The operating profit margin is a key sign of a company's operational efficiency. It lets companies compare themselves to others in their field. A higher margin means better cost control and efficiency.
The table below shows the operating profit margins of Coca-Cola and PepsiCo for 2021:
| Company | Operating Profit Margin | Net Profit Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Coca-Cola | 28.84% | 25.36% |
| PepsiCo | 14.74% | 9.66% |
Comparison in Different Industries
Net operating profit is vital for comparing companies across different industries. By looking at operating profit margins, investors and analysts can see how companies compare. This helps them make smart investment choices and spot growth chances.
The Role of Net Income in Financial Analysis
Net income is key to knowing if a company can keep running and grow. It shows how well a company makes money and how it spends it. When looking at operating vs net income, remember that non-operating costs like interest and taxes matter too.
Understanding the link between operating profit and net income is vital. Net income, or net profit, shows how much money a company makes after all costs are subtracted from its income. For instance, Exampt Inc. made $2,450,000 in net income from $26,000,000 in revenue and $5,900,000 in expenses.
Important things to think about when looking at net income include: * Net income helps figure out earnings per share (EPS), which is important for investors. * The net profit margin, found by dividing net income by total revenue, shows how profitable and efficient a company is. * Comparing net income to EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) helps understand a company's true financial health, showing the effect of interest and taxes.
How Operating Profit Affects Company Valuation
Operating profit, or earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT), is key in valuing companies. It's used in ratios like the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio and enterprise value to EBITDA (EV/EBITDA). These ratios help compare companies with different financial structures.
Using operating profit in these ratios gives a clearer view of a company's health. It ignores non-operating items like interest and taxes. This helps analysts and investors see a company's true value. For instance, a company with high operating profit margins is seen as more attractive. It shows strong management and a market edge.
Some common ratios that use operating profit include:
- Price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio
- Enterprise value to EBITDA (EV/EBITDA)
- Operating profit margin
These ratios offer insights into a company's financial health. They help compare companies across different fields.
| Valuation Ratio | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio | P/E = Market Value per Share / Earnings per Share | Compares a company's market value to its earnings |
| Enterprise value to EBITDA (EV/EBITDA) | EV/EBITDA = Enterprise Value / EBITDA | Compares a company's enterprise value to its EBITDA |
| Operating profit margin | Operating Profit Margin = Operating Profit / Revenue | Measures a company's operating efficiency |
In summary, operating profit is vital in valuing companies. Its use in various ratios offers deep insights into a company's financial health. Understanding this relationship helps investors and analysts make better decisions and stay ahead in the market.

The Influence of Net Income on Investor Perception
Net income greatly affects how investors see a company and the market. A higher earnings per share (EPS) usually means a higher stock price. The gap between operating and net income is key to knowing if a company is really profitable. Investors keep a close eye on net income, calling it the "bottom line."
The link between net income and EPS is critical for financial analysis. EPS is found by dividing net income by the number of shares outstanding. Knowing this helps investors make better choices. When a company meets or beats earnings expectations, its stock price often goes up.
Several factors affect how net income and EPS are related. These include:
- Share buybacks and dividend payments
- Diluted EPS, which gives a more cautious look at earnings for shareholders
- Changes in net income, which directly affect EPS and how investors see the company and its stock value
| Factor | Influence on Net Income and EPS |
|---|---|
| Share buybacks | Increases EPS by reducing the number of shares outstanding |
| Dividend payments | Affects net income and EPS, as dividends are paid out of net income |
| Fluctuations in net income | Directly influences EPS and impacts investor perception and stock valuation |
In summary, net income's impact on investor views is big. It's important to understand the difference between operating and net income to judge a company's real profit.
Common Misconceptions About Operating Profit
Many people get confused about operating profit because of the similar terms used. Terms like operating income, operating profit, and earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) are often mixed up. But, the way a company reports its profits can make a big difference. For example, operating income is found by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit. Gross profit is what you get after taking away the cost of goods sold (COGS) from revenue.
It's important to know the difference between operating and non-operating revenue. Operating revenue comes from a company's main business, like Apple's iPhone sales. Non-operating revenue, on the other hand, comes from things like interest, investments, or other secondary sources. Knowing these differences helps in understanding a company's net operating profit better and making smart financial choices.
Misinterpretation in Financial Reporting
Comparing operating profits between companies can be tricky because of different accounting practices. To get it right, it's key to look at how each company reports its profits. This way, financial experts can better understand a company's net operating profit and make better decisions.
Overemphasis on Operating Metrics
Operating profit is very important, but focusing too much on it can be a mistake. It's important to look at other financial numbers too, like net income and gross profit. This gives a full picture of a company's financial health. By looking at everything, financial experts can make better choices and help the business grow.
Tax Implications of Net Income
When figuring out net income, it's key to think about taxes. Taxes can really change how much money a company makes. The difference between net profit before and after taxes is important. Net income is what's left after taxes are taken out. The amount of taxes owed can change based on where the business is and how it's set up.
The tax rate a company pays can be different from the official rate. This is because of deductions and credits. Businesses can use tax deductions to lower their taxes. For instance, operating income can be affected by these deductions. Knowing about tax implications of net income is important for financial experts, investors, and others who need detailed financial data.
Some common tax deductions that businesses can use include:
- Depreciation and amortization
- Interest expenses
- Research and development costs
In summary, the tax side of net income is a big deal in finance. By knowing about tax rules and deductions, companies can handle their taxes better. This can help them make more net income. It also affects their operating vs net income performance.
| Company | Operating Income | Net Income |
|---|---|---|
| Macy's | $382 million | $105 million |
| NVIDIA Corporation | $2.5 billion | $1.9 billion |
Conclusion: Importance of Both Metrics in Business Strategy
Operating profit and net income are key for checking a company's financial health. They help in making smart choices for the future. Operating profit shows how well a company turns sales into profit by managing costs well. Net income gives a full picture of profit, including taxes and other costs.
It's important to look at both operating profit and net income together. This helps leaders and financial experts make better decisions. Operating profit helps focus on short-term goals and improving processes. Net income helps see the big picture of financial health and goals for the future.
By using both operating profit and net income, companies get a complete view of their finances. This helps everyone make smart choices, use resources wisely, and keep improving the business.
FAQ
What is the difference between operating profit and net income?
Operating profit shows how much money a company makes from its main activities. Net income, on the other hand, looks at the company's overall profit. It includes things like non-operating income, interest, taxes, and special items.
How is operating profit calculated?
To find operating profit, you subtract COGS and operating expenses from total revenue. You don't include non-operating income and expenses in this calculation.
What are the key components of net income?
Net income is found by adjusting operating profit. You add in non-operating income, subtract interest expenses, taxes, and special items.
How does the treatment of depreciation and amortization differ between operating profit and net income?
Depreciation and amortization are part of the core business costs in operating profit. But, they're not included in net income.
Why is operating profit an important metric for assessing a company's operational efficiency?
Operating profit shows how well a company does from its main activities. It shows how efficient and cost-effective the company is.
How is net income used in financial analysis and investment decision-making?
Net income is key for checking a company's overall profit. It helps calculate important ratios like return on equity (ROE) and earnings per share (EPS). These ratios help investors make decisions.
How does operating profit impact company valuation?
Operating profit is used in valuation ratios like price-to-earnings (P/E) and enterprise value to EBITDA (EV/EBITDA). These ratios help figure out a company's true value and compare it to others.
How can the influence of net income on investor perception lead to potentially pitfalls?
Focusing too much on net income can lead to short-term thinking. It might also hide the company's true financial health through earnings manipulation.
What are some common misconceptions about operating profit?
People often confuse terms like operating income, operating profit, and EBIT. Misunderstanding these can lead to wrong comparisons between companies.
How do tax implications affect the net income metric?
Taxes directly affect a company's bottom line. Knowing about effective tax rates, deductions, and international tax rules is key to understanding net income.