Net Revenue vs. Net Sales: Are They Identical?
Revenue is the total income a company makes from its main activities. Sales are the money a company gets from selling things to customers. So, is net revenue the same as net sales? Knowing the difference between these two is key for any business.
Net revenue is found by taking total revenue and subtracting costs like discounts and refunds. Net sales revenue is total sales minus costs like returns. Understanding these differences helps a company see its financial health and make better choices.
Key Takeaways
- Net revenue and net sales are two distinct financial metrics used to assess a company's financial health.
- Net revenue is calculated by subtracting total transactional costs from the total revenue during a set time period.
- Net sales revenue is the total sales revenue minus transactional expenses such as returns.
- Understanding the difference between net revenue and net sales is vital for making informed business decisions.
- Is net revenue the same as net sales? The answer is no, and understanding the distinction is essential for businesses of all sizes.
- Calculating net revenue and net sales requires accurate data and a thorough understanding of the underlying financial metrics.
- Net revenue and net sales are key metrics for assessing a company's financial health and profitability.
Understanding the Concepts of Net Revenue and Net Sales
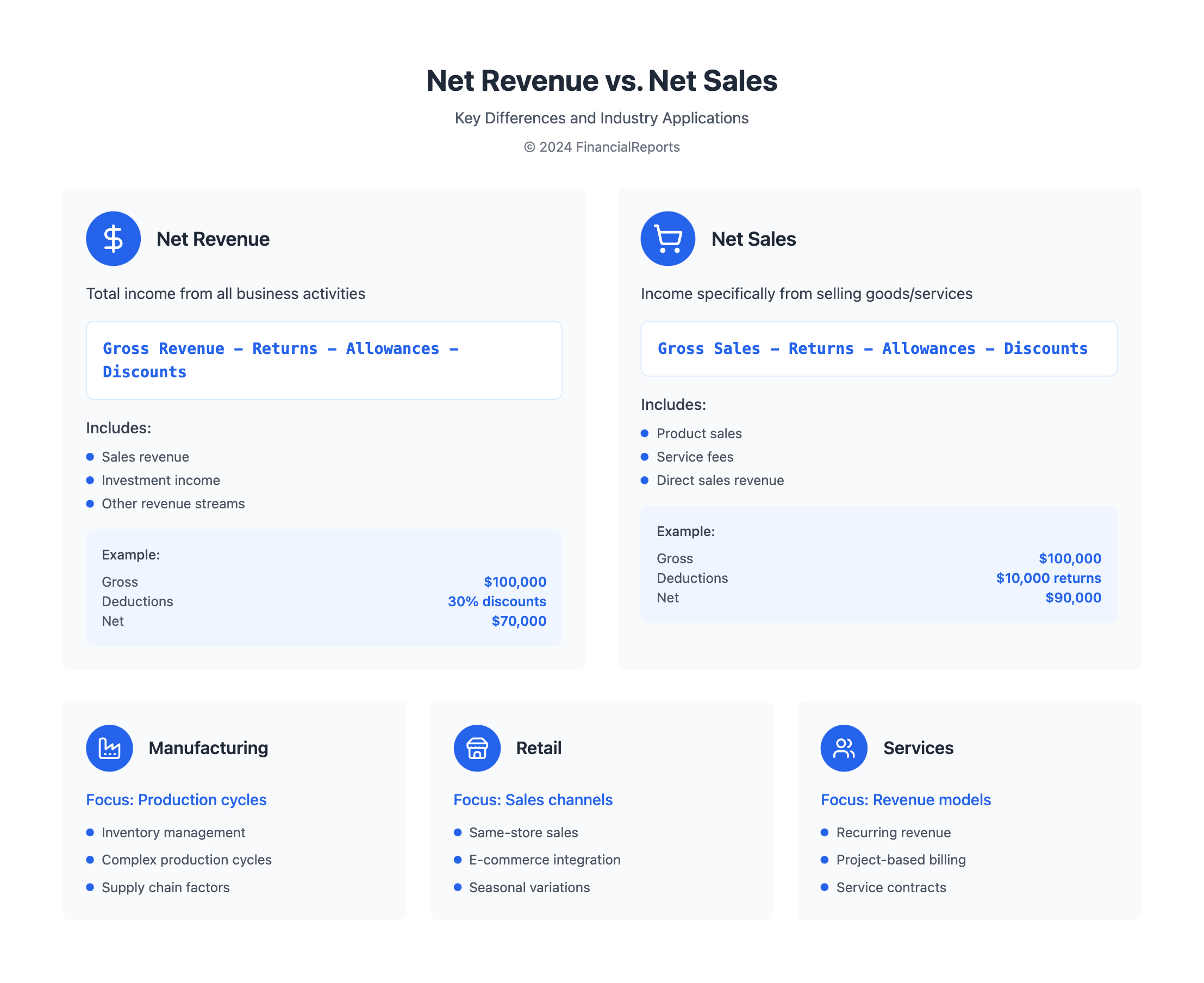
Net revenue and net sales are key terms in business finance. Net revenue, also known as net sales, is the money a company makes after removing non-operating costs. This includes discounts and customer returns. To find net revenue, companies subtract returns, allowances, and discounts from their total sales.
For instance, a shoe store with $100,000 in sales and a 30% discount would have $70,000 in net revenue. This figure is vital for understanding a company's financial health and making smart business choices. Net sales is found by subtracting returns, allowances, and discounts from the total sales.
Definitions of Net Revenue
Net revenue is the income a company gets from selling goods and services, minus transactional costs. It shows how much cash is left for reinvestment or other financial choices.
Definitions of Net Sales
Net sales is the total sales minus the costs of products sold and operational expenses. Changes in net sales affect a company's gross profit and margin. Companies might not share net sales details because of its complex calculation.
| Concept | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Net Revenue | Total income minus transactional expenses | $100,000 sales - 30% discount = $70,000 net revenue |
| Net Sales | Total sales minus returns, allowances, and discounts | $100,000 sales - $10,000 returns = $90,000 net sales |
It's important for financial experts, investors, and clients to grasp net revenue and net sales. By understanding these, companies can make better decisions and grow their business.
Key Differences Between Net Revenue and Net Sales
Understanding the difference between net revenue and net sales is key in financial reporting. These terms are often mixed up, but they are not the same. They have different ways of being calculated and used in reports.
Net revenue shows a company's total income. Net sales, on the other hand, only show a part of that income. For example, a company with $1,000,000 in gross sales might have different figures for net sales and net revenue. This is because of deductions and other income sources.
Calculation Methods
How you calculate net revenue and net sales is different. Net sales are found by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from gross sales. Net revenue is found by subtracting operational expenses or COGS from gross revenue.
Context and Usage in Financial Reporting
In financial reports, net revenue and net sales help check a company's health. Net revenue shows how profitable a company is. Net sales show how well a company sells and grows. Knowing the difference helps businesses make better choices and improve their finances.
| Concept | Calculation Method | Usage in Financial Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Net Revenue | Gross Revenue - Operational Expenses | Evaluate profitability |
| Net Sales | Gross Sales - Cost of Goods Sold | Evaluate sales generation capacity and growth |
Importance of Net Revenue in Business Analysis
Net revenue is key in business analysis, giving a full picture of a company's finances. It's important to know that is net revenue the same as net sales is a common question. But they are not the same. Net revenue includes income from all sources, helping businesses track profits over time.
Financial ratios like net profit margin and revenue growth rate use net revenue. These ratios compare net revenue to total revenue and past periods. For instance, a high net profit margin shows a company is running well and pricing things right.
Assessing Company Performance
Net revenue is essential for checking a company's financial health and growth. It helps investors and analysts see if a company can make profits. By looking at net revenue, businesses can find ways to get better and make more money.
Financial Ratios that Utilize Net Revenue
Some important financial ratios that use net revenue include:
- Net profit margin
- Revenue growth rate
- Return on sales (ROS)
These ratios give valuable insights into a company's financial health. They help investors and analysts make smart choices.
Importance of Net Sales in Business Analysis
Net sales are key to understanding a business's sales success. They show how well a company's products or services sell. Net sales are more accurate than gross sales because they don't include returns, allowances, or discounts.
To find net sales, you subtract returns, allowances, and discounts from gross sales. This helps businesses see how well they make money from sales. It also helps them check if their sales plans work well.
Improving net sales means making more money from sales. Companies can do this by selling more products, upselling, and setting the right prices. By looking at net sales and other numbers, businesses can make their sales better.
Here are some reasons why net sales matter:
- They give a true picture of a company's success and profit
- They help see if sales efforts are working and guide inventory choices
- They are key for understanding how well SaaS companies keep customers
| Metric | Definition | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Sales | Total sales not adjusted for discounts, allowances, or returns | Provides a general idea of a company's sales performance |
| Net Sales | Total revenue generated by a company, excluding sales returns, allowances, and discounts | Offers a more accurate picture of a company's core business performance |
How Businesses Calculate Net Revenue
Understanding a company's financial health starts with net revenue. It's found by subtracting returns, allowances, and discounts from the total revenue. The formula is simple: Net Revenue = Gross Revenue - Returns - Allowances - Discounts. This shows a company's true earnings after all deductions.
Many things can change net revenue. Pricing, market trends, and how well a company runs are key. For example, discounts can boost sales but cut into earnings. Returns and allowances also play a role, reducing what a company makes.
Factors Influencing Net Revenue
- Pricing strategies: Companies may adjust their pricing to stay competitive, which can impact net revenue.
- Market conditions: Economic downturns or upswings can influence consumer spending habits, affecting net revenue.
- Operational efficiency: Streamlining operations can help reduce costs and increase net revenue.
When looking at net sales and net revenue, it's important to know the difference. Net sales don't include the cost of goods sold (COGS). But net revenue gives a fuller view of a company's financial health. By comparing both, businesses can see how sales are doing, manage discounts, and find ways to improve.
How Businesses Calculate Net Sales
Net sales revenue is found by adding all sales income and then subtracting costs like returns and discounts. This step is key to grasp the sales and revenue difference and make smart business choices. The formula, as explained by net sales calculations, is: Total sales income minus transaction costs equals Net sales revenue.
The sales and revenue difference greatly affects a company's financial health. To figure out net sales, businesses must look at several deductions. For example, a retail store might see high sales during holidays but also more returns, which can lower its net sales.
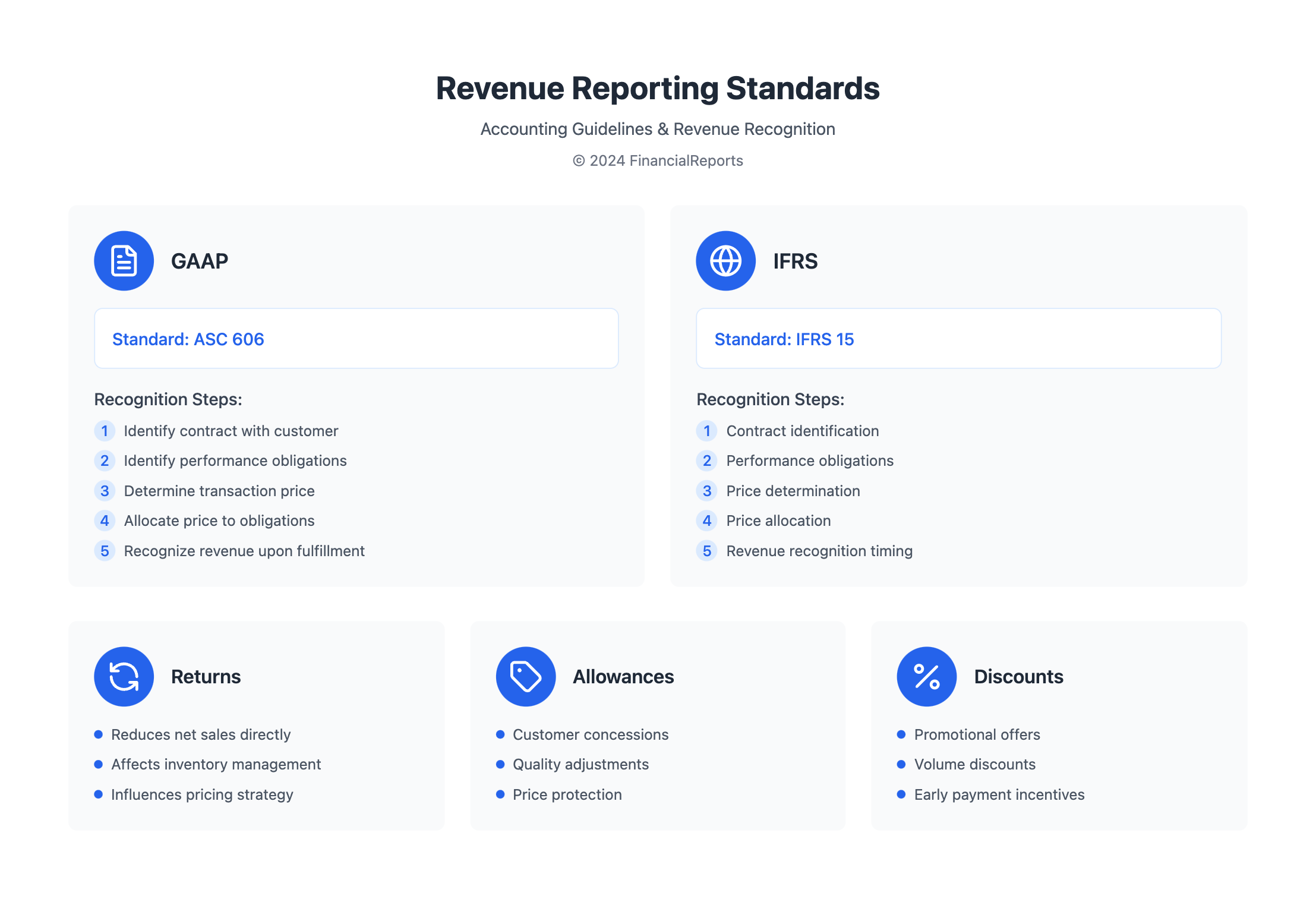
Deductions Impacting Net Sales
- Returns: Customers returning products can significantly reduce net sales revenue.
- Allowances: Discounts or concessions given to customers can also impact net sales.
- Discounts: Promotional discounts or loyalty rewards can affect net sales revenue.
Knowing these deductions and their effect on net sales helps businesses manage their sales and revenue difference better. This way, they can make informed decisions to boost growth and profits.
Industry Variations in Revenue and Sales Measurement
Looking at the difference between gross sales and revenue, we see how different industries measure these. The manufacturing sector, for example, faces complex production cycles and inventory. This affects how they recognize revenue.
In retail, same-store sales are key to measuring revenue. The growth of e-commerce has changed how sales are reported. Now, online sales are a bigger part of total revenue. The service sector, on the other hand, focuses on recurring revenue and project-based billing. This changes how they calculate sales and revenue.
Key Industry Variations
- Manufacturing: Complex production cycles and inventory management
- Retail: Same-store sales, online sales, and brick-and-mortar sales
- Service: Recurring revenue models and project-based billing
It's important for investors and financial experts to understand these differences. This helps them evaluate a company's performance better. By knowing the differences between gross sales and revenue, businesses can understand their operations better. This knowledge helps them make strategic decisions to grow and be more profitable.
Common Misconceptions About Net Revenue and Net Sales
When looking at financial statements, it's key to know the difference between net revenue and net sales. Many companies mix these terms up, but they're not the same. Sales are part of revenue, but not all revenue comes from sales. This mix-up can lead to mistakes in financial analysis and decision-making.
The question of is net revenue the same as net sales is often asked, and the answer is no. Net revenue includes all a business's income, like sales, investments, and more. Net sales, on the other hand, only includes income from selling goods or services.
Misinterpretations in Financial Statements
Not understanding net revenue and net sales can cause big problems. For example, if a company shows high net sales but low net revenue, it might mean they're not making enough money. Or, if they show high net revenue but low net sales, it could mean they're making money from other sources, like investments.
Some important things to think about when looking at net revenue and net sales include:
- Revenue recognition: How and when revenue is recorded can greatly affect financial statements.
- Cost of goods sold: The cost of making and selling goods can cut into profit margins and affect net revenue.
- Non-sales revenue: Income from sources other than sales, like investments or partnerships, can add to net revenue.
Clarifying Industry Jargon
To avoid confusion, it's important to understand industry terms. For example, top-line growth means an increase in net sales. Gross profit is the difference between net sales and the cost of goods sold. Operating revenue is the income from a company's main operations, not including non-operating income.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Net Revenue | Total income generated by a business, including sales, investments, and other revenue streams. |
| Net Sales | Revenue generated from the sale of goods or services. |
| Gross Profit | Difference between net sales and the cost of goods sold. |
By knowing the difference between net revenue and net sales, businesses can make better decisions. They can avoid common mistakes that can affect financial analysis and performance.
Real-World Applications: Case Studies
Knowing about net revenue and net sales is key for businesses to make smart choices. Let's look at two examples: a software company and a big retail store. These show how net revenue and net sales work in different fields.
In the software world, a company's net revenue changes based on how it recognizes revenue. For example, a SaaS model brings in ongoing subscription fees, unlike one-time fees. Looking at the company's financials, we see how these differences affect its numbers.
Case Study: A Retail Giant
A big retail store has its own set of challenges when figuring out net sales. Things like seasonal sales, return policies, and selling through many channels can all play a part. By checking the company's financials, we can spot trends and areas to get better. For instance, starting customer loyalty programs can bring in more repeat business and higher sales.
Some ways to boost net sales include:
- Starting customer loyalty programs
- Customizing seasonal promotions
- Managing inventory better and making the supply chain smoother
- Using AI and machine learning for sales insights
These methods can help businesses grow and increase their net revenue. By grasping the ideas of net revenue and net sales, companies can make better choices and stay competitive.
The Role of Accounting Standards in Revenue Reporting
Accounting standards are key in revenue reporting. They give companies a clear guide on when and how to report revenue. The main standards are Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Knowing the sales and revenue difference is vital for understanding net income variations.
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) have set guidelines. For instance, ASC 606 offers a single approach for revenue from contracts with customers. It requires a five-step process to recognize revenue, including identifying the contract and performance obligations, determining consideration, allocating consideration to obligations, and recognizing revenue upon fulfilling obligations.
| Accounting Standard | Revenue Recognition Guideline |
|---|---|
| GAAP | ASC 606 |
| IFRS | IFRS 15 |
In conclusion, knowing how accounting standards guide revenue reporting is critical. By adhering to GAAP and IFRS guidelines, companies can ensure their revenue reporting is clear and consistent. This helps reduce the sales and revenue difference and gives a clearer financial performance picture.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways on Net Revenue and Net Sales
When looking at a company's financial data, it's key to understand the context. You need to know the difference between gross sales, net sales, and net revenue. Gross sales are the total income from selling things. Net sales and net revenue take into account deductions like returns and discounts.
It's important to know how these numbers differ to really get a picture of a company's health. Financial experts should keep in mind the specific practices and rules of each industry. Tools like Salesforce's Revenue Intelligence can offer real-time data to guide sales teams.
The world of business is changing fast, with digital shifts and global markets. Knowing the difference between gross sales and revenue is more critical than ever. Keeping accurate records and staying current with new reporting rules helps companies share their financial health clearly with investors and others.
FAQ
What is the difference between net revenue and net sales?
Net revenue and net sales are related but different. Net revenue is a company's total income from all sources. Net sales, on the other hand, only include income from selling goods or services.
How are net revenue and net sales calculated?
To find net revenue, you subtract total transactional expenses from total revenue. For net sales, you start with gross sales. Then, you subtract returns, allowances, and discounts.
Why are net revenue and net sales important for business analysis?
Net revenue gives a full picture of a company's financial health, including all income sources. Net sales are key for managing sales, forecasting, and checking a company's main activities.
How do different industries approach the measurement of revenue and sales?
Industries like manufacturing, retail, and services have unique challenges. Inventory management, recurring revenue, and selling through multiple channels affect how they calculate net revenue and net sales.
What are some common misconceptions about net revenue and net sales?
Many think net revenue and net sales are the same. But they have different meanings and uses in financial reports and analysis.
How do accounting standards like GAAP and IFRS affect the reporting of net revenue and net sales?
GAAP and IFRS have different rules for when and how to report revenue and sales. This can change how net revenue and net sales look on financial statements, affecting analysis and comparisons between countries.