Market to Book Ratio Formula Explained
The market to book ratio formula is a way to check if a company's stock price is fair. It compares the current market value to the book value. This is done by dividing the market capitalization by the book value of equity.
This ratio is important for investors. It helps them see if a company's stock is too expensive or not. The market value is the current price of all shares. The book value is what's left if the company sold everything and paid off debts.
This formula is key for certain businesses. It's used for insurance, financial, real estate, and investment trusts. It shows how much a company's assets are worth compared to its stock price.
Key Takeaways
- The market to book ratio formula is used to evaluate a company's market value relative to its book value.
- The ratio is calculated by dividing the market capitalization by the book value of equity or the share price by the book value per share.
- The market to book ratio helps determine whether a company's stock is overvalued or undervalued.
- The ratio is essential for insurance and financial companies, real estate companies, and investment trusts.
- A low market to book ratio may indicate undervaluation, while a high ratio may indicate overvaluation.
- The market to book ratio formula is a key metric in financial analysis, providing insights into a company's asset value and market price.
- The market to book ratio is used to compare a company's market value to its book value, helping investors make informed decisions.

What is the Market to Book Ratio?
The market to book ratio is a way to check how much a company is worth compared to its book value. It's found by dividing the current stock price by the book value per share. Knowing how to calculate this ratio is key for investors to make smart choices.
Definition of Market to Book Ratio
The market to book ratio compares a company's market value to its book value. The market value is found by multiplying the current share price by the number of shares. The book value is the total of all business assets minus total liabilities.
Importance in Financial Analysis
This ratio is vital in financial analysis. It shows if a company's stock is overvalued or undervalued. A ratio close to 1 is perfect. A ratio under 1 means the stock is cheap, and a ratio over 3 might mean it's too expensive.
But, this ratio might not always show a company's true worth. This is because it doesn't account for things like intangible assets or future earnings growth.
Some important things to remember about the market to book ratio include:
- A price-to-book (P/B) ratio measures a company's market value relative to its book value.
- P/B ratios under 1.0 are typically considered solid investments by value investors.
- A high P/B ratio suggests a stock might be overvalued, while a lower P/B ratio could indicate undervaluation.
Components of the Market to Book Ratio
The market to book ratio is a way to value a company. It compares the company's market value to its book value. To figure this out, we look at two main parts: the market value of equity and the book value of equity.
The market value of equity is found by multiplying the number of shares by the current price per share. This shows the company's total market worth.
The book value of equity is found by subtracting liabilities from assets on the balance sheet. It shows what's left for shareholders if the company were to be sold off.
The market to book ratio formula is used to compare these two values. It divides the market value by the book value. This ratio helps us see if a company is fairly valued or not.
Some important things to remember about the market to book ratio are:
- It works best when comparing companies in the same industry.
- A low ratio might mean the stock is cheap, while a high ratio might mean it's overpriced.
- Things like return on equity and cost of equity can affect the ratio.
By understanding the market to book ratio and how to use the market to book ratio formula, investors can make better choices. This ratio is a helpful tool for checking a company's value and finding good investment opportunities.
How to Calculate the Market to Book Ratio
To find the market to book ratio, you need to know the formula. It's Market Capitalization / Net Book Value or Share Price / Net Book Value per Share. The Net Book Value is what you get by subtracting Total Liabilities from Total Assets.
Breaking it down into steps makes it easier. First, find the company's market capitalization, which is the total value of all shares. Then, find the net book value by subtracting total liabilities from total assets.
Step-by-Step Calculation Guide
Here's how to calculate the market to book ratio:
- Determine the market capitalization of the company.
- Calculate the net book value by subtracting total liabilities from total assets.
- Divide the market capitalization by the net book value to get the market to book ratio.
For instance, if a company's market capitalization is $1 billion and its book value is $800 million, the ratio is 1.25. This ratio helps figure out if a company's stock is cheap or expensive.
| Company | Market Capitalization | Book Value | Market to Book Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
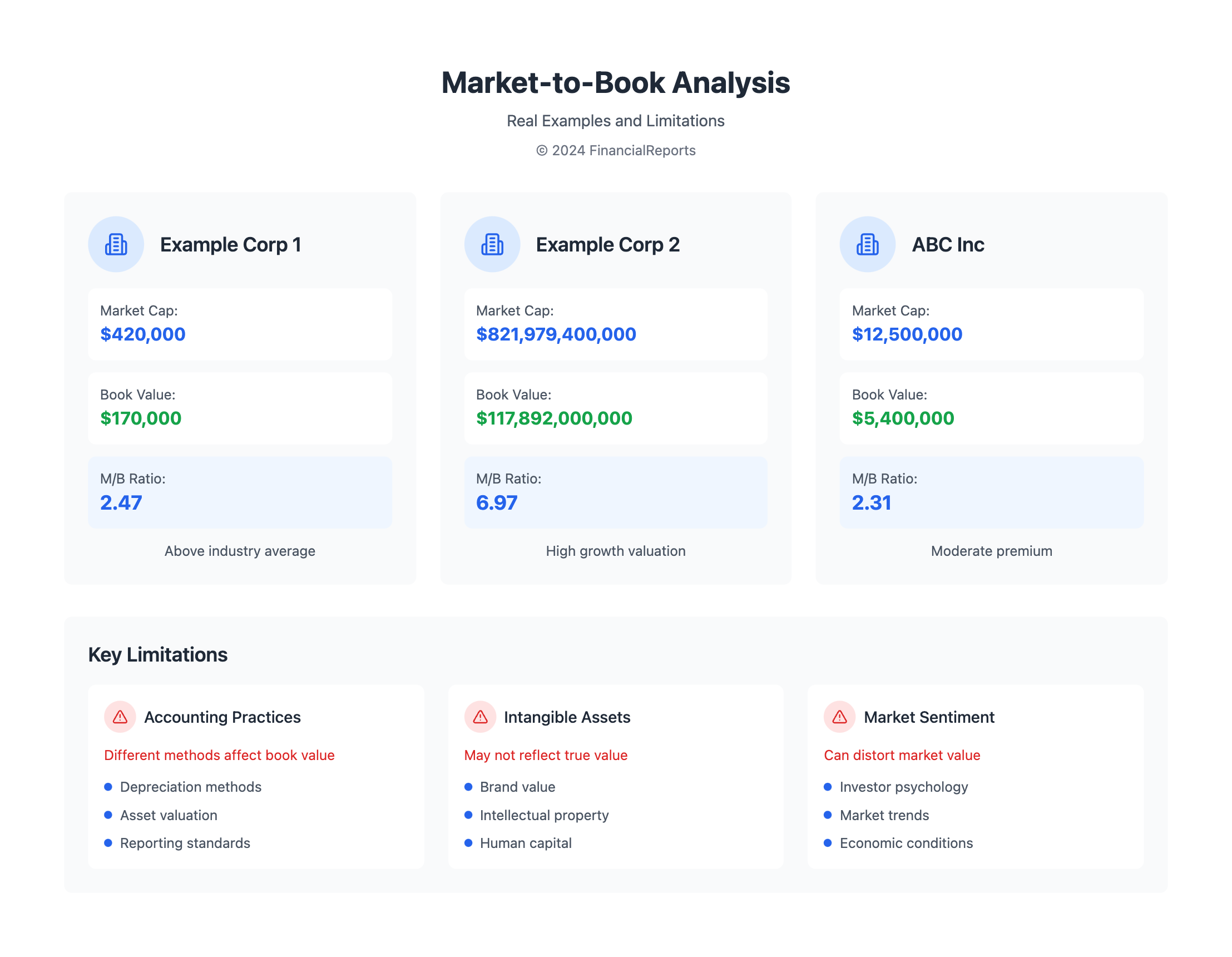
| Example 1 | $420,000 | $170,000 | 2.47 |
| Example 2 | $821,979,400,000 | $117,892,000,000 | 6.97 |
By following these steps and using the formula, you can find the market to book ratio for any company. This helps you make better investment choices.
Interpreting the Market to Book Ratio
The market to book ratio compares a company's market value to its book value. To understand this ratio, knowing the formula is key. It's the current stock price divided by the total book value. A ratio of 1 means market and book values are equal. A ratio below 1 might show the company is undervalued or facing issues.
A high ratio could mean the stock is overvalued. Investors might pay more than the company's assets are worth. A low ratio suggests the stock is undervalued. The company's assets might be worth more than its current market value. This ratio is best for comparing companies in the same industry to find undervalued investments.
When looking at the market to book ratio, keep these points in mind:
- Industry comparisons: The ratio varies by industry. It's important to compare within the same sector.
- Book value: The book value is found by subtracting liabilities from assets. It might not show the company's true worth.
- Market value: The market value is what investors think the company is worth. It's found by multiplying shares by the current market price.
Understanding the market to book ratio helps investors make better choices. It's important to look at industry comparisons and the company's financial health. This gives a full picture of the company's value.
Factors Influencing Market to Book Ratio
The market to book ratio is shaped by many things, like how well a company does and what's happening in the market. To figure out this ratio, it's key to look at these factors. Things like how profitable a company is, its growth, and its return on equity matter a lot.
What investors think, trends in the industry, and big economic changes also affect the ratio. For example, a company with a high book value but low market value might have a high ratio. This could mean its stock is cheap. But, a company with a low book value but high market value might have a low ratio. This could mean its stock is overpriced.
Some important things that affect the market to book ratio include:
- Company size and industry
- Financial performance and growth prospects
- Market sentiment and investor expectations
- Macroeconomic conditions and industry trends
To find the market to book ratio, investors use a simple formula: market value of equity / book value of equity. This ratio tells us a lot about a company's value and its growth chances. By knowing what affects the ratio and how to calculate it, investors can spot good deals or overpriced stocks.
| Company | Market Value | Book Value | Market to Book Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | $100 million | $50 million | 2 |
| Company B | $50 million | $100 million | 0.5 |
Applications of Market to Book Ratio
The market to book ratio is a key tool for investors and companies. It shows a company's value and growth chances. The formula for this ratio is simple: it's a company's market value divided by its book value. This helps investors spot undervalued companies and make smart choices.
Here are some main uses of the market to book ratio:
- Identifying undervalued companies: A low ratio means a company might be cheap, a good buy.
- Assessing growth: A high ratio suggests a company could grow a lot, making it more appealing.
- Comparing companies: This ratio helps see how different companies in the same field are valued. It shows who might be over or underpriced.
The market to book ratio is vital for investors and companies. It gives a quick look at a company's worth and growth prospects. By using the ratio formula and understanding its uses, investors can make better choices. Companies can also see how the market sees them and plan their finances and stock sales.
| Company | Market Capitalization | Book Value | Market to Book Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| XYZ Corp | $100 million | $75 million | 1.33 |
Limitations of the Market to Book Ratio
The market to book ratio is a useful tool for investors. Yet, it has its downsides. One big issue is how accounting practices can change the book value of equity. Different companies and industries use different accounting methods, which can skew the ratio.
Another problem is how market sentiment can influence the market value. Quick changes in stock prices can make the ratio seem off. To get a true picture, it's key to know how to calculate the market to book ratio and keep these issues in mind. This ratio can help spot undervalued stocks, but it should be paired with other metrics.
Some important things to think about when using the market to book ratio include:
- Accounting practices: Different companies and industries may use varying accounting practices, which can affect the book value.
- Market sentiment: Short-term fluctuations in stock prices can lead to misleading ratio values.
- Intangible assets: The market to book ratio may not accurately capture the value of intangible assets, such as intellectual capital.
By grasping these limitations and how to calculate the market to book ratio, investors can see its value. They can use it as part of their investment strategy, alongside other metrics and specific company factors.
| Company | Market Capitalization | Book Value | Market to Book Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC | $12,500,000 | $5,400,000 | 2.31 |
Case Studies of Market to Book Ratio Usage
The market to book ratio is a key tool for investors and financial analysts. It compares a company's market value to its book value. A high ratio means the market values the company's assets more than their book value.
For example, a company with a market value of $13.17 and a book value per share of $10.50 has a ratio of 1.25. This ratio helps spot undervalued or overvalued companies. Value investors look for low ratios, seeing these companies as undervalued.
Here are some key points to consider when using the market to book ratio:
- It is a useful tool for comparing a company's market value to its book value.
- A high market to book ratio may indicate that the market values the company's assets more than their book value.
- A low market to book ratio may indicate that the company is undervalued compared to its book value.
The market to book ratio formula is simple. It divides the market value per share by the book value per share. This formula helps find the implied cost of capital from a company's value and cash flow. For instance, ABC Inc. has a book value per share of $20 and a market value of $30. This gives a ratio of 1.5, showing investors are willing to pay more for the company's assets than their book value.
| Company | Market Value | Book Value per Share | Market to Book Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Inc. | $30 | $20 | 1.5 |
| XYZ Corp. | $15 | $10 | 1.5 |
In conclusion, the market to book ratio is a valuable tool for investors and financial analysts. It helps compare a company's market value to its book value. This comparison can reveal undervalued or overvalued companies. By using the ratio formula and considering market and book values, investors can make better decisions.
Conclusion: The Relevance of Market to Book Ratio
The market to book ratio is a key tool for financial experts and investors. It compares a company's market value to its book value. This ratio shows a company's true worth and growth chances.
A higher ratio means the market sees the company as cheap. A lower ratio might show worries about its future.
Summary of Key Points
In this article, we explored how to calculate and understand the market to book ratio. It helps in making smart investment choices, checking company performance, and finding good deals. We also talked about its limits, like how market feelings and accounting rules affect it.
This highlights the need to look at it as part of a bigger financial picture.
Future Considerations in Financial Analysis
The business world is changing fast, with more focus on intangible assets and digital shifts. The market to book ratio might change too. Financial analysts need to keep up, finding new ways to value companies.
By staying ahead, they can keep the market to book ratio useful. This helps in making better investment and business choices.
FAQ
What is the market to book ratio?
The market to book ratio compares a company's market value to its book value. It shows if a stock is cheap or expensive. This ratio is key for investors to make smart choices.
How is the market to book ratio calculated?
To find the market to book ratio, you divide a company's market capitalization by its book value of equity. This gives you a clear view of the stock's value.
What are the components of the market to book ratio?
The ratio has two main parts: market value of equity and book value of equity. The market value is what the shares are worth today. The book value is what shareholders would get if the company were to close down.
How can the market to book ratio be used in investment decisions?
Investors use this ratio to spot undervalued stocks. A ratio below 1 means the stock might be cheaper than its book value. But, it's best to look at other metrics and the company's overall health too.
What factors influence the market to book ratio?
Many things affect the ratio, like a company's financial health and growth chances. Industry trends and the overall market also play a role. These factors can change the ratio's value.
What are the limitations of the market to book ratio?
The ratio has its downsides. Accounting practices can skew the book value. Market mood can change the market value. It also doesn't account for a company's intangible assets. These should be considered when analyzing the ratio.