Margin vs Gross Margin: Key Financial Insights
Gross margin and gross profit are key to seeing how well a company does financially. They show how good a company is at managing costs. Gross profit is what's left after subtracting the cost of goods sold from revenue. Gross margin is the percentage of revenue that is the gross profit.
Knowing the difference between margin and gross margin is vital. It helps investors and analysts see how well a company is doing. High gross margins often mean a company is doing well financially.
Introduction to Financial Metrics
Gross margin is found by subtracting the cost of goods sold from revenue. It's a key way to check a company's health. By understanding gross margin and profit, companies can make better choices about pricing and production.
Key Takeaways
- Gross margin and gross profit are key financial metrics that provide insight into a company's profitability and cost management, highlighting the importance of margin vs gross margin.
- Gross margin is calculated by deducting COGS from revenue, dividing the result by revenue, and multiplying by 100 to find a percentage, and is often compared to gross profit.
- Companies with high gross margins tend to have better financial performance, with a 1% increase in gross margin resulting in a 12% increase in earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT), demonstrating the significance of gross margin vs gross profit.
- Gross margin varies widely between industries, with companies in the software industry typically having higher gross margins than those in the retail industry, and is a key factor in comparing margin vs gross margin.
- A high gross profit and margin are considered positive indicators of a company's financial health, but other factors such as operating expenses, taxes, and interest payments must be considered, and are essential in understanding gross margin and gross profit.
- Gross margin provides insight into a company's profitability as a percentage of its revenue, with a higher gross margin indicating a company can profit more from each sales dollar, and is a critical metric in analyzing margin vs gross margin.
- Understanding the difference between gross margin and gross profit is essential for making informed decisions about pricing, production, and marketing strategies, and is vital in comparing gross margin vs gross profit.

Understanding Financial Margins in Business
Financial margins are key in business, showing how profitable and efficient a company is. It's important to know the difference between gross and net margin. Gross margin includes only revenue and direct costs. Net margin includes all costs, like operating expenses and taxes.
Definition of Margin
A margin shows how much profit a company makes, found by subtracting costs from revenue. Knowing the difference between net and gross margin is key. It helps businesses find areas to improve and set better prices.
Importance of Margins in Financial Analysis
Gross and net margin are essential in financial analysis. They help investors, analysts, and managers see a company's health. By looking at gross and net margin, businesses can spot trends and compare with competitors.
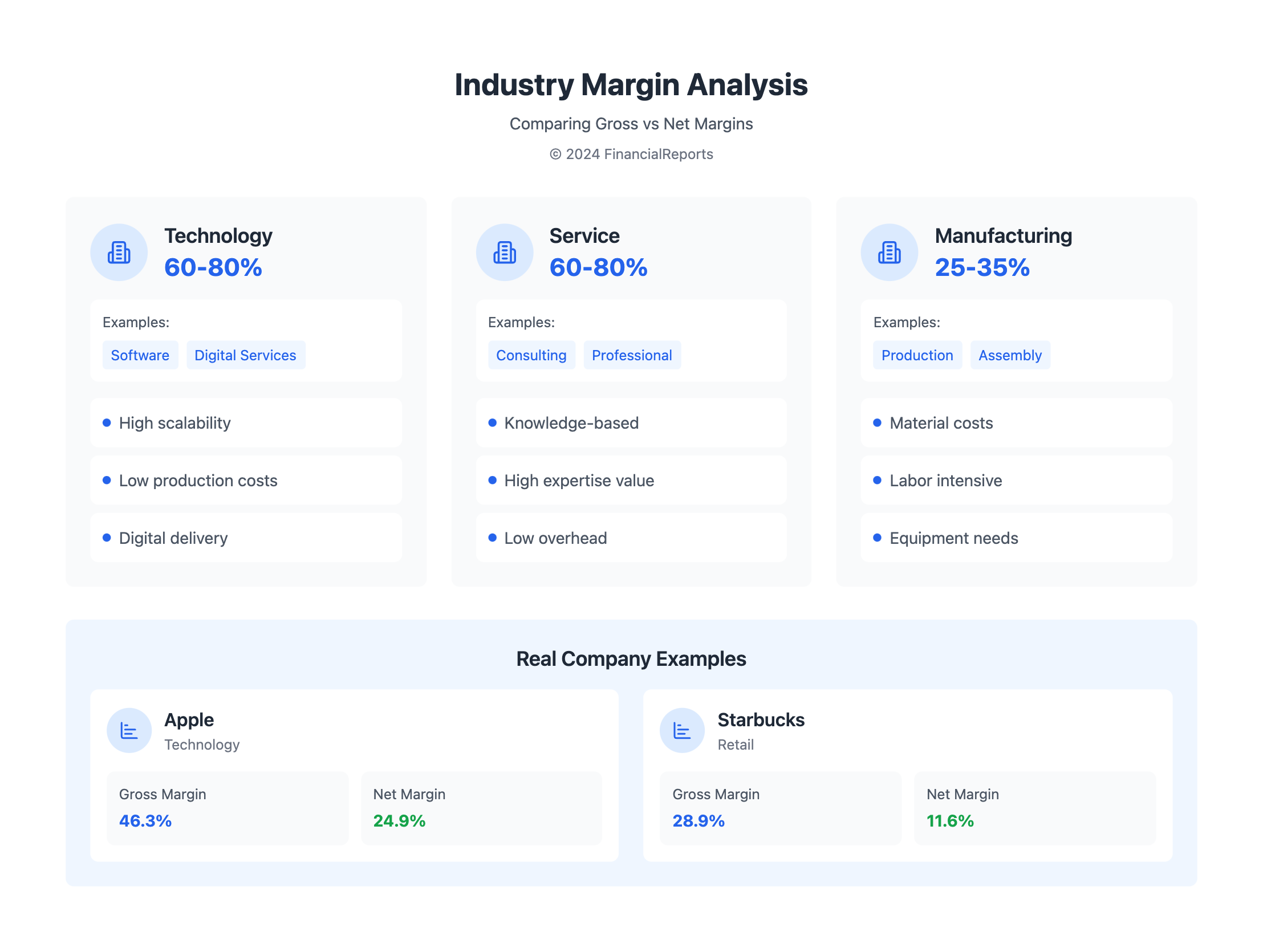
For example, Apple Inc. can look at its gross profit margin, 38% for the quarter ending June 27, 2020. It can also see its net profit margin, 18.9% for the same quarter. This helps Apple evaluate its performance and plan for growth.
Difference between Margin and Gross Margin
Understanding the difference between margin and gross margin is key when looking at a company's finances. The net vs gross profit margin shows how businesses see their profits. Gross margin vs profit margin shows how sales and costs are related.
Gross margin is easy to figure out. It's the revenue minus the cost of goods sold, divided by revenue, then multiplied by 100. For example, with $250 billion in sales and $145 billion in costs, the gross profit is $105 billion. This gives a 42% gross margin. This number is important because it shows how much money is left for other expenses and profits.
Key Variations Between the Two
The main difference is in how they're calculated. Margin vs profit looks at all expenses, like operating costs and taxes. Gross margin only looks at the cost of goods sold. This difference is important for pricing and efficiency.
Insights from Financial Statements
Financial statements give us clues about a company's gross margin and profits. By looking at the income statement, we can see how well a company can keep prices up and control costs. A good gross profit margin is usually over 50%, but it depends on the industry. Companies can boost their margin by raising prices, getting better deals from suppliers, and being more efficient.
Calculating Margin: A Step-by-Step Guide
To find the margin, it's key to know the difference between profit vs gross margin and product margin vs gross margin. The formula for margin is simple: subtract the cost of goods sold from the total revenue. For example, if a company makes $500,000 and spends $250,000 on goods, they make $250,000 in profit. This is a key step in figuring out the gross profit vs profit margin.
Calculating margin is important for businesses to check their financial health. By looking at the profit vs gross margin, companies can spot where to get better and make smart choices. Here are some important things to remember when calculating margin:
- Gross profit margin formula: GPM = (Net sales - COGS) / Net sales × 100
- Operating profit margin formula: OPM = Operating Income / Revenue × 100
- Net profit margin formula: NPM = (Net income or (R - CGS - OPE - OTE - I - T) / R) × 100
By getting how to calculate margin and why it matters, businesses can tweak their pricing and boost their finances. The gross profit vs profit margin check is a great way for companies to see how profitable they are and make choices based on facts.
| Company | Gross Profit Margin | Operating Profit Margin | Net Profit Margin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starbucks | 28.9% | 14.1% | 11.6% |
Calculating Gross Margin: Detailed Metrics
To figure out gross margin, we must know the difference between profit and profit margin. Gross margin is a percentage that shows how much money is left after subtracting the cost of goods sold. For example, a 25% gross margin means a business keeps 25 cents for every dollar it makes.
The formula to calculate gross margin is: [(total revenue - cost of goods sold) / total revenue] x 100 = gross margin. Let's say a jewelry business makes $32,000 and spends $14,000 on production. Their gross margin would be 56%. This shows why it's key to know the difference between gross margin and net margin. Net margin includes all costs, like operating expenses and taxes.
Gross Margin Formula Explained
The gross margin formula is vital for businesses to check their profit levels. It answers the question: is gross margin the same as gross profit? While they're related, they're not the same. Gross profit is the actual amount, while gross margin is a percentage. This formula gives a clear view of a company's financial health and points out areas for betterment.
Example of Gross Margin Calculation
Consider this: a company makes $1,000 and spends $700 on goods. Their gross profit is $300, and their gross margin is 30%. This example helps businesses see how profit and profit margin differ. It guides them in setting prices and managing costs.
| Revenue | Cost of Goods Sold | Gross Profit | Gross Margin |
|---|---|---|---|
| $1,000 | $700 | $300 | 30% |
In conclusion, calculating gross margin is key for businesses to check their financial health. By grasping the gross margin formula, companies can tweak their strategies to boost profits and stay ahead in their field.
Significance of Margin in Business Operations
Knowing the difference between gross profit and gross margin is key for businesses. It helps them decide on pricing and how profitable they can be. A McKinsey & Company report shows gross margin is vital for most industries' profits.
The gap between gross profit margin and profit margin is important too. It shows how operating costs affect a company's earnings. By looking at these numbers, businesses can find ways to cut costs and boost profits. For instance, tech companies with a 60% gross margin often have higher profit margins.
When checking margin in business, consider these points:
- Gross margin calculation: subtract production and distribution costs from total revenue, then divide by total revenue
- Operating margin calculation: subtract all overhead and operational expenses from revenues to show profit before taxes and interest
- Comparing gross margin and operating margin to see a company's profit and efficiency
Understanding margin's role in business helps companies make smart choices. They can tweak pricing, cut costs, and grow profits. This gives them an edge in their markets.
Importance of Gross Margin in Financial Health
Gross margin is key to a company's financial health. It shows the profit made after selling goods minus the cost of those goods. The difference between gross profit margin and net profit margin is big. Gross profit margin looks only at the cost of goods sold. Net profit margin includes all costs, like operating expenses, interest, and taxes.
Knowing the difference between gross and net profit margin helps investors and analysts see how profitable a company is.
A Deloitte report shows that retailers with a gross margin of 40% or more do better financially. Those with higher gross margins see bigger increases in earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). This shows how important gross profit vs gross profit margin is for business growth and profit.
| Company | Gross Margin | Net Profit Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Apple | 46.3% | 24.9% |
In conclusion, gross margin is a vital metric for checking a company's financial health. Understanding the difference between gross profit margin and net profit margin is key for smart investment choices.
How to Improve Margin Performance
Improving margin performance is key for businesses to stay ahead and grow. It's important to understand the difference between gross profit and gross profit margin. Knowing these concepts helps spot areas for betterment. For example, getting better deals from suppliers can greatly boost a business's profit margin.
Cost Reduction Strategies
There are several ways to cut costs and boost margins. Here are a few:
- Optimizing production to cut waste and boost efficiency
- Renegotiating with suppliers for better prices
- Using lean management to make operations smoother
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Boosting operational efficiency is also vital. This can be done by:
- Buying new equipment and automation to increase output without high costs
- Reviewing labor schedules to ensure they're just right
- Adopting industry best practices to cut waste and boost productivity
By using these strategies, businesses can see their margins improve. This leads to more revenue and keeps them competitive.
Improving Gross Margin: Best Practices
To boost gross margin, companies need to cut down on production costs and set smart prices. They can do this by lowering labor costs, finding cheaper suppliers, and making production more efficient. For example, using lean manufacturing can make production better and raise gross margins in the manufacturing field.
It's also important to know the difference between standard margin vs gross margin. And, is profit margin the same as gross margin is a question many ask. Gross margin is (Net sales - COGS) / Net Sales x 100. Profit margin is (Net income / Net Sales) x 100. By working on gross margin, companies can grow their profits and stay competitive.
Some top ways to up gross margin include:
- Using price optimization to see what customers think is worth it
- Always looking for ways to cut down on overhead and operational costs
- Embracing lean principles to boost production efficiency
- Switching to subscription models for more stable income
By sticking to these best practices and understanding the role of gross margin, companies can do better financially and succeed in the long run.
| Industry | Average Gross Margin |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 25-35% |
| Technology | 60-80% |
| Service | 60-80% |
Common Mistakes in Margin Calculations
When figuring out margin vs gross margin, businesses often miss important details. They might not include indirect costs, which can mess up gross margin and gross profit numbers. For example, forgetting to add overheads like rent and utilities to the cost of goods sold can make the gross margin vs gross profit ratio look better than it really is.
To get it right, businesses need to use the correct sales figures and all relevant costs for gross margin calculations. Here are some important things to remember:
- Make sure to accurately identify and add indirect costs
- Use the latest and most accurate sales data
- Have strong systems for tracking costs and sales
By steering clear of these common errors, businesses can get their margin calculations right. This helps them make better choices about pricing, production, and investments. For instance, a company with $150,000 in annual sales and a gross margin of 33% can tweak their pricing to boost profits.
| Industry | Gross Margin Range |
|---|---|
| Remodeling Contractors | 34% to 42%+ |
| Specialty Contractors | 26% to 34%+ |
| New Home Builders | 21% to 25%+ |
Understanding the need for precise margin calculations and avoiding common pitfalls can help businesses. It lets them see how they're doing financially and make smart choices to grow and increase profits.
Leveraging Margin Analysis for Strategic Decisions
Companies use gross margin and gross profit for big decisions. They look at these numbers to figure out how to price things, make more, and market better. Knowing the difference between gross margin and net margin is key. It helps them set prices and manage costs.
When checking their place in the market, companies use gross and net margin analysis. They look at the gross margin, which shows how much profit they make on each sale. The formula is: Gross Margin = (Gross Profit / Revenue) x 100. This helps them see if they're getting better at making money and working efficiently.
Investment Decisions Based on Margin Insights
Margin analysis helps with big choices like new products or growing in new markets. For example, it can show how different customers cost to serve. This helps companies set prices and use resources wisely to make more money. Looking at net vs gross margin also shows how well a company is doing financially.
Assessing Market Position through Margins
Margin analysis helps companies see where they stand in the market. By looking at gross and net margin, they can check their pricing, costs, and how well they're doing. This info guides their big decisions, like investing in new products or markets. It helps them find ways to grow and get better.
Tools for Margin and Gross Margin Analysis
Understanding your financial performance is key for businesses. Tools like QuickBooks, Xero, and Zoho Books help with this. They offer features for profit margin analysis. These tools help track margins, including net vs gross profit margin, gross margin vs profit margin, and margin vs profit.
It's important to keep an eye on gross margin, operating margin, and net margin. You can calculate these using formulas like Gross Margin = (Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue × 100. This helps spot areas for improvement and fine-tune pricing and costs. For example, knowing which products have the highest gross margin can guide pricing or cost-cutting efforts.
Businesses can also use data visualization tools and financial modeling software to better understand their margins. These tools help spot trends and patterns for strategic planning. By using these tools, businesses can make more informed decisions to boost growth and profitability, improving their margin vs profit ratio.
Case Studies: Margin vs Gross Margin in Action
Looking at real-world examples shows how important it is to compare margin and gross margin. For instance, Microsoft is known for its high profit margins. Even with lower gross margins than some competitors, Microsoft keeps its net profit margins high. This is thanks to its smart management of costs.
On the other hand, Walmart has lower profit margins than Microsoft. But Walmart's huge size and efficient supply chain help it keep high gross margins. These margins are key to its overall success.
Sears is a lesson in what happens when margins aren't managed well. Sears saw its gross and net profit margins drop as it failed to keep up with changing times and online shopping. This shows why it's vital to watch both margins closely to stay profitable.
In the end, these examples highlight the significance of profit vs gross margin for a company's health and efficiency. By understanding the differences between these metrics, businesses can make better choices. This helps them boost product margin vs gross margin and grow in a sustainable way.
FAQ
What is the difference between margin and gross margin?
Margin is the difference between what a company earns and its costs. Gross margin looks at the difference between what's sold and the direct costs to make it.
Why are margins important in financial analysis?
Margins help investors and analysts see if a company is making money well. They show how profitable a company is and its financial health.
How do margin and gross margin differ in terms of their calculations and implications?
Margin is total revenue minus all costs. Gross margin is revenue minus just the direct costs of making what's sold. Gross margin gives a clearer picture of a company's core profit.
What is the step-by-step process for calculating margin?
To find margin, use this formula: Margin = (Revenue - Total Expenses) / Revenue. This means subtracting all costs from revenue to get the profit margin.
How is gross margin calculated, and what does it reveal about a company's financial performance?
Gross margin is found with this formula: Gross Margin = (Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue. It shows how much profit a company makes from selling what it produces, showing its efficiency and profit ability.
What is the significance of margin in a company's pricing strategy and overall profitability?
Margin is key in setting prices. It affects how much profit a company can make. Analyzing margin helps businesses set prices that are competitive yet profitable.
How can companies use gross margin analysis to assess their financial health compared to industry benchmarks?
By comparing their gross margin to the industry average, companies can see how they stack up. This helps spot areas for improvement and ensures they're competitive.
What are some common mistakes in margin calculations, and how can businesses avoid them?
Mistakes include forgetting indirect costs and using wrong sales data. To avoid these, track all costs and use reliable systems for sales data to get accurate margins.
How can businesses leverage margin analysis to inform strategic decision-making?
Margin insights help with decisions on investments, product development, and market expansion. They also show how a company compares to its competitors.
What tools and techniques are available for effective margin and gross margin analysis?
Financial software can make tracking margins easier. Advanced analytics, like predictive modeling, offer deeper insights and help forecast margins.