Income Statement Accounts List: A Complete Guide
Understanding an income statement accounts list is key to seeing your finances clearly. It is vital for those focusing on financial analysis and strategies. The income statement is a tool showing a company's financial success over time. It provides a clear view of how a company makes money and its spending patterns, leading to its net profit. This shows if the company is managed well and how it stacks up against others.
This guide explains all parts of the income statement accounts. It helps you add precision to your financial tools and confidently handle income and expenses. You'll learn the importance of each account, understand how they work together, and make smarter decisions.
Key Takeaways
- An income statement is crucial for showing a company's financial performance, detailing income, expenses, and net profit.
- Know the role and impact of different account types, including assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses.
- Companies can choose their income statement structure, picking between single-step or multi-step formats based on their needs.
- Income statements are essential for evaluating financial health, offering key data like revenue, OPEX, EBT, and EBITDA.
- Understanding specific terms such as COGS, Depreciation, and Amortization is crucial for deep knowledge of financial statements.
- Income statements require careful preparation to ensure they are accurate, consistent, and comply with regulations.
- Financial experts should use income statements for strategy, watching trends, comparing figures, and making informed choices.
Understanding the Income Statement Basics
An income statement is important for understanding a company's financial performance over time. It shows if a business is doing well financially by tracking all money made and spent. This gives a clear picture of the company's net earnings and how well it's managing its operations.
What Is an Income Statement?
The income statement is key in financial reports. It shows how a company's total sales turn into net profit, which impacts earnings per share (EPS). It lists all sales and subtracts costs like the cost of goods sold (COGS) and other expenses. This includes income account definition, which tells us if a business is profitable by looking at key numbers such as gross profit and net income.
Importance of Income Statements
Income statements are crucial for understanding a company's financial health. They offer insights that help people make smart decisions. These statements are updated regularly, providing a current look at financial trends. They're vital for planning and for investors to see how a business is performing over time. A detailed income statement shows how well a company is making money and handling its resources.
Key Components of an Income Statement
To truly get what an income statement is about, it's key to know its parts. We must identify which items belong on the income statement and see how they affect a company's financial health. The key components of an income statement include revenue, expenses, and net income. These categories help give everyone a clear idea of how well a company did money-wise during a certain time.
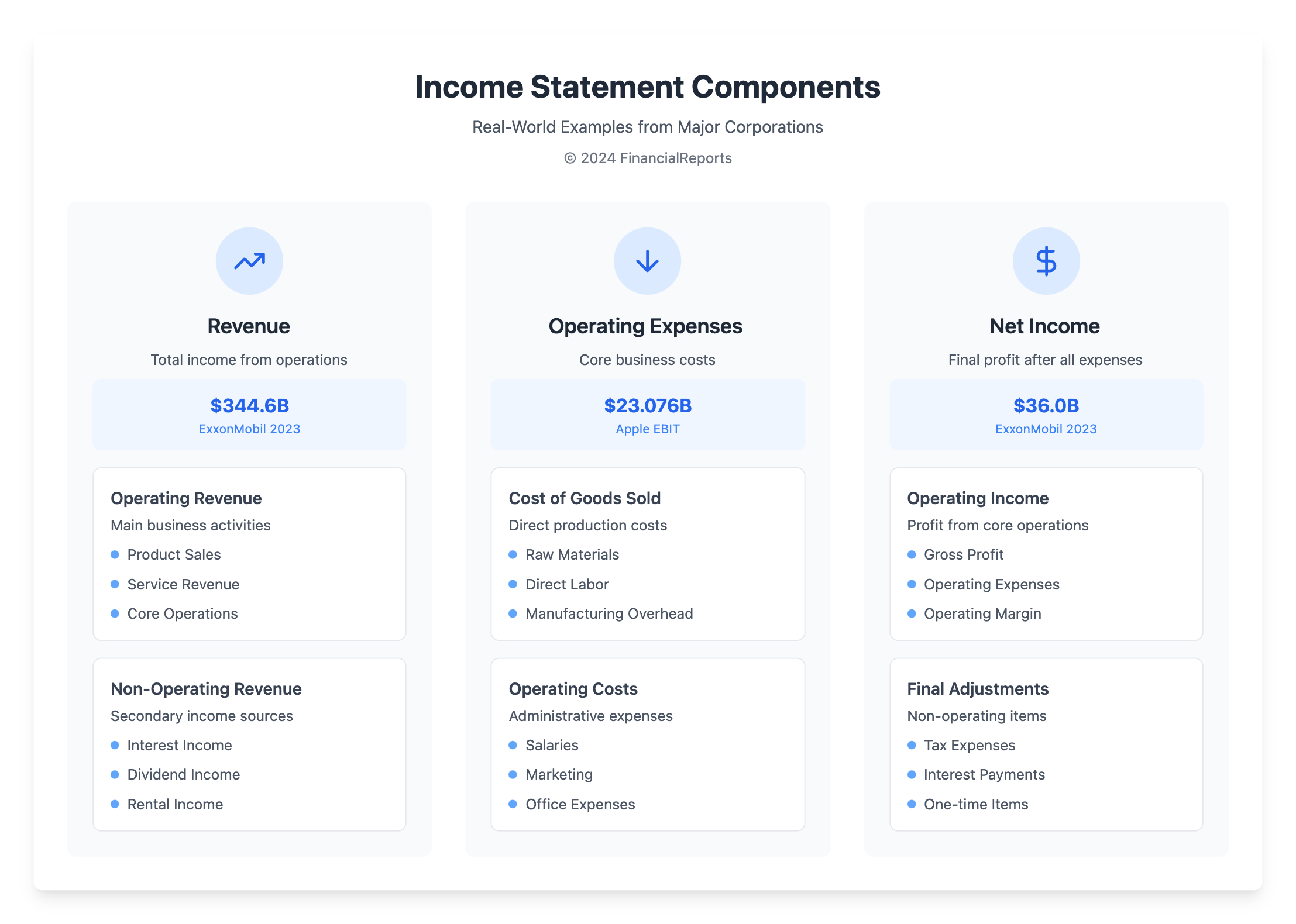
Revenue
Revenue is where the income statement begins. It shows the total money made from the company’s main and extra activities. Take XYZ Corporation, for example. It made $505,000 in total from its operations by the end of December 31, 2023. This number helps us understand how profitable the main business activities are.
Expenses
Expenses show the costs a company had during a time period. They're vital for seeing how well the business spends its money. XYZ Corporation spent $95,000 in operations during the same time. This shows what it costs to run the main parts of the business. Also, money lost or gained from things like financial deals or selling assets, which was -$26,000, sheds light on how the company handles money outside of its main jobs.
Net Income
Net income is figured out by subtracting total expenses and losses from total revenues and gains. It finishes the income statement by showing the company’s real profit after taking everything into account. XYZ Corporation’s net income was $69,000 after handling all money made and spent, including $15,000 for taxes. This final number clearly shows how the company did financially for that period.
Getting a deep understanding of these parts helps those involved make smart choices. It also helps companies plan well, using detailed money insights.
Types of Revenue Accounts
Revenue is the starting point on an income statement. It shows how important it is to know about different types of revenue. Most revenues come from sales revenue and service revenue, along with others. Each plays a unique role in making a business financially healthy.
Sales Revenue
Sales revenue is key for businesses, especially in manufacturing and retail. It comes from selling goods or products. It's important for evaluating a company's main activities. Things like sales returns and allowances lower total sales revenue. They affect how well the business is doing financially.
Service Revenue
Service revenue, on the other hand, comes from providing services, not selling goods. It's vital for businesses like consulting and education. Here, skilled labor and knowledge add value, not physical items.
Other Revenue Sources
Companies also make money from things like rent, interest, and royalties. These sources are important. They help the main business activities and significantly affect profits during big changes or strategic moves.
- Sales Discounts: This lowers sales revenue due to customer payment incentives. It changes the net sales.
- Rent Income: Comes from leasing property, helpful for businesses with extra real estate.
- Interest Income: Earned from investing in assets that earn interest.
- Commission Income: Made through services like brokerage or by sales staff who help with deals.
- Royalty Income: Comes from allowing others to use intellectual property. It boosts revenue without selling goods.
Understanding these revenue types helps financial experts and investors focus on what's working. It guides efforts to boost profit and strategic growth. Knowing deeply about sales, service revenue, and other sources leads to better decisions and stronger financial plans.
Types of Expense Accounts
Understanding what comprises expense accounts is key for good financial management. These accounts are usually grouped by the type and amount of costs. Knowing the three main types helps make financial reports better.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
The Cost of Goods Sold is very important for a business's finances. It shows the costs of making the products a company sells. This includes costs of inventory, work, and overhead for making the products.
For example, if a company makes clothes, the COGS would cover the fabric cost, use of sewing machines, and worker wages.
- Purchase expenses
- Factory labor costs
- Production supplies expenses
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses are costs of running a business daily, not including production. They cover sales and marketing, admin tasks, and maintenance costs. Operating expenses show if a company's main activities are efficient.
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Rent and utilities for office spaces
- Salaries, benefits, and wages for non-production staff
- Professional fees for services such as legal and accounting
Non-Operating Expenses
Non-operating expenses are costs not related to what a business mainly does. This includes interest on loans, losses from currency changes, or costs for restructuring. Knowing these costs helps understand what outside factors affect a business's finances. Watching these costs closely can help make better business decisions.
- Interest expenses on loans
- Losses due to currency exchange rate fluctuations
- Costs associated with restructuring and reorganization
Proper sorting and deep analysis of what comprises expense accounts, COGS, and operating expenses help businesses manage costs better. This leads to more accurate forecasts and plans. Financial experts are crucial for understanding these costs and finding ways to spend less.
Gross Profit and Its Significance
Gross profit is extremely important when analyzing an income statement. It shows how much a company earns after paying production costs from its total revenues. This reveals how efficiently a company operates.
Calculating Gross Profit
To calculate gross profit, the formula is: Gross Profit = Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). Think of a bike company that makes $60,000 but spends $25,000 on making those bikes. After adjusting for returns, its gross profit would be $34,000.
This calculation helps businesses figure out how well they are doing. For example, if a company's gross margin is low, it might need to cut costs or charge more.
Importance of Gross Profit
- Insight into Production Efficiency: The gross profit margin shows how well a company uses labor and materials. High gross profit margin is key for a company's growth and survival.
- Strategic Decision Making: Watching gross profit changes helps companies make smart choices. A bike maker might change where it gets parts or how it makes bikes based on this info.
- Benchmarking Performance: Comparing gross profit margins with others in the industry helps companies understand their position. Being in the 20% to 40% range is generally good.
- Financial Planning: Knowing past and present gross profit is essential for planning. It helps businesses make future investment and expansion decisions.
Gross profit is just one piece of understanding a company's financial health. A thorough income statement analysis, including net income, provides a complete picture. This overall view helps see beyond just the direct costs of making products.
For a business to succeed, understanding and making the most of gross profit is key. It influences pricing, cost management, and many strategic decisions in competitive markets.
Operating Income vs. Net Income
Knowing the difference between operating income and net income is key to understanding a company's financial health. These two figures from the income statement tell us about a company’s success. They show us different sides of the business's money-making.
Defining Operating Income
Operating income shows how much profit a company makes from its main business, minus the operating expenses. It is also called Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT). For instance, Apple reported a recent operating income of $23.076 billion. This was a small drop from $24.126 billion the previous year. This number does not include things like interest and taxes, showing how well the company is doing in its day-to-day business.
Calculating Net Income
Net income is what remains after all expenses, taxes, and one-time costs are subtracted from total revenue. This is also seen as the company's total profit. It is crucial for figuring out the earnings per share (EPS). EPS tells us how profitable a company is for each share of stock owned.
Key Differences
The main difference between operating income and net income lies in what they measure. Operating income looks just at earnings from the company's core operations. Net income takes in all money matters, including extra income and costs. The table below uses Apple's recent financials to show these differences.
| Financial Metric | Apple Inc. Data | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Income (EBIT) | $23.076 billion | Income from main business activities, without interest and taxes. |
| Net Income | Data not specified | All earnings after expenses, including those outside main business. |
| Operating Profit Margin | Data not specified | Shows how effectively costs are managed (Operating Profit / Revenue x 100). |
Both operating and net income are crucial for understanding a company's finances. Operating income offers insights into the company’s main business effectiveness. Net income gives a fuller picture, including all income and expenses.
Non-Operating Income and Expenses
Understanding a company’s financial health is key. We separate operating items from non-operating ones on the income statement for clarity. Non-operating income and expenses give a clear view of the company's true financial performance. This is aside from its core business operations.
Examples of Non-Operating Income
Non-operating income comes from sources outside the main business activities. It includes things like dividend income and profits from selling off assets. For example, earnings from foreign exchange or when asset values go down are part of this. These are shown separately on the income statement. This shows earnings that are not from everyday business. Sometimes, companies report more non-operating income to cover up lower profits from their main activities. This can affect the earnings reported on the income statement.
Examples of Non-Operating Expenses
Non-operating expenses are not from main business operations. These expenses might be interest paid on loans or losses from getting rid of assets. They're listed separately on the income statement. This highlights that they're not usual business costs. It's crucial for analysts and investors to look closely at these. They can indicate special financial events that might change how the company's financial health looks.
| Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Operating Income | Income from non-core business activities | Dividend income, gains from investments, foreign exchange gains |
| Non-Operating Expenses | Expenses not related to core operations | Interest on debt, losses from asset sales |
In summary, reporting non-operating income and expenses clearly helps stakeholders. They can then tell apart the results of main operations from other activities. This clearer financial picture shows the company’s overall health and spots risks or benefits from side activities. Understanding this separation is crucial for reading income statements. It helps in analyzing finances and making investment choices.
Income Statement for Different Business Types
It's important to understand how income statements vary. This variance can be seen in corporations, partnerships, and sole proprietorships. Each has a unique format that affects how we see their financial health and success.
Corporations
Corporations have detailed income statements because of their size and regulatory needs. Such statements show revenues, expenses, and profits including EBITDA. They also cover non-operational activities in depth.
Take ExxonMobil Corporation as an example. In 2023, it had $344.6 billion in revenue and $36 billion in net income. Their statement shows in-depth financial activities and asset management, with assets totaling $376.3 billion.
Partnerships
Partnerships use a special income statement format. It highlights how income and expenses are shared among partners. This includes details on each partner's share based on their input and rights.
Sole Proprietorships
Sole proprietorships use simpler statements. They often choose the single-step income statement. This format puts all revenues and expenses together, making it easy to understand the business's financial condition.
Understanding these income statement differences is key for anyone in corporate finance. It helps in better analysis and comparison of financial data. This, in turn, supports making informed strategic decisions.
Common Income Statement Formats
Financial statements are vital for checking a company's economic health. The income statement is especially important. It comes in two main styles: single-step and multi-step. Each serves different needs and reveals different aspects of a company's finances.
Single-Step Format
Smaller businesses or those with simple finances prefer the single-step income statement. This method subtracts all expenses and losses from total revenues and gains. It uses a clear formula—(Revenue + Gains) - (Expenses + Losses). This provides a quick look at the net income.
Multi-Step Format
The multi-step income statement fits larger companies or those in complex fields better. This format breaks down financial performance into detailed parts. It starts with gross profit (revenues minus cost of goods sold) and ends with operating income. Operating income comes from subtracting operating expenses from gross profit.
| Financial Aspect | Single-Step Income Statement | Multi-Step Income Statement |
|---|---|---|
| Formula | (Revenue + Gains) - (Expenses + Losses) | Gross Profit, Operating Income, Other Income and Expenses, Net Income |
| Complexity | Low | High |
| Best for | Small businesses, simple structures | Larger businesses, complex industries |
| Detail Level | Minimal | Detailed, with subtotals for major financial categories |
| Example of Use | Service firms with less frequent transactions | Manufacturing companies with various product lines |
Knowing the differences between these formats helps in choosing the right one for financial analysis. Public companies have to follow rules from groups like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The correct format, single-step or multi-step, is key to accurately showing a company's financial state.
How to Analyze an Income Statement
Understanding a company’s financial health is key. Analyzing income statements helps make strategic decisions. It shows financial performance, revealing trends in revenue, expenses, and profits.
Key Ratios to Consider
When evaluating a company's success, some ratios are very important:
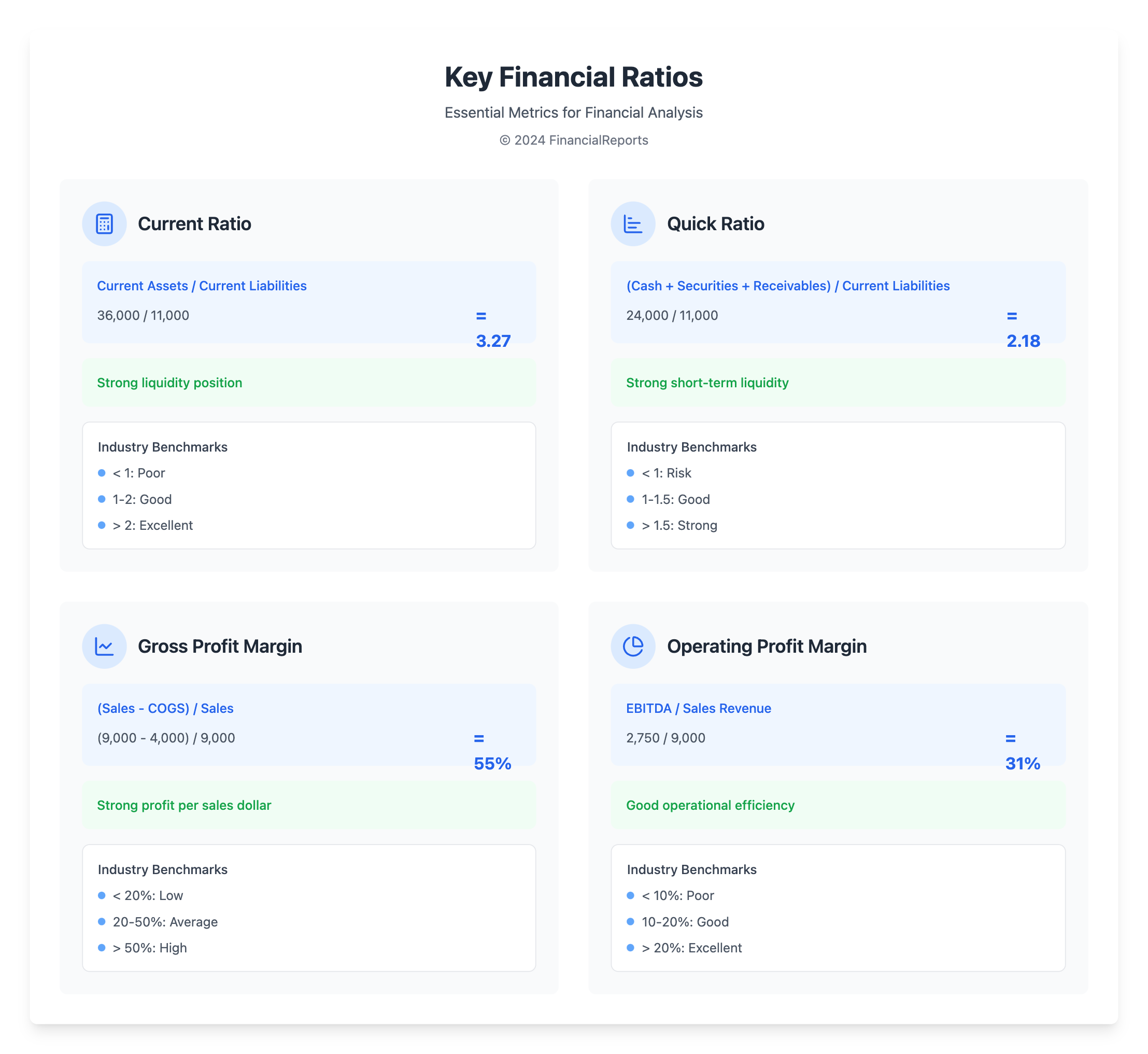
- Current Ratio: Current Assets / Current Liabilities. Example: 36,000 / 11,000 = 3.27, showing strong liquidity.
- Quick Ratio: (Cash + Marketable Securities + Accounts Receivable) / Current Liabilities. Example: 24,000 / 11,000 = 2.18, for assessing short-term liquidity.
- Debt to Equity Ratio: Total Debt / Owner’s Equity. Example: 10,000 / 25,000 = 0.4, indicating less reliance on debt.
- Gross Profit Margin: (Sales Revenue - COGS) / Sales Revenue. Example: (9,000 - 4,000) / 9,000 = 55%, showing profit from each sales dollar after COGS.
- Operating Profit Margin: EBITDA / Sales Revenue. Example: 2,750 / 9,000 = 31%, shows profitability after major costs.
- Net Profit Margin: Net Income / Sales Revenue. Example: 1,850 / 9,000 = 21%, shows efficiency in turning sales into net profit.
Knowing these metrics is key for sound financial planning and smart investment choices.
Trends and Comparisons
Good income statement analysis looks at trends and comparisons to others:
Reviewing past data shows growth or signs of financial troubles. It makes seasonal and market cycle impacts more understandable.
Comparing with industry standards or competitors gives a richer perspective. It helps understand financial strengths or weaknesses better.
Spotting these details is crucial for predicting future performance. It guides towards growth and financial stability.
Best Practices for Preparing Income Statements
Being precise in preparing income statements is crucial. It shows how well a company is doing and helps in making smart financial choices. Making sure everything is right and consistent is key. Let's look at some important best practices now.
Consistency and Accuracy
Consistency and accuracy are very important. They build trust. An income statement shows a company's financial health through its revenues, expenses, and profits. Regular checks and reconciliations show a company is serious about correct data. Being clear about things like total revenue and expenses helps with transparency and future financial checking.
Regulatory Compliance
Following rules like GAAP or IFRS is a must for being trusted. For companies that share their financials publicly, being right and following the rules make sure financial health is shown correctly. Showing true numbers, like EBIT and EPS, shows a company follows strict accounting rules. This builds a good reputation and avoids the cost of mistakes or breaking rules.
Regular Updates
Keeping financial statements up-to-date shows good management. Updating income statements often gives a fresh look at the company's finances. This lets decision-makers see the latest data to make good choices or improve operations. With the economy always changing, current financial reports are essential. Using these best practices strengthens a company's financial story. It helps make global financial data easier to access and understand.
Best Practices for Preparing Income Statements
What Is an Income Statement?
An income statement is a key financial document. It shows a company's financial performance over a certain time. This statement details income, expenses, and the net profit or loss. It offers insights into how well the company operates and its efficiency.
Why Are Income Statements Important?
Income statements are vital for checking a company's financial health. They also help in judging management's efficiency and making smart investment choices. They track profitability and success over time.
What Does Revenue Include on an Income Statement?
Revenue on an income statement includes all money made from the company's main and side activities. This covers sales revenue, service charges, and non-operating revenue like interest or rent.
What Types of Expenses Are Listed on an Income Statement?
Expenses listed include cost of goods sold (COGS) and selling, general, and administrative expenses (SG&A). It also covers non-operating expenses such as interest.
How Is Net Income Determined?
Net income comes from adding all revenue and gains and subtracting all expenses and losses. This calculation shows the company’s final profit.
What Is Sales Revenue?
Sales revenue is the money earned from selling goods or products. It is usually a company's main revenue source.
What Constitutes Service Revenue?
Service revenue comes from providing services to clients. This includes consultancy, repairs, and other professional services.
What Are Other Revenue Sources on an Income Statement?
Other sources include non-operating income like dividends, royalties, rent, and profits from selling assets.
What Is the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)?
COGS includes direct costs tied to making goods that are sold. This involves material and labor expenses linked directly to product creation.
What Are Operating Expenses?
Operating expenses are costs from daily business operations. These include rent, salaries, and utilities, as well as SG&A expenses.
What Are Non-Operating Expenses?
Non-operating expenses are costs not related to main business activities. Examples include interest expenses and losses from asset sales.
How Do You Calculate Gross Profit?
Gross profit is found by subtracting COGS from total sales. It shows how profitable a company's main activities are before other expenses.
Why Is Gross Profit Important?
Gross profit tells us how well a company uses its resources and sets its prices. It shows the money left after covering production costs.
What Is Operating Income?
Operating income, or EBIT, is profit from regular business activities. It doesn't include non-operating income and expenses.
How Is Net Income Calculated?
Net income is revenue plus other income minus all expenses, like COGS and taxes. It shows the company's total profit.
What Are Key Differences Between Operating Income and Net Income?
Operating income only looks at core business profits. Net income includes all revenue and expense types for a full financial view.
Can You Give Examples of Non-Operating Income?
This income includes interest, dividend earnings, rent, and profit from selling non-business assets.
What Are Some Examples of Non-Operating Expenses?
Examples include interest on debt, asset sale losses, and lawsuit costs.
How Does an Income Statement Vary for Corporations?
Corporations’ income statements have detailed revenue and expense breakdowns, including EBITDA. They follow strict accounting and reporting standards.
What Are Income Statement Considerations for Partnerships?
Partnerships’ statements focus on profit and loss sharing among partners. They detail partnership agreement specifics.
Why Might Sole Proprietorships Have Different Income Statements?
Sole proprietorships have simpler statements due to less complex finances and fewer regulations than corporations.
What Is a Single-Step Income Statement?
A single-step statement sums all revenues and deducts all expenses in one step. It shows net income or loss simply.
How Does a Multi-Step Income Statement Differ?
A multi-step statement offers a detailed revenue and expense breakdown. It includes subtotals like gross profit for deeper analysis.
What Key Ratios Should Be Considered When Analyzing an Income Statement?
Important ratios are gross margin, operating margin, and net profit margin. They help gauge efficiency and profitability.
Why Are Trends and Comparisons Important in Income Statement Analysis?
They give context to financial performance. Comparing over time and to competitors helps evaluate growth and cost control.
Why Are Consistency and Accuracy Key in Preparing Income Statements?
They ensure financial reports are reliable. This builds trust among stakeholders and investors.
Why Is Regulatory Compliance Essential in Income Statement Preparation?
Following GAAP or IFRS standards is critical. It legitimizes reports, ensures transparency, and meets financial guidelines.
How Important Are Regular Updates to Income Statements?
Regular updates keep track of financial status, helping stakeholders make well-informed decisions about the business.