How to Find Net Income EBITDA: Easy Guide
If you're into finance or just curious about how companies do, you'll want to know about net income and EBITDA. These are key to seeing if a company is making money and how well it's running. Net income, or the "bottom line," tells us the final profit after all costs. EBITDA, however, looks at earnings before certain expenses. It gives a fair comparison across different fields.
Getting the hang of net income EBITDA is crucial for smart investing and financial analysis. There's a lot of data out there. Being able to tell these two apart is a valuable skill. This guide is here to help, making it easier to understand financial reports. We're here to make complicated financial info more accessible to everyone.
Key Takeaways
- Net income includes all expenses and is a crucial indicator of overall profitability in line with GAAP standards.
- EBITDA focuses on operational performance and is vital for comparing businesses within asset-intensive industries and early-stage tech companies.
- The calculation of EBITDA can start with either net income or operating income, ultimately reflecting normalized operating cash flow.
- Net profit margin benchmarks, such as less than 10% being insufficient and over 20% being excellent, are vital for assessing a company's financial health.
- While EBITDA offers valuable insights into cash-generating abilities, it should not be the sole metric for company valuation due to its non-GAAP nature and potential to obfuscate true valuation.
- Understanding the proper reconciliation of EBITDA to net income is mandatory, as per SEC regulations, for listed companies reporting these figures.
- Utilizing EBITDA along with other financial measures can provide a more comprehensive understanding of a company's operation and performance.
Understanding Net Income and EBITDA
For finance buffs, knowing the difference between ebitda vs net income is crucial. It's key to grasp ebitda vs net profit too. For tech sectors, it's important to get how calculating ebitda for new tech companies works. This helps see how well a company is doing by leaving out costs that don't relate to daily operations.
What is Net Income?
Net income, also called the bottom line, is what remains after paying all bills from the revenue. It shows if a company is making money after covering taxes and interest. Net income reflects how financially healthy a company is because it includes every bit of money made and spent, following official accounting rules.
What is EBITDA?
EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. It's a way to look at money made strictly from business tasks without other factors. It's really useful for businesses that spend a lot on stuff like factories since it shows cash flow and operational success well.
Why Are They Important?
EBITDA and net income are key for several people:
- Investors need these numbers to check if a business is a good choice for their money. They especially want to understand ebitda vs net income. This helps them when they're looking at businesses that have a lot of expenses that don't involve cash directly.
- Managers use these to see how well the company's doing day-to-day and overall. They look closely at ebitda vs net profit to make choices that could change costs and what they invest in.
- Financial Analysts dig into these metrics a lot. They compare companies or see how industries are doing. Often, they need to work out calculating ebitda for new tech companies. This gives them better insight into new businesses that are still finding their footing.
So, EBITDA and net income help a lot in understanding the financial side of businesses. They are basic but crucial parts of making financial decisions and valuing a company.
The Relationship Between Net Income and EBITDA
Understanding how net income and EBITDA work is key for anyone looking into a company's health. These two terms might seem similar but they play different roles in understanding finances. They show unique aspects of a company's financial state.
How They Differ
Net income and EBITDA do different things and are figured out in different ways. Net income comes from total revenue minus expenses. This includes costs of goods sold, operating costs, taxes, and interest. It follows GAAP standards, offering a clear picture of profitability.
On the other hand, EBITDA looks at operational profits by removing non-operational costs. This means ignoring interest, taxes, and non-cash expenses like depreciation. The EBITDA formula adds these back to net income. It shows earnings before the effect of finance and accounting choices.
How They Complement Each Other
Even though they're different, net income and EBITDA together give a full view of a company's finances. The Net income and EBITDA difference matters because they offer insights the other can't. EBITDA is great for evaluating operational efficiency by ignoring taxes and financing effects. It's especially useful in industries with high depreciation costs.
Net income gives a complete picture, counting all expenses. This is vital for looking at profitability and meeting legal rules. Watching both figures lets analysts understand a company's performance fully. It helps in making decisions about operations, finance, and investments.
To wrap up, "is EBITDA the same as net income"? No, each one offers important insights for different needs in business. Using both gives a full picture of a company's financial and operational health. Keeping track of these helps guide business strategies for the best outcomes.
Calculating Net Income
Net income calculation is essential for understanding how profitable a company is. It factors in all earnings and expenses. This figure helps investors, managers, and financial analysts make decisions. It also helps them evaluate the company's performance.
Step-by-Step Calculation
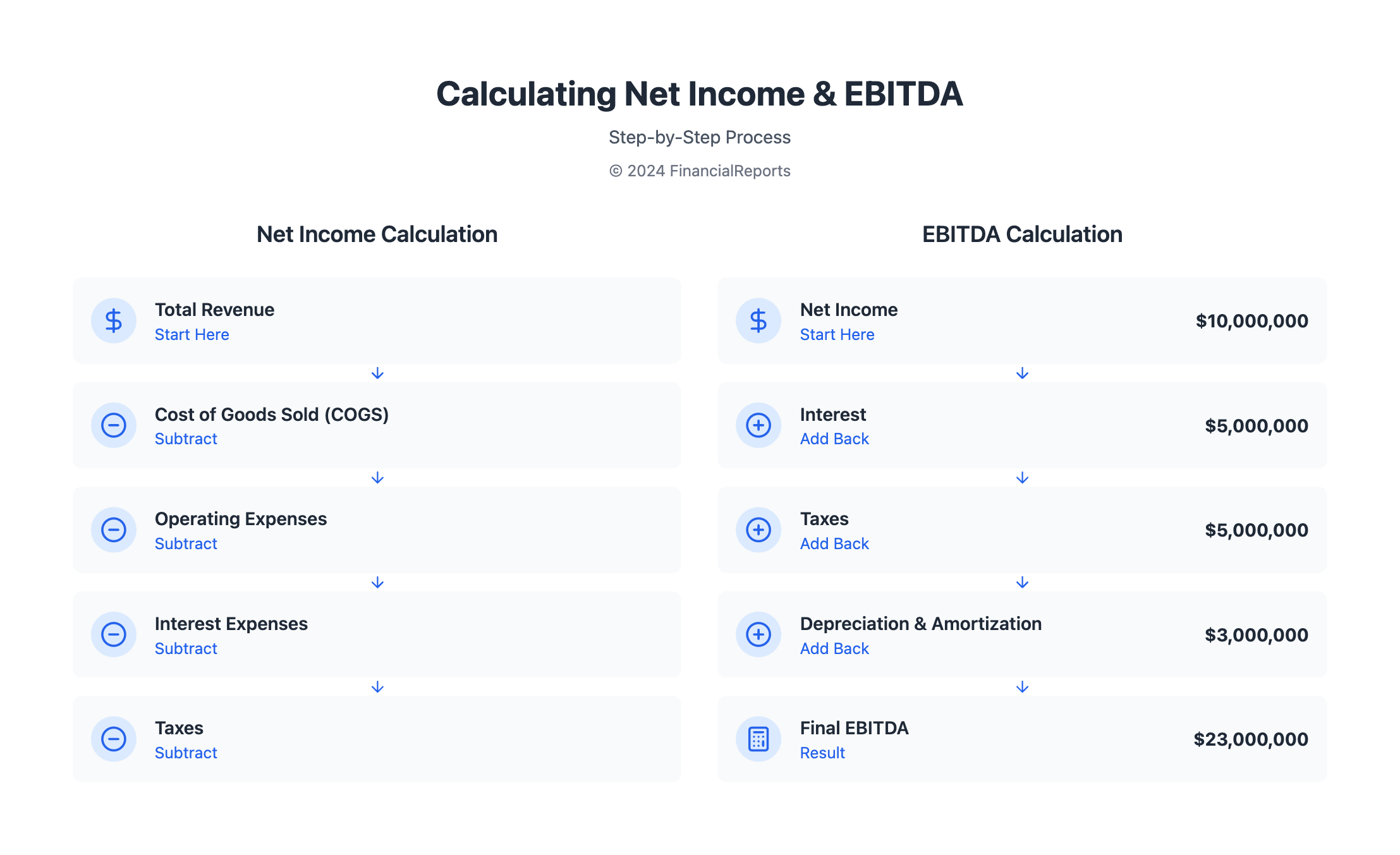
To calculate net income, start with total revenue. Then, subtract the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). This subtraction gives you the gross profit.
Next, from the gross profit, take away all operating expenses. This includes salaries, utilities, and rent. What remains is your operating income.
Then, you subtract other non-operating expenses, like interest on debt. Debt interest varies by company due to different financing. Finally, take away taxes, which also differ based on location, to find the net income. This shows the profit a company keeps after all expenses.
Common Adjustments Made
Adjustments in net income are vital for a true view of profit. They correct for one-time events that might distort the data. Here are some adjustments:
- Depreciation and Amortization: These adjustments account for the wear and use of long-term assets, even though they don't involve cash.
- Non-Recurring Items: This includes one-time sales or losses. Adjusting these gives a clearer picture of ongoing operations.
- Interest Expenses: Interest is left out when calculating EBITDA. This is because EBITDA looks at operational profitability without financing impacts.
With these adjustments, financial experts can deeply understand a company's finances. This leads to better investment choices and company decisions. Net income calculation and analysis are thus key in modern financial analysis.
Calculating EBITDA
Understanding EBITDA is key to assessing a company's performance. You need to know the ebitda calculation formula well. It helps investors and financial pros figure out a company's real earning power. Here, we explain how to calculate EBITDA step by step.
Step-by-Step Calculation
EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. It's a crucial finance metric. It shows a company's profit from its core business operations. This way, it does not get mixed up with other factors like loans, tax strategy, or certain accounting practices.
There are two main ways to calculate EBITDA:
- EBITDA = Net Income + Interest + Taxes + Depreciation + Amortization
- EBITDA = Operating Income + Depreciation + Amortization
Let's say a company has a net income of $10,000,000. It also has depreciation and amortization costs of $3,000,000, taxes of $5,000,000, and interest expenses of $5,000,000. If you use the first formula to calculate, it would look like this:
| Component | Value |
|---|---|
| Net Income | $10,000,000 |
| Depreciation & Amortization | $3,000,000 |
| Taxes | $5,000,000 |
| Interest Expense | $5,000,000 |
| Total EBITDA | $23,000,000 |
Common Adjustments Made
Adjusting EBITDA makes it more accurate. These adjustments help remove one-time costs and misleading numbers. They're key for fair value assessment and comparing companies.
Here are key adjustments:
- Removing unusual costs like legal fees or expenses from natural disasters.
- Excluding income not related to usual business, like from selling assets.
- Adjusting owner's salaries in smaller companies to match industry norms.
Knowing these adjustments and the ebitda calculation formula helps finance pros. They can better understand a company's real earning potential and its worth as an investment.
Combining Net Income and EBITDA
Financial experts often mix key financial metrics, like Net Income and EBITDA, for deep analysis. This method not just looks at pure profit but also includes non-cash costs. It provides a clear look at how well a company operates and its growth possibilities.
Why Combine Them?
Finding net income and EBITDA is more than knowing numbers. Net Income shows real profit after all costs. EBITDA, however, adds back some costs to show true operating profit. This ignores the company's financial setup and tax situation. Together, they offer a full view that helps in decision-making.
Benefits of Combining Both Metrics
Mixing Net Income and EBITDA gives analysts a better look at a company’s health. Here are the main perks:
- Enhanced Financial Insight: This blend helps see not just earnings (Net Income) but how a company makes money (EBITDA). It's crucial for judging operational success minus tax and finance factors.
- Better Comparison: EBITDA is adjusted to remove unusual and once-off items. This makes for a cleaner comparison across companies in the same field.
- Precise Valuation: Using these combined metrics, investors can better gauge a company's worth. The EBITDA margin, for example, directly measures operational efficiency.
Imagine Gemma’s Jewelry reports a net loss (Net Income of -$5,000) but an operational profit (EBITDA of $1,500). This shows underlying strengths or issues not obvious from earnings alone.
Combining Net Income and EBITDA gives financial experts vital tools for deep analysis. In today’s complex business world, this approach is key for thorough financial evaluation.

Practical Applications of Net Income and EBITDA
Exploring EBITDA vs net profit shows us how businesses can thrive. This part talks about using these key financial measures in the real world. They help in making smart choices for operations and strategy.
For Investors
Investors look at net income and EBITDA to check a company's profit and cash flow. Net income application tells if shareholder dividends are reliable. It also predicts the company’s long-term financial well-being.
EBITDA reveals how operations are doing without the impacts of finance and non-cash items like depreciation. Using both figures helps investors understand company value and the risks of investing.
For Managers
Managers use practical uses of EBITDA to compare their company with others. It helps in making operations more efficient. EBITDA helps spot where costs can be reduced, easing the stress of finance and taxes.
Net income, however, shows if the business is healthy overall. It helps align company strategies with what shareholders want. This affects how business success is judged and plans are made.
For Financial Analysts
Both EBITDA and net income are tools for financial analysts. EBITDA makes it easier to compare companies by leaving out varying expenses. These include interest and taxes.
Analysts use net income to see profitability after all bills are paid. It offers a clear picture of how well the company is doing. This reflects the impact of decisions and external events.
In wrapping up, knowing EBITDA vs net profit is key for many in finance. Each metric shows a different side of company finance and operations. Combined, they give a full view of a firm’s health and efficiency. This guides better management and strategic choices.
Common Mistakes in Calculating Net Income and EBITDA
Trying to keep financial metrics accuracy on point often hits snags, especially with net income and EBITDA. These mistakes can skew how we see a company's financial health. They can also change the way strategic decisions are made.
Overlooking One-Time Expenses
Not accounting for one-time expenses is a big mistake in net income calculation errors. Costs like legal settlements or asset write-downs should not be ignored. Otherwise, net income appears much lower than it really is, as if one-time costs are regular expenses.
Misinterpreting Revenue
Getting revenue recognition wrong leads to serious calculating EBITDA mistakes. This happens when revenue is counted too early or when non-cash items are seen as cash. Such mistakes pump up net income and EBITDA. They make a company look stronger financially than it actually is in terms of cash flow.
| Financial Metric | Common Error | Impact on Financial Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Net Income | Omission of one-time expenses | Understated operational costs, inflated net income |
| EBITDA | Incorrect allocation of non-cash revenue | Overstated operational profitability |
| Net Income | Improper revenue recognition | Inflated financial health |
| EBITDA | Failure to adjust for amortization | Misrepresented cash generation capability |
These financial metrics accuracy problems highlight the need for careful checks and following accounting rules. Mistakes in net income calculation errors or calculating EBITDA mistakes affect more than just numbers. They impact how investors see us, the conditions for loans, and key business choices. So, it's crucial to get financial calculations right to keep a company's integrity and fiscal responsibility in check.
Tools and Resources for Calculating Metrics
For those in finance, it's crucial to have the right tools to check key metrics like Net Income and EBITDA. The right tools not only make sure your numbers are accurate but also make your work much easier. This helps you do your financial reviews better and faster.
Excel Formulas
Microsoft Excel is really important for financial analysis because it's so versatile. The EBITDA calculator Excel template is super helpful for figuring out EBITDA. You just plug in your numbers, and it calculates EBITDA for you: EBITDA = Net Income + Interest + Taxes + Depreciation + Amortization. This template is customizable and great for dealing with complex calculations.
Financial Software Recommendations
Nowadays, advanced financial analysis tools are a must-have. These software solutions do more than just simple math. They help you see trends, analyze data, and make predictions. They're really good for working with a lot of data, letting you dig deep into your financial analysis.
Online Calculators
If you need quick results, net income calculators online are really handy. They give you Net Income calculations fast, based on simple info you provide. These calculators are great for a fast check before using more detailed tools. They're a good starting point for more complex analyses.
| Tool Type | Use Case | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| EBITDA Calculator Excel Template | Detailed financial modeling and reporting | Customizable, accurate, handles complex scenarios |
| Financial Analysis Software | Comprehensive data analysis and forecasting | Robust features, large dataset management, predictive insights |
| Online Net Income Calculators | Quick preliminary assessments | Fast results, user-friendly, accessible anywhere |
Finding the right tools is key for accurate and efficient financial analysis. Whether you use an EBITDA calculator Excel template, high-tech software, or simple net income calculators online, these resources help you get deep, insightful results in today's fast-paced finance world.
Conclusion: Mastering Financial Metrics
The journey through mastering EBITDA and net income is crucial for advanced financial analysis skills. EBITDA is a key metric that shows a company's profitability without non-cash expenses and capital structure effects. Unlike GAAP, EBITDA is often used in reports of publicly traded companies, offering valuable performance benchmarks.
Recap of Key Points
We've discovered different ways to calculate EBITDA, focusing on a company's operational profits. PwC finds that 68% of businesses see EBITDA as a key performance metric. This highlights its importance in financial talks. McKinsey & Company shows firms that monitor EBITDA are 30% more likely to forecast finances accurately.
Further Reading and Resources
To better understand financial metrics, dive into resources on how EBITDA affects lender views and credit terms, as Deloitte and S&P Global suggest. HBR's study shows high EBITDA margins can lead to ongoing growth. For those keen to improve their financial skills, learning never stops. It's about linking theory with real-world financial analysis complexities.
FAQ
How do you calculate net income?
To figure out net income, first note the company's total revenue. Then, deduct the cost of goods sold (COGS). Next, subtract total operating expenses, including depreciation and amortization.
After that, take away any paid interest and taxes. Sometimes, you'll need to adjust for unusual or one-time items. The number you end up with is the net income.
What is EBITDA and how is it calculated?
EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. You can calculate EBITDA by starting with net income. Then, add back interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization to it.
Or, begin with operating profit (EBIT). And simply add depreciation and amortization to find EBITDA.
What is the importance of EBITDA?
EBITDA is vital as it gives insight into how well a company is doing operationally. It removes the impact of financing choices, tax situations, and non-cash charges. This gives a clearer view of the company's performance and cash flow possibilities.
How does net income differ from EBITDA?
Net income is different from EBITDA because it includes all expenses and income. This includes taxes, interest, depreciation, and amortization. It shows how profitable a company is after all its financial activities.
EBITDA, however, just looks at operating profitability before these factors.
Why would a company combine net income and EBITDA in their analysis?
Combining net income and EBITDA helps companies see the full picture of profitability (net income). And it measures cash flow potential and operational efficiency (EBITDA). This mix helps stakeholders grasp the impact of financing, tax policies, and capital investments on the company's financial health.
What are the benefits of using both net income and EBITDA for investors?
For investors, having both net income and EBITDA offers a deeper look into a company's financial state. EBITDA shows operating efficiency. Net income highlights overall profitability and the quality of earnings.
This helps investors judge a company's dividend sustainability and growth opportunities.
Can you use EBITDA in company valuations?
Yes, EBITDA is commonly used in valuations. It works to compare profitability across companies with different tax rates, financing structures, and assets. It's often applied in valuation multiples, like the EV/EBITDA ratio.
What are common mistakes to avoid when calculating EBITDA?
When calculating EBITDA, avoid these common errors: not adding back non-cash expenses like depreciation and overlooking one-time items. Also, be careful with misinterpreting revenue or expenses. These mistakes can skew the operational earnings view.
What tools are available for calculating net income and EBITDA?
There are many tools for figuring out net income and EBITDA. Excel spreadsheets are great for tailored financial modeling. There are also several financial software solutions. They offer automated features along with online calculators for quick estimates.
Where can I find further resources for understanding net income and EBITDA?
For more on net income and EBITDA, check out financial education platforms and industry publications. Financial analysis books and university courses are also excellent. Plus, the web is full of articles and tutorials by financial experts.