How to Calculate Realized Return on Investments
If you're looking to tweak how well your investments are doing, it's key to know about realized return. This concept covers your total gains or losses on an investment, during the time you've held it. It looks at how much the asset's price has changed. Plus, it considers any money made through dividends or interest. Knowing how to figure this out helps investors judge and pick the best investment paths, big or small.
Imagine an investor buys stock at $50 but sells it for $49. During this time, they also get $1 every three months as dividends. This person then makes a total of $3. But, just looking at dollars doesn't show if the investment was smart. You need to see the return as a percent. To find this, divide the gain by the original price, then multiply by 100. This method shows a 6% return on the investment.
This approach works whether you're looking at bonds or stocks. It ensures you can equally weigh returns from different kinds of assets. This makes comparing across your investments straightforward and fair.
Key Takeaways
- Realized return reflects the true financial gains or losses from an investment, including price changes and supplemental income such as dividends.
- The formula for realized return allows investors to determine the actual return on investments by accounting for the initial investment versus the exit value, adjusted for any additional income and costs.
- Calculating realized return as a percentage is imperative for an appropriate comparison of investments with different scales.
- Realized yield, particularly relevant in bond markets, considers cash distributions and changes in principal values to illustrate the actual returns.
- Annualizing returns presents a standardized metric for benchmarking the performance of various investment periods.
Understanding Realized Return and Its Importance
Realized return measures how well an investment has done over time. It includes gains from growth and income from dividends or interest. Knowing about realized returns helps investors make smart choices. It matches their strategies with their financial goals and rules they need to follow.
What is Realized Return?
Realized return is the total gain or loss from an investment that's been sold. It counts all money made and all costs until the sale. It includes dividends or interest, and the rise or fall in value. Realized return shows the actual profit or loss, while unrealized gains are just on paper.
Difference Between Realized and Unrealized Return
The difference between realized and unrealized return is essential in tracking investment performance. Realized return gives a clear picture of gains or losses from sold investments. Unrealized return, however, only shows what could happen based on the market now. It's not confirmed until selling.
This difference is crucial for planning. It involves knowing when to sell to get the best return. This strategy depends on market changes.
Key Components of Realized Return
To manage investments well, it's key to get the basics of realized return. Realized return includes important parts that show us how income from investments performs. By looking at these parts together, we know how well investment strategies are doing.
Initial Investment Amount
The first amount you invest is your starting point for tracking returns. It helps figure out capital gains and the growth level of your investment.
Sale Price of the Investment
The sale price tells us what the market thinks our investment is worth. It shows the capital gains when we compare it to our initial investment amount.
Additional Costs and Taxes
Real investment earnings also consider extra costs. These costs can include:
- Brokerage fees that impact the income from investments.
- Taxes on transactions that can lower capital gains.
- Fees for upkeep or management, especially with properties or physical assets.
We must factor in these expenses to see the true profit from an investment. Knowing these details helps investors and financial experts make smarter choices. It helps them plan better for future investments to increase their returns.
The Formula for Calculating Realized Return
In finance, knowing how to calculate correctly is key to reliable analysis of investments. A vital part is figuring out the realized return. This tells us how well an investment did over time.
Basic Formula Explained
The basic calculation begins simply. Take the final sale price of the investment and subtract the price when you bought it. Then, add any money made from dividends or interest. In math terms, it looks like this:
Realized Return = (Sale Price - Purchase Price) + Dividends/Interest
This approach helps us understand our real financial gain or loss. It puts complex market activities into simple outcome terms. This is crucial for deep analysis of investment returns.
Example Calculation
Imagine an investor buys shares for $50 each and sells them for $60. Plus, they get $5 in dividends. Here's how to use the formula:
- Purchase Price = $50
- Sale Price = $60
- Dividends = $5
The calculation goes like this:
Realized Return = ($60 - $50) + $5 = $15
To find the return as a percentage of the investment, divide the $15 gain by the initial $50:
Percentage Return = (Realized Return / Initial Investment) x 100 = ($15 / $50) x 100 = 30%
This percentage shows how effective the investment was, which is important for managing portfolios and planning strategies.
Knowing how to calculate realized return correctly helps analyze past investments. This guides future investment choices.

Factors Influencing Realized Return
Realized return on investments depends on many factors, both inside and outside factors. It's vital for investors to get these details to manage their returns well.
Market Conditions
Market changes greatly affect the realized return. For example, high inflation times, like in 2022, often cause big differences between what you think you'll get and what you actually get. Imagine a situation where you earn 3.0% but inflation is 5.0%. This means you actually lose 2.0%. So, it shows how crucial investment risk factors are in financial planning.
Individual Investment Strategies
Strategic asset allocation is key for realized returns. It means spreading your investments to balance risk and reward. This matches your goals, risk comfort, and how long you plan to invest. By doing this, you can handle unexpected losses in one area with gains in another.
| Investment Condition | Nominal Rate | Inflation Rate | Real Rate of Return |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Inflation Scenario | 10% | 7% | 2.8% |
| Low Inflation Scenario | 10% | 3% | 6.8% |
| Negative Impact | 3% | 5% | -2.0% |
Understanding and using strategic asset allocation well can guide investors. Along with watching the market, this helps manage investment risks. Thus, good investment management means knowing the market and matching strategies with your financial goals.
Realized Return vs. Other Return Metrics
When we explore investment metrics, it's key to know how realized return differs from others. Realized return measures actual gains or losses after selling an investment. This makes it unique compared to broader financial tools.
Comparing to Total Return
Total return includes interest, capital gains, and dividends over an investment's life. It shows the investment’s growth in percentage form. For example, buying 100 shares at $20 each and getting a 5% dividend leads to a 15.5% total return with reinvestment and a price increase to $22.
This way of measuring is crucial for evaluating mutual funds. It helps compare returns to benchmarks over different times. By doing this, investors can see how funds perform relatively.
Understanding Annualized Return
Annualized return tells us the average growth rate each year over a set time. It considers compounding effects, allowing comparison across different investments. This metric is vital for predicting future growth and making smart, long-term choices.
The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is a key financial indicator. It shows how an investment can grow annually over time. This ease of comparison helps in understanding an investment’s growth potential.
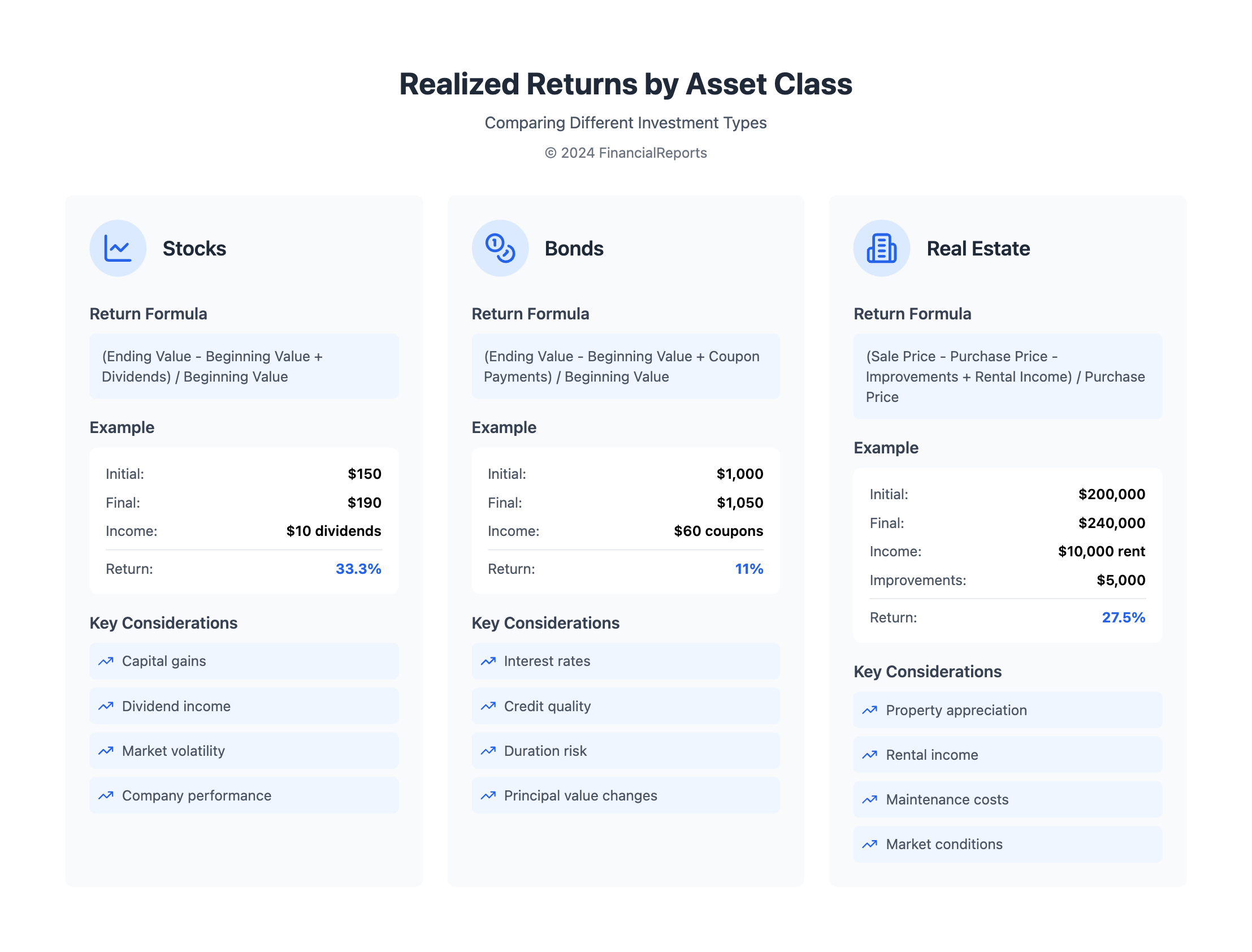
Calculating Realized Return for Different Asset Classes
Calculating realized returns is different for each asset class due to their unique features. These assets, like stocks, bonds, and real estate, have special ways of creating income. Understanding these methods is vital for assessing how well each asset type performs.
Stocks
With stocks, you look at capital gains and dividends to find the realized return. The Holding Period Return (HPR) is a simple calculation: HPR = (Ending value - Beginning value + Dividends) / Beginning value. For a stock bought for $150 and sold for $190, plus $10 in dividends, the HPR is 33.3%. This shows why dividends are key in measuring how well stocks are doing.
Bonds
Bonds mix interest payments with changes in price. To find their realized return, use the Adjusted HPR Formula, adding in coupon payments. If a bond is bought for $1000 and sold for $1050, with $60 in coupons, the realized return is 11%. This highlights the role of coupon payments in bond returns.
Real Estate
Real estate takes into account rental income and improvements for its returns. By using the Adjusted HPR, if you buy a property for $200,000, spend $5,000 on it, and make $10,000 from rent, with a sale price of $240,000, the return is 27.5%. This shows the impact of rent and upgrades on real estate returns.
To really understand and calculate realized returns, you need to know what boosts each asset's overall performance. This knowledge is crucial for handling a portfolio well. It helps in making smart decisions about where to put your money.
Common Mistakes in Calculating Realized Return
Two main mistakes often mess up the accurate investment analysis: forgetting about transaction fees and not thinking about taxes. These errors can mess up the real performance numbers of an investment. This leads investors to make wrong choices based on wrong numbers.
Overlooking Transaction Fees
Transaction fees are costs that come with buying and selling investments, but people often forget to include them when they figure out their realized return. These fees lower the net gain from an investment because they reduce the money you get from selling the asset. To get a true picture of an investment's performance, include these fees in your return calculations.
Ignoring Taxes
Taxes are very important in figuring out the real gains from an investment, especially for short-term investments which usually have higher tax rates. Not including taxes in the calculations can make the investment net gains seem much larger than they really are. To accurately evaluate an investment, all tax effects need to be looked at.
| Calculation Method | Consideration | Impact on Net Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Excluding Transaction Fees | Fees Paid on Acquisition and Sale | Overestimates Net Gains |
| Ignoring Tax Implications | Tax Rate Based on Holding Period | Substantial Underestimation of Real Costs |
| Inclusion in Analysis | Comprehensive Inclusion of Fees and Taxes | Reflects True Investment Performance |
It's vital to accurately calculate realized returns by including all costs like fees and taxes. This thorough method improves the trustworthiness of investment analysis. It also helps in making smart choices for chasing investment net gains.
Tools and Resources for Calculating Returns
To really nail returns calculation, especially the RRR, you'll want top-notch investment tools. These tools are key for tapping into detailed financial analysis. They consider everything from market shakes to how steady dividend incomes are. This helps make your investment decisions sharp and informed.
Investment Calculators
Investment calculators are essential for bringing financial theories into the real world. They use important financial concepts like CAPM and WACC. With these tools, you can see how different market conditions and times affect your investments. The US Stock Returns Calculator from Vested is a standout. It helps you understand what you might earn from US stocks.
Financial Software
Going deeper, financial analysis software doesn't just look at RRR. It also gives forecasts and analyses that are more in-depth. These platforms adjust your strategy with up-to-the-minute financial data and currency changes. This is especially valuable for those playing in global markets. In today's tech-savvy world, these software tools are at the heart of smart financial planning and analysis.
| Feature | Investment Calculators | Financial Software |
|---|---|---|
| RRR Calculation | Utilizes CAPM, dividend discount models | Applies CAPM, WACC, and other discounting models |
| Market Analysis | Limited to specific investment evaluations | Comprehensive market scenarios and forecasting |
| Currency Impact | Basic conversion features | Detailed analysis reflecting real-time currency exchange rates |
| User Interface | Straightforward, focused on singular investments | Complex, suited for detailed financial planning and multiple investments |
| Feedback Capability | Static analysis based on inputted data | Dynamic feedback incorporating latest financial data |
Using investment tools and financial analysis software simplifies tough calculations like RRR. They also boost decision-making with projections based on past and current market data. For investors and financial gurus, these are not just helpful tools. They are crucial in mastering today's complex financial world.
Case Studies: Realized Return in Action
Investment theory and practice closely relate. Real-world case studies offer insights into how choices impact returns. These insights show how stock prices and fund distributions change. They also show the effect of transaction timing on returns.
Stock Market Investments
Investment case analysis in stocks involves looking at lots of data. The S&P 500 index grew at an average annual rate of 10% from 2013 to 2023. When adjusting for inflation, this growth shows strong performance. Furthermore, buying a stock at $60 and selling at $90 represents a 50% return. This example shows the high rewards of wise stock investment.
Mutual Funds
Mutual funds spread risks and seek opportunities by pooling assets. Diverse portfolios in these funds can see returns over 3x, indicating major gains. Evaluating these funds includes analyzing their performance and personalized metrics based on buy and sell times.
| Investment Type | Average Return (2013-2023) | Specific Case ROI | MOIC Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stocks | 10% annually | 50% on $60/share investment | N/A |
| Mutual Funds | Varies by fund composition | Dependent on fund performance | >3x (successful scenario) |
Case studies show possible outcomes and the strategies to reach them. By looking at actual examples, financial experts can improve their strategies. This helps them boost their market performance and investment returns.
Strategies to Maximize Realized Return
To boost your portfolio, it's smart to use strategies like spreading out investments and timing the market. Knowing how these tactics work helps you navigate complex markets. They give you a better chance to succeed in today's financial world.
Diversification
Spreading your investments around is crucial for managing risk. It leads to steadier, more reliable gains over time. By investing in different areas, industries, and countries, you lessen the blow of bad investments. This strategy uses data to make the most of varying market conditions. It smooths out your returns and cuts down on risk.
Diversification's big pluses include:
- Less ups and downs in your portfolio
- More chances for growth
- Lower risk from a single investment tanking
Timing the Market
Timing the market is tricky but can pay off if you're careful. It's about guessing when prices will change and acting on those guesses. Perfect predictions are rare. Still, a disciplined approach to timing can leverage market quirks and cycles.
Good timing strategies need:
- Lots of research on market trends and signs
- Technical tools and algorithms for help
- Smart plans for when to buy or sell
Mixing diversification with timing strategies can make your portfolio stronger. While diversification shields you from certain risks, smart timing aims to grab quick gains. Both methods are key for serious investors. They help you manage your investments better and go after better results.
Conclusion: Making Sense of Your Returns
We've learned that tracking realized returns is key to understanding investment success. These returns show the real outcomes of our financial choices. For those who seek precise evaluation, knowing how to calculate these returns is essential. This process must consider taxes, inflation, and other important factors. This way, we truly understand an investment's performance.
Importance of Tracking Realized Returns
Statistics like a real return rate of 9.333% show why taxes and inflation matter. This analysis helps us see if investments are truly successful. For example, Roth IRA accounts show how taxes can affect wealth building. Thus, tracking returns thoroughly ensures our decisions are informed and forward-looking. It helps us keep real tabs on our money's value.
Final Thoughts on Investment Success
Let's not forget about risk and return. Seeing Investment A with much higher volatility than Investment B teaches us something important. Higher risk should bring higher potential returns. Using the expected return formula helps investors predict average results. This balances their strategies between risk and reward. So, with better access to financial data, investors can enhance their success and knowledge.
FAQ
How do you calculate realized return on investments?
To figure out the realized return, first find the difference between the final sale price and the initial purchase price. Then, add any earnings from the investment while you owned it, such as dividends or interest. Finally, turn this amount into a percentage by dividing it by the initial investment amount and multiplying by 100.
What is realized return?
Realized return is what an investor earns or loses after selling an investment. It includes capital gains or losses and any dividends or interest received while holding the investment.
What is the difference between realized and unrealized return?
Realized return involves gains or losses on investments that have been sold. Unrealized return, on the other hand, refers to the potential gains or losses on investments that are still owned and not yet sold.
What are the key components of realized return?
Key parts of realized return are the amount you initially invested, the sale price, and any additional costs and taxes. Don't forget any income received, like dividends or interest.
Can you provide an example of a realized return calculation?
Let's say you bought an investment for $50 and sold it for $60. You also received $5 in dividends. The realized return is $15 (($60 - $50) + $5). To find the percentage, divide $15 by $50 and then multiply by 100. This gives you a 30% realized return.
What factors influence realized return?
The market's conditions and how you decide to invest play a big role in realized return. This includes how market prices change and what you focus on, like growth or earning income.
How does realized return compare to other return metrics like total return or annualized return?
Realized return tells you about the actual gains or losses after selling an investment. Total return, however, covers all gains, losses, and reinvested money over the investment's lifetime. Annualized return, or CAGR, shows the average yearly growth rate during a specific period.
How do different asset classes affect the calculation of realized return?
Different assets like stocks, bonds, and real estate add unique factors to realized return calculations. These factors include dividends for stocks, coupon payments for bonds, and rental income for real estate.
What are common mistakes when calculating realized return?
One common mistake is not considering transaction fees and taxes. Both significantly impact how much you really earn from an investment.
What tools can assist investors in calculating realized returns?
Tools like investment calculators and financial software are handy. They automatically include changes in price, income distributions, transaction fees, and taxes for you.
How can diversification and market timing influence future realized returns?
Diversifying spreads out your risk across various asset types. Market timing tries to make buying and selling decisions based on future market forecasts. Both can affect how much money you might make or lose in the future.
Why is tracking realized returns important for investment success?
Keeping track of realized returns helps you understand how well your past investments worked. This information can guide your future investment choices and ensure you rely on accurate financial data.