How Do You Figure Out Dividends: A Simple Guide
Investors aiming to earn passive income from the stock market must grasp understanding dividend payments. Dividends are a part of a company's profits given to shareholders, rewarding their trust. Getting the hang of how to calculate dividends and knowing important financial metrics is crucial. This guide will show you easy steps for dividend calculations. This ensures you can weigh the worth and growth chances of dividend-paying stocks wisely.
Key Takeaways
- Knowing how to calculate dividends is crucial for estimating passive income from your investments.
- The dividend payout ratio formula—(annual dividend payments / annual net earnings) * 100—tells the profit share given to shareholders.
- To find the dividends per share amount, divide the total paid dividends by the outstanding shares number.
- For preferred stocks, annual dividends per share are set by the dividend percentage and par value.
- Total cash dividends are figured by multiplying the dividends paid per share by the total shares.
- Knowing the ex-dividend date, record date, and payment date is key to knowing if you get dividends.
- Dividend yield and payout ratio are key to understanding a company's financial health and its appeal to income-focused investors.
What Are Dividends?
Dividends are part of a company's profits given to its shareholders. They show if a company is doing well financially. Knowing how to find and analyze dividends is key for investors interested in earning from stocks.
Definition of Dividends
Corporations pay dividends to their shareholders. It's a way to share profits. Dividends usually come in cash, but sometimes in stocks or other forms. The board of directors chooses the amount, based on profits, policy, and future plans.
The formula for dividends is simple: Annual income minus changes in retained earnings equals dividends. To find dividends per share, you divide total dividends by the number of shares.
Importance in Investing
Dividends are crucial for investors for many reasons. They give a steady income, which is great during unstable market times. Reinvesting dividends can buy more shares, leading to bigger returns later.
Understanding the dividend payout ratio is key. It shows how much profit goes to dividends. It's calculated by dividing total dividends by net income. This helps judge if a company can keep paying dividends.
Certain sectors like basic materials and utilities often pay regular dividends. They're seen as stable. Tech sectors might pay less in dividends. They focus on reinvesting for growth.
Ultimately, dividends indicate a company's current and future health. Firms known as Dividend Kings or those in the Dividend Achievers List attract those looking for steady dividends and growth.
How Are Dividends Paid?
Understanding how dividends are paid is key for investors wanting steady income from their stocks. Dividends come in forms like cash or stock, depending on the company's choice and financial status. Let's explore how dividends work and how to calculate them.
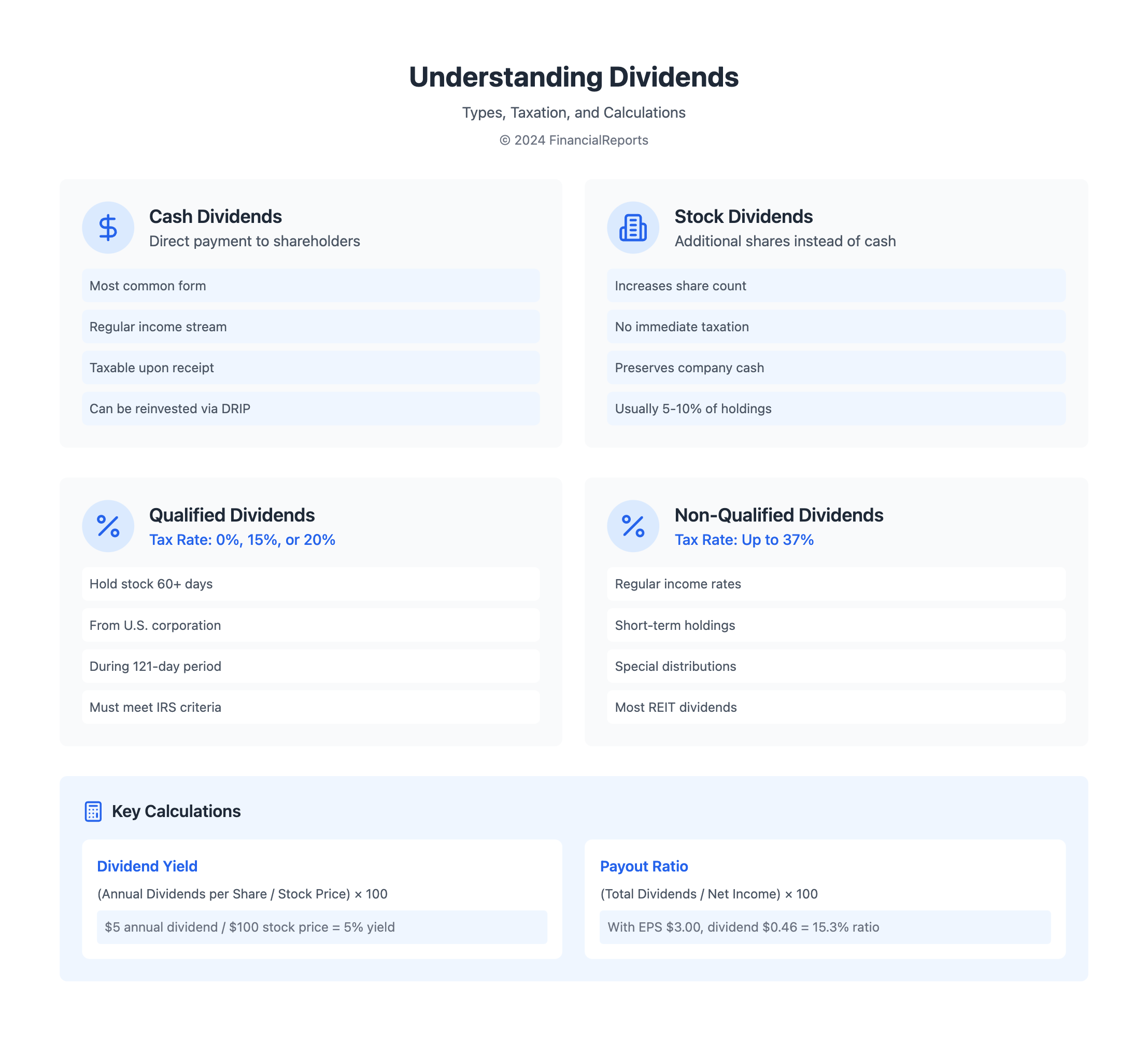
Cash Dividends
Cash dividends mean a company gives a direct payment from its profit or saved earnings to shareholders. If a company pays a $0.50 dividend per share and you have 1,000 shares, you get $500. Calculating this is simple: multiply the dividend per share by your number of shares. If Company A announces a dividend of $0.50 with 7 million shares out there, it will pay out $3.5 million in total.
Stock Dividends
Stock dividends are not cash but extra shares given to shareholders. If there's a 10% stock dividend, owning 10 shares means getting 1 extra. This approach can lower the share value but helps the company save cash.
Other Forms of Dividends
Some companies give dividends in property or commodities, though it's less common. These unusual dividends might be something like real estate or oil. There can also be special dividends given during times of great profit, outside the regular schedule.
Calculating dividends means also knowing the important dates: declaration, ex-dividend, record, and payment dates. These dates affect when and how you get dividends, and knowing them helps with investment strategies. This is especially true for the ex-dividend date, which decides if you're eligible for the next payment.
Overall, dividends play a big part in investment decisions. They offer a regular income, show company health, and contribute to overall investment returns.
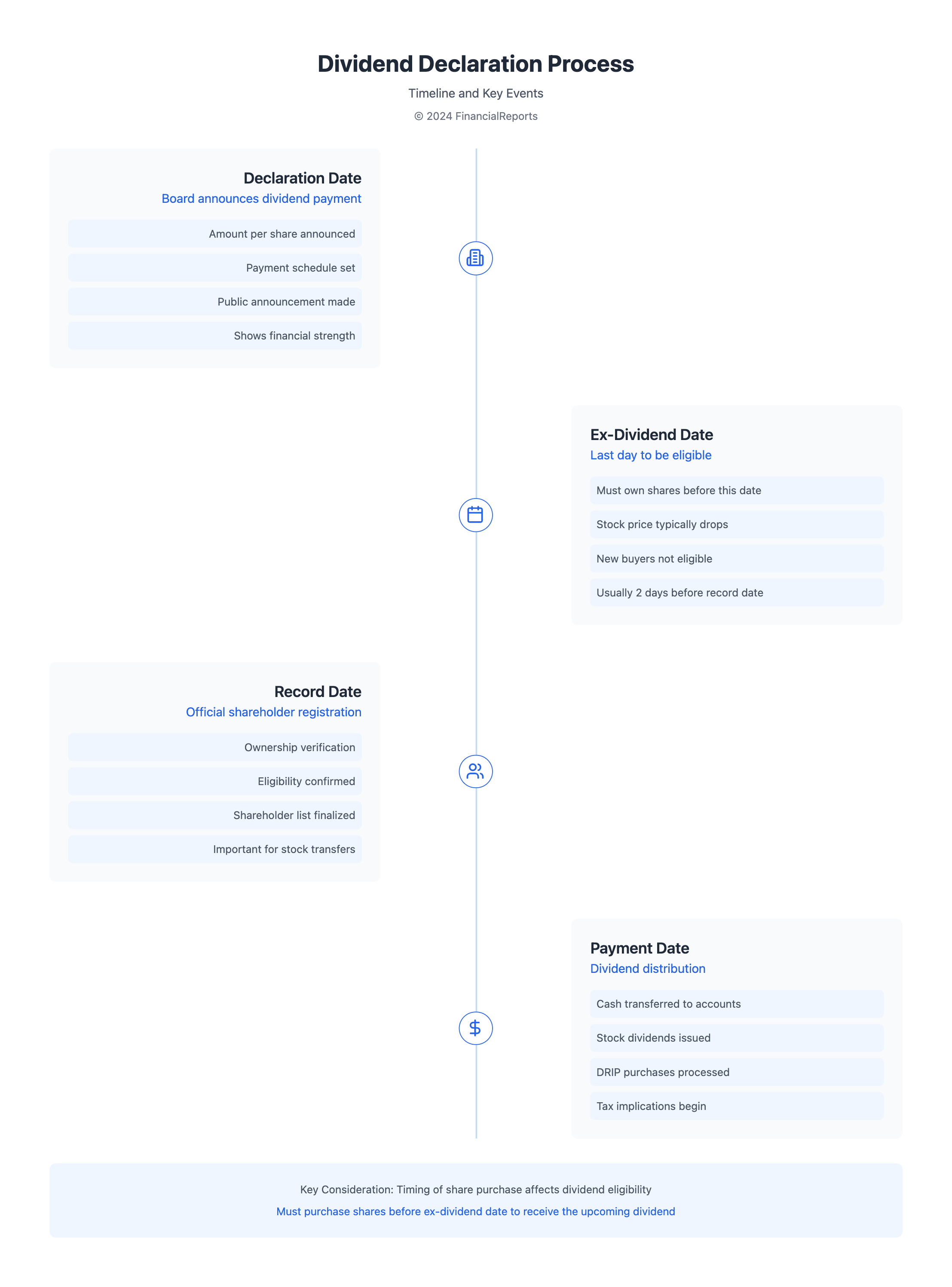
The Dividend Declaration Process
The dividend payment process is key for investors looking to gain more income through dividends. It's important to understand the dividend declaration process to learn how to calculate stock and dividend payments. This process starts with the company's board of directors.
Board of Directors' Role
The board of directors decides on paying dividends after reviewing the company’s financials. The decision to declare dividends is a big deal. It shows the company is doing well financially and has steady cash flow. Companies like Procter & Gamble are known for regularly increasing dividends, rewarding their loyal investors.
Announcing the Dividend
Dividend announcements are made public on a set schedule. This keeps everything transparent for investors. They detail how much the dividend will be per share and important dates all shareholders should know:
| Date Type | Description | Impact on Investors |
|---|---|---|
| Declaration Date | The official announcement by the board of declaring a dividend. | Signals to the market about the company’s profitability. |
| Record Date | Investors must be on the company’s books to receive dividends. | Determines the official list of shareholders eligible for dividends. |
| Ex-Dividend Date | Typically two days before the Record date, after which the stock trades without its dividend. | Investors need to purchase shares before this date to receive the dividend. |
| Payment Date | The date when the dividend payment is made to shareholders. | Shareholders receive their dividend payments; direct financial benefit. |
Companies like AbbVie and Procter & Gamble regularly give dividends. This shows they're financially strong and committed to their shareholders. For investors, these dates are not just opportunities. They also show a company's financial stability.
Key Terms to Know
When diving into dividend investing, it's crucial to understand some key terms. Knowing about dividend yield, dividend payout ratio, and ex-dividend date is vital. These terms help shape your investment strategies and the outcomes of your portfolio. They are essential for anyone wanting to make the most out of their dividends per share.
Dividend Yield
The dividend yield measures how much you earn from dividends compared to the stock's price. It's found by dividing the annual dividends per share by the stock’s current price. Then, it's shown as a percentage. This tells you how much you can earn in dividends, based on the stock price, without considering capital gains. Essentially, it shows the yield you get from dividends per share.
Dividend Payout Ratio
The dividend payout ratio shows the percentage of earnings paid as dividends. To calculate it, divide the total dividends by the company’s net income. This ratio indicates how much profit is returned to shareholders versus reinvested in the company. It's vital for understanding the sustainability of dividend payments and assessing a company's health and growth potential.
Ex-Dividend Date
The ex-dividend date is key for anyone investing in dividend stocks. It's the date when the stock price drops by the dividend amount on the stock exchange. Investors must buy the stock before this date to receive the dividend. Those buying on or after won't get the dividend. This date is crucial for eligibility, highlighting the importance of timing in dividend investing.
Knowing how to calculate and understand dividend yield, payout ratio, and ex-dividend date is critical. These concepts help investors make smart choices in their portfolio. They aid in crafting a strong and profitable investment strategy focused on dividends.
How to Calculate Dividend Yield
Knowing how to calculate dividends paid and how to figure out dividend payment is key for investors. They use this to see how good a stock is at making money through dividends. Dividend yield shows the percent of return paid to shareholders as dividends.
Formula for Dividend Yield
The formula for dividend yield uses the annual dividends per share against the stock’s market price. It helps investors understand what they can earn relative to the price of the stock. The formula looks like this:
(Annual Dividends per Share / Current Share Price) × 100%
This method shows the dividend as a percent of the stock price. It makes it clear how much the investment makes relative to its cost.
Example Calculation
Let's look at an example. Imagine a company's stock costs $100 and it gives a dividend of $5 per share each year. Here's how to work out the yield:
(5 / 100) × 100% = 5%
This means the yield is 5%. So, for every $100 invested, a shareholder gets $5 back every year in dividends.
| Company Stock Price | Annual Dividend Per Share | Dividend Yield |
|---|---|---|
| $100 | $5 | 5% |
| $50 | $2.5 | 5% |
| $200 | $10 | 5% |
This table shows that the dividend return stays the same no matter the stock price. But remember, high dividends on cheap stocks may not mean the company is strong.
In short, understanding how to calculate dividends paid and how to figure out dividend payment through dividend yield is crucial. It helps investors decide where to put their money for the best income.
Understanding Dividend Payout Ratio
Investors often look at how much a company pays as dividends. They use the dividend payout ratio (DPR) for this. This ratio shows what portion of a company's net income goes to dividends. It tells us about the company's financial health and how it handles profits.
What Is Payout Ratio?
The dividend payout ratio is the total dividends paid, divided by the company's net income. It's also "{Total Dividends per Share} divided by {Earnings Per Share (EPS)}." For example, if Apple has an EPS of $3.00 and pays a dividend of $0.46 per share, its payout ratio is 15.3%. This shows Apple is careful with how it distributes its profits.
Why It Matters
Understanding the dividend payout ratio is key. A high ratio might mean a company is profitable but has less money for growth. A low ratio suggests a company is keeping more money for expansion, buying other companies, or paying off debt. This could mean more value for shareholders in the future.
Some industries, like Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), must pay most of their earnings as dividends. They often have a high payout ratio. This attracts investors looking for income. In contrast, high-tech companies usually have a lower ratio. They focus on using profits for fast growth.
For investors, knowing a company's dividend payout ratio helps them see its focus. It shows if a company prefers to give immediate returns or reinvest for future growth.
Finding a Company's Dividend History
Looking into a company's dividend history matters a lot for investors. It's key for those who focus on dividend yields and their sustainability. Knowing how to check dividends paid and compute dividends payable is vital. This requires trustworthy historical data and understanding financial documents.
Researching Past Dividends
Investors must dig into financial statements and Notes to Accounts in annual reports for this. Especially, the 10-K filings are resourceful. They reveal info on dividends declared. This helps investors see the pattern and growth of dividends.
By looking into the company's retained earnings and net income, investors can gauge if a company can keep up or raise dividend payouts over time.
Sources for Dividend Information
There are several places to find dividend data:
- Financial news sites like The Wall Street Journal and Investopedia share updates on dividend payouts and policy changes.
- Stock exchanges like the NASDAQ and the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) have tools. They offer dividend calendars and history screeners. These help investors find high-yielding stocks and understand their dividend schedules.
- Brokerage platforms provide screening tools. These make it easier to filter stocks by dividend yield and payment histories.
- Form 1099, submitted to the IRS by firms, shows the previous year's dividend payments. This aids investors in their financial analysis.
This mix of sources doesn't just show how to figure out dividends paid. It also aids in making strategic investment plans. It does this by spotting trends like dividend stability and growth in various market conditions.
How to Analyze Dividend Stocks
Understanding dividend stocks begins with how we figure out dividends and their future trends. It's important for investors to choose companies known for steady dividends and the chance for growth. Looking into these aspects sheds light on a company's financial health and future.
Look for Consistent Payers
To find the best dividend stocks, investors look at companies that regularly pay dividends. A sign of a good investment is its ability to keep paying dividends. This shows a company's ongoing success and financial strength. Companies that pay dividends without fail tend to have a good dividend coverage ratio. This ratio shows they are likely to keep up with dividend payments.
Consider Dividend Growth
Understanding dividends means looking at their growth. This growth shows a company's increasing profits and hopeful future. Companies that up their dividends often are likely doing well financially. They have the money to grow the business and increase dividends further.
| Parameter | Data | Impact on Dividend Stocks |
|---|---|---|
| Trailing & Forward Dividend Yield | > 4.67% | Indicates high-yielding stocks, compared to the U.S. 10-year Treasury yield of 4.67% |
| Dividend Payout Ratio | < 50% | Signifies healthy financial management and potential for earnings growth |
| Average Dividend Yield of S&P 500 | 1.25% | Lower than double the 10-year yield, potentially attractive under current metrics |
| Net Debt to EBITDA Ratio | Lower ratios preferred | Highlights companies with less leverage, better positioned to sustain dividends |
| Dividend Growth | Companies growing dividends tend to outperform | Reflects upward financial trends and sound management practices |
Analyzing dividend yield, payout ratios, and growth wisely helps investors make smart choices. As the financial world changes, using detailed, data-driven methods is key. This strategy ensures a profitable and stable investment portfolio.
The Impact of Economic Factors on Dividends
It's key for investors to grasp how economic shifts affect dividends. This is especially true in sectors where dividends play a big role. When the economy grows or shrinks, companies might change their dividend policies. This can greatly affect investor decisions.
How Market Conditions Affect Dividends
When the economy is doing well, companies often increase their dividends thanks to higher profits and stable finances. But in tough times, they might cut back to save money. For instance, in a good economic period, FG Corp might give an extra 10% in stock dividends, handing out 100,000 more shares at $5 each. This move can change the game for investors.
Knowing a company's dividend amount and its change during different times can show its financial strength and policy consistency.
Economic Cycles and Dividend Policies
Dividend strategies reflect more than just current money matters. They are also about long-term planning based on the economic cycle. For example, in good times, companies may offer dividends that shareholders can take as cash or more shares. This approach meets the needs of different investors as the economy changes.
Here's a simple look at how companies handle dividends in various economic conditions:
| Condition | Action on Dividends | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Expansion | Increase dividend issue | FG Corp issues a 10% stock dividend during prosperous times. |
| Economic Downturn | Reduce or suspend dividends | Companies retain capital by reducing dividends. |
| Stable Economic Period | Maintains or slight increase in dividends | Steady dividend payout ratio in line with industry norms. |
Understanding dividend ratios in different economic times is key for investors. It shows a company's long-term financial plan and its ability to last. This knowledge helps investors make smarter choices through changing economic cycles.
Dividends in Taxation
For investors, knowing how dividends are taxed is key to keeping more money after taxes. There are two types of dividends: ordinary and qualified. Each type affects taxes differently. This is important because it changes how much tax you pay on dividends.
Understanding Tax Implications
Ordinary dividends get taxed like regular income. In 2024, tax rates on them could be as high as 37%. Qualified dividends get a break and are taxed less. They have rates of 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on your income. People earning less than $47,025, or less than $94,050 for joint filers, might pay no tax on qualified dividends. This makes it crucial to understand dividend calculations for financial plans.
Qualified vs. Non-Qualified Dividends
To be taxed less, qualified dividends have rules. The company's stock must be owned for over 60 days around the dividend's date. This rule is key for planning and ensuring dividends get taxed less. Non-qualified dividends don't meet these rules, so they're taxed more, like regular income.
Large dividend incomes can lead to more taxes. For instance, the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) adds a 3.8% tax for high earners. In 2024, singles making over $200,000 and joint filers over $250,000 will pay this. So, knowing how to report dividends correctly is crucial for those with higher incomes.
Also, if you get over $1,500 in ordinary dividends, you must report it on Schedule B (Form 1040). Being accurate with dividend reporting is essential. Knowing tax rules and managing investments well can make your portfolio more tax-efficient.
Getting good at understanding dividend taxes can lessen your tax load and increase what you keep from investments. It's a crucial skill for those who get dividends.
Reinvesting Dividends: A Smart Strategy
Dividend reinvestment plans (DRIPs) are key for investors wanting to grow wealth over time with stocks or mutual funds. Knowing how to calculate dividends per share and using the benefits of dividend reinvestment boosts an investment portfolio's growth.
Benefits of Dividend Reinvestment
Dividend reinvestment has many perks. These plans let investors put their dividend money right back into more shares. Often, this is at a lower price and without paying fees to a broker. The main perks include:
- Compound growth: More shares mean more dividends, leading to a snowball effect.
- Lower cost: DRIPs often come with discounts and no fees, making your investment stretch further.
- Accessibility: You can buy parts of shares, making it easy to invest what you can afford and build up over time.
- Convenience: Automatic reinvestment means you don't have to put much effort into growing your investment.
Reinvesting dividends can lead to higher earnings. For example, over 20 years, putting dividends back in can make your potential return jump by 47% versus taking the cash.
Setting Up DRIPs
It's usually easy to start with a Dividend Reinvestment Plan. Many companies and brokers provide a way to automatically sign up for DRIPs. When setting them up, investors should keep in mind:
- Enrollment: Sign up via your broker or directly with the company if they have their own DRIP.
- Investment options: Plans might let you reinvest in single stocks or in bigger funds or ETFs.
- Tax considerations: Taxes apply to reinvested dividends unless they're in accounts like Roth IRAs or 401(k)s.
- Long-term goals: DRIPs suit those not needing cash now and looking at the big picture.
Using DRIPs helps investors benefit from market fluctuations. They can buy more shares when prices are low and fewer when they're high. Thinking about these points can help investors boost their portfolio, meeting their financial aims.
To sum up, learning how to calculate dividends per share and making the most of dividend reinvestment with DRIPs can massively grow your portfolio. This leads to better financial success over time.
Common Myths About Dividends
Dividends interest many in the finance world. Yet, myths can lead to wrong choices. For example, a high dividend yield seems positive at first. But, it's crucial to look deeper. A high yield with a falling stock price might show trouble instead of value. Understanding dividend calculations is not simple.
Debunking Dividend Misconceptions
Many see dividend stocks as safer than growth stocks. This view explains their popularity, especially among new investors. But, this safety can be misleading. Dividends change with the company’s success and market changes. Sectors like real estate investment trusts (REITs) and master limited partnerships (MLPs) often have high yields. Yet, high yields don’t always mean more value. It's vital to check a company's strength before focusing on yields.
Realities of Dividend Investing
Smart dividend investing requires careful analysis. Understanding dividends includes knowing how the ex-dividend date affects prices and the tax perks. But, dividends aren't risk-free. Even top companies' dividends might not be stable. Dividend decisions are influenced by many factors. As markets change and companies face financial challenges, dividends need careful review. This new view on dividends leads to smarter investing. It's key for improving global financial data understanding.
FAQ
What Are Dividends and Why Are They Important for Investors?
Dividends are profit shares given to shareholders. They're seen as a reward for their investment. They show a company is doing well and cares about its shareholders.
How Are Dividends Paid to Shareholders?
Dividends are paid in cash, stocks, or sometimes property. Cash dividends go right into accounts. Stock dividends provide more company shares to the shareholders.
What Is the Role of the Board of Directors in the Dividend Declaration Process?
The board of directors decides on dividends based on earnings and company health. They set the amount, and when and if it will be paid.
How Can Investors Calculate Dividend Yield?
To find the dividend yield, divide yearly dividends by the share price. Then multiply by 100. This shows the return compared to the share price.
What Is the Significance of the Dividend Payout Ratio?
The dividend payout ratio shows how much profit is given as dividends. It helps investors see if a company can keep paying or increase its dividends.
Where Can Investors Find Information on a Company's Dividend History?
Dividend history is in financial statements, annual reports, or the company's website. It shows the company's consistency and reliability in paying dividends.
How Should Investors Analyze Dividend Stocks?
Look for consistent dividends and growth potential. Check the company's financial health, payout ratio, and future earnings.
How Do Market Conditions and Economic Cycles Affect Dividends?
Market changes and economic shifts can impact dividends. In tough times, companies might cut dividends. They may increase them when profits rise.
What Is the Tax Treatment of Dividends?
Dividends are taxed as qualified at lower rates or as ordinary at standard rates. This depends on stock holding periods and dividend types.
What Are the Benefits of Reinvesting Dividends?
Using a DRIP to reinvest dividends buys more shares automatically. This can grow wealth as share numbers and value increase over time.
What Are Some Common Myths About Dividends?
A common myth is high dividend yields are always good. Another is dividend stocks are low risk. But dividends can change with company and market performance.