Gross Margin vs Operating Margin: Key Insights
Gross margin and operating margin are key metrics for understanding a company's financial health. They show how well a company can cover its costs and make profits. Knowing the difference between these two is important for anyone who works with money or invests in companies.
Gross margin is about the cost of making a product. It's the total revenue minus the cost of goods sold, shown as a percentage. Operating margin, on the other hand, shows profit after all operating expenses are subtracted. This highlights the importance of understanding both in financial analysis.
Introduction to Margin Analysis
This article will explore gross margin versus operating margin. We'll look at what they are, how to calculate them, and why they matter. We'll also talk about what affects these margins and when to use each one. This will give you a full picture of these important financial metrics.
Key Takeaways
- Gross margin and operating margin are essential metrics for assessing a company's financial health and operational efficiency.
- Gross margin focuses on direct production costs, while operating margin shows profit after operating expenses are deducted.
- Understanding the difference between gross margin and operating margin is critical for thorough financial analysis and making smart decisions.
- Gross margin versus operating margin is a key distinction that impacts a company's ability to cover costs and make profits.
- Examining both gross and operating margins is vital for evaluating a company's profitability and operational efficiency, highlighting the importance of gross margin versus operating margin.
- Publicly traded companies must report quarterly earnings to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), making gross margin and operating margin key metrics for investors and financial professionals.
Understanding Gross Margin
Gross margin is a key financial metric. It shows a company's profit from sales minus the cost of goods sold, as a percentage. The formula is: Gross Margin = (Total Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold) / Total Revenue. This gives insight into how profitable a company is at the production level.
Unlike operating margin, gross margin only looks at the cost of goods sold compared to total sales. It's usually higher because fewer costs are subtracted from gross income. For example, a women's apparel retailer might keep 46 cents for every $1 sold. Knowing gross margin is vital for investors and analysts, as it shows if a company can cover expenses and make a profit.
Definition of Gross Margin
Gross margin, or gross profit margin, is found by subtracting direct costs from total revenue and dividing by total revenue. It's important for companies to check their pricing and cost of goods sold with this metric.
Calculation of Gross Margin
The formula for gross margin is simple: [(total sales revenue - cost of goods sold) / total sales revenue] x 100 = gross margin. This shows how profitable a company is at the production level. It helps in making decisions about pricing, production costs, and expenses.
Importance of Gross Margin in Financial Analysis
Gross margin is a key sign of a company's financial health. It shows how well a company manages production costs and stays profitable. By looking at a company's gross margin, investors and analysts can understand its financial performance and make smart choices.
In comparison to operating margin, gross margin focuses on production-level profitability. It's a vital part of financial analysis. The main difference is that gross margin only looks at the cost of goods sold, while operating margin includes other expenses. This makes gross margin a critical tool for financial analysis, giving insights into a company's performance and growth.
Understanding Operating Margin
Operating margin is a key financial metric. It shows how well a company manages its costs compared to its revenue. It's the operating profit as a percentage of total revenue. The formula is: Operating Margin = (Operating Income - Operating Expenses) / Total Revenue.
This metric helps evaluate a company's efficiency and profitability. It's important for financial experts and investors to understand it.
Now, let's talk about if can profit margin be higher than operating margin. Yes, it can happen. This is because profit margin includes all expenses, including interest and taxes. But operating margin only looks at operating expenses and fixed costs.
Here are some important points about operating margin:
- It's found by dividing operating income by net sales.
- It's shown as a percentage.
- It shows profitability after variable costs but before taxes and interest.
By looking at operating margin, companies can see how profitable each sale is. They can also compare themselves to competitors. This helps find ways to improve and make smart business choices.
| Margin Type | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Margin | (Operating Income - Operating Expenses) / Total Revenue | Measures a company's profitability and efficiency |
| Gross Margin | (Net Sales - Cost of Goods Sold) / Net Sales | Measures a company's profitability after deducting cost of goods sold |
Key Differences Between Gross Margin and Operating Margin
The main difference between gross margin and operating margin is what costs they include. Gross margin only subtracts direct costs of goods sold. On the other hand, operating margin also includes operating expenses like sales, R&D, and admin costs. This difference is key to understanding a company's financial health and operational efficiency.
When looking at gross margin versus operating margin, it's important to know their focus areas. Gross margin shows how well a company produces goods. Operating margin, on the other hand, gives a wider view of how profitable operations are. For example, a company with a high gross margin but low operating margin might have high operating expenses.
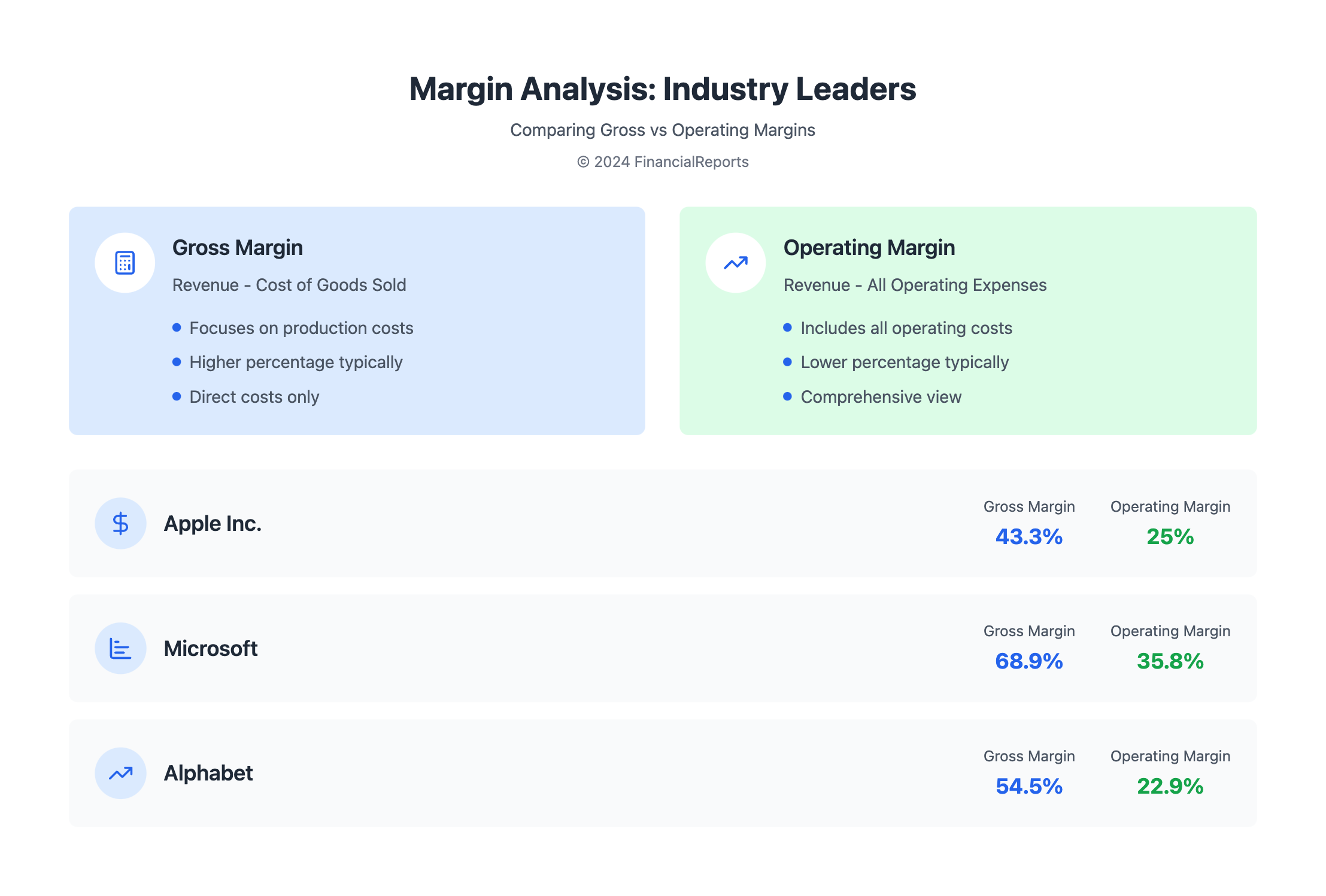
| Company | Gross Margin | Operating Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Apple Inc. | 43.3% | 25.0% |
| Microsoft Corporation | 68.9% | 35.8% |
| Alphabet Inc. | 54.5% | 22.9% |
It's essential to understand the differences between gross margin and operating margin for business decisions. By analyzing these metrics, companies can spot areas for improvement. This helps in optimizing their financial performance.
Factors Affecting Gross Margin
When looking at a company's financial health, it's key to understand what affects its gross margin. Gross margin shows how much profit a company makes after selling its products or services. It's influenced by pricing, the cost of goods sold, and market conditions.
A company's pricing strategy is a big factor in its gross margin. If prices go up without the cost of goods sold increasing, the gross margin gets better. But if costs rise and prices don't, the margin goes down. Industries like banking and software often have higher margins than others.
Pricing Strategies and Cost of Goods Sold
The cost of goods sold is very important for a company's gross margin. It includes direct costs like raw materials, labor, and overhead. Changes in these costs can greatly affect the gross margin. For example, if raw material costs go up, the gross margin might drop unless the company can raise its prices.
Market Conditions
Market conditions, like competition and demand, also play a role. In a competitive market, companies might have to lower prices, hurting their gross margin. But in a market with high demand and little competition, companies can keep or raise prices, boosting their margin. Knowing these factors helps companies make better pricing decisions and improve their financial health.
Factors Affecting Operating Margin
Operating margin is key for businesses, showing how much profit comes from operations. The question of whether can profit margin be higher than operating margin is common. The answer depends on several factors, like operating expenses, how well operations are run, and revenue growth.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses, like sales and marketing, research, and general admin costs, greatly affect operating margin. Companies with high expenses might have a lower margin. But those with efficient operations and low costs can have a higher margin.
Efficiency of Operations
How well operations are run is also important for operating margin. Companies that make their processes more efficient can boost their margin. But, if operations are not efficient, costs go up, and margins go down.
Revenue Growth
Revenue growth also plays a role in operating margin. Fast growth can mean more expenses but also bigger margins due to economies of scale. Yet, if growth is not managed well, margins can drop, and profits suffer. It's vital for businesses to understand how revenue growth affects their margins to make smart decisions and grow sustainably.

When to Use Gross Margin
Gross margin is key in financial analysis. It shows how much profit is made before operating costs are subtracted. Unlike operating margin, which shows profit after operating costs, gross margin is used for decision-making.
It's very useful for checking how each product does. By looking at the gross margin of each product, businesses can see which ones are most profitable. This helps them decide where to put their resources. Companies like Apple and Microsoft have high gross margins, showing they keep prices high and costs low.
Evaluating Product Performance
Gross margin helps compare the profit of different products. This lets businesses spot where they can improve and focus on the best products. It also helps set prices that are competitive yet profitable.
Pricing Decisions
Gross margin is vital for setting prices. It tells businesses the lowest price they can charge and stay profitable. Companies with high gross margins, like Visa, have more room to play with prices. Those with lower margins, like Tesla, have less.
Comparisons with Industry Standards
Comparing a company's gross margin to industry standards is important. It shows how well a company does compared to others in terms of efficiency and pricing. By looking at companies like Coca-Cola and Procter & Gamble, businesses can see where they stand and where they can get better.
When to Use Operating Margin
Operating margin is key for checking a company's health and how well it turns sales into profit. It's important to know when to use it to understand a company's financial health. The question of whether can profit margin be higher than operating margin is common, and the answer depends on the relationship between different profit metrics.
Operating margin, or return on sales (ROS), shows how well a company manages costs. It's found by subtracting operating expenses from gross margin. This gives a clear view of a company's efficiency. Using operating margin helps spot where a company can cut costs and improve.
Assessing Overall Business Health
Operating margin is a key sign of a company's health, showing its profit-making ability. By looking at operating margin, companies can spot trends and plan for the future. It helps predict earnings, find cost savings, and set goals.
Operational Performance Assessment
The operating margin also shows how well a company manages its expenses. By comparing margins, investors can see how companies handle costs. This is shown in the table below:
| Company | Operating Margin | Gross Margin |
|---|---|---|
| ABC Co. | 10% | 20% |
| XYZ Inc. | 15% | 25% |
In summary, operating margin is essential for checking a company's health and efficiency. By knowing when to use it, companies can understand their finances better. The link between can profit margin be higher than operating margin is complex. Companies need to analyze their data carefully to judge their profitability.
Analyzing Margin Trends
When looking at a company's finances, it's key to check margin trends. This means looking at how gross margin versus operating margin change over time. It helps us see how the company's financial health and efficiency are doing.
To do this, we need to figure out the gross margin and operating margin for each period. We use the formulas: Gross Margin = ((Revenue − COGS) / Revenue) × 100 and Operating Margin = (Operating Income / Net Sales) × 100.
When we analyze margin trends, we should keep a few things in mind:
- Look at how margins change from year to year to spot trends and patterns.
- Consider seasonal changes that might affect margin performance.
- Compare margins to competitors to see how the company stacks up.
By studying these trends and comparing them to industry standards, investors and financial experts can learn a lot. They can see what the company does well and what it needs to work on. This helps them make smart choices about investing.
Tools and Techniques for Margin Analysis
When looking at gross margin versus operating margin, the right tools are key. Financial software like Margin Bridge Analyzer automates calculations and offers real-time insights. It helps companies track margin changes and spot areas for betterment.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are vital in margin analysis. By monitoring revenue growth, cost of goods sold, and operating expenses, companies understand their financial health better. Tools like waterfall charts make complex margin data easy to grasp, helping stakeholders make informed decisions.
For instance, a company can use margin analysis to check its pricing strategies. It can find ways to cut costs. With these tools, businesses can make smart choices and boost profitability.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Margin Bridge Analyzer | Automates margin calculations and provides real-time insights |
| Data Visualization Tools | Presents complex margin data in a clear and concise manner |
| KPIs | Tracks metrics such as revenue growth, cost of goods sold, and operating expenses |
Conclusion: The Significance of Both Margins
Both gross margin and operating margin are key to understanding a company's health and efficiency. They give different views but together show how well a business is doing.
Knowing the difference between gross margin and operating margin helps leaders make better choices. It affects pricing, cost control, and how resources are used. Sometimes, profit margin can be higher than operating margin due to income from investments or real estate. By watching both closely, leaders can find ways to grow and improve.
When you analyze finances, look at industry standards and use data tools. Add key performance indicators (KPIs) to your analysis. This way, you can make your business strong in today's tough market.
FAQ
What is the difference between gross margin and operating margin?
Gross margin shows how well a company makes its products. Operating margin looks at the whole company's profit. Gross margin only looks at direct costs, while operating margin includes all costs, like sales and marketing.
Can a company's profit margin be higher than its operating margin?
No, a company's profit margin can't be higher than its operating margin. Profit margin is a part of operating margin, without sales and marketing costs. Operating margin shows the company's total profit, while profit margin shows the profit after all costs are subtracted.
What are the key factors that can impact a company's gross margin?
Several things can change a company's gross margin. Pricing, the cost of goods sold, and market conditions are key. Companies must watch these to keep or boost their gross margin and stay efficient.
How can operating margin analysis be used for long-term financial planning?
Operating margin gives a full picture of a company's health and profit. It's useful for planning, budgeting, and setting goals. By looking at trends, companies can spot areas to improve and make better financial choices.
What are the benefits of benchmarking a company's margins against industry competitors?
Comparing margins with competitors offers insights. It shows a company's standing in efficiency, pricing, and profit. This comparison can show strengths and weaknesses, guiding strategic and operational changes.