Does Revenue Go Under Assets on Balance Sheet
Understanding financial statements, like balance sheets, can be tough. People often wonder about where revenue should go. The key question is: does revenue go under assets on balance sheet? It's important to know that revenue affects assets but it's not an asset itself. Revenue belongs on the income statement. This shows a company's financial health over time. It highlights how money comes in and goes out.
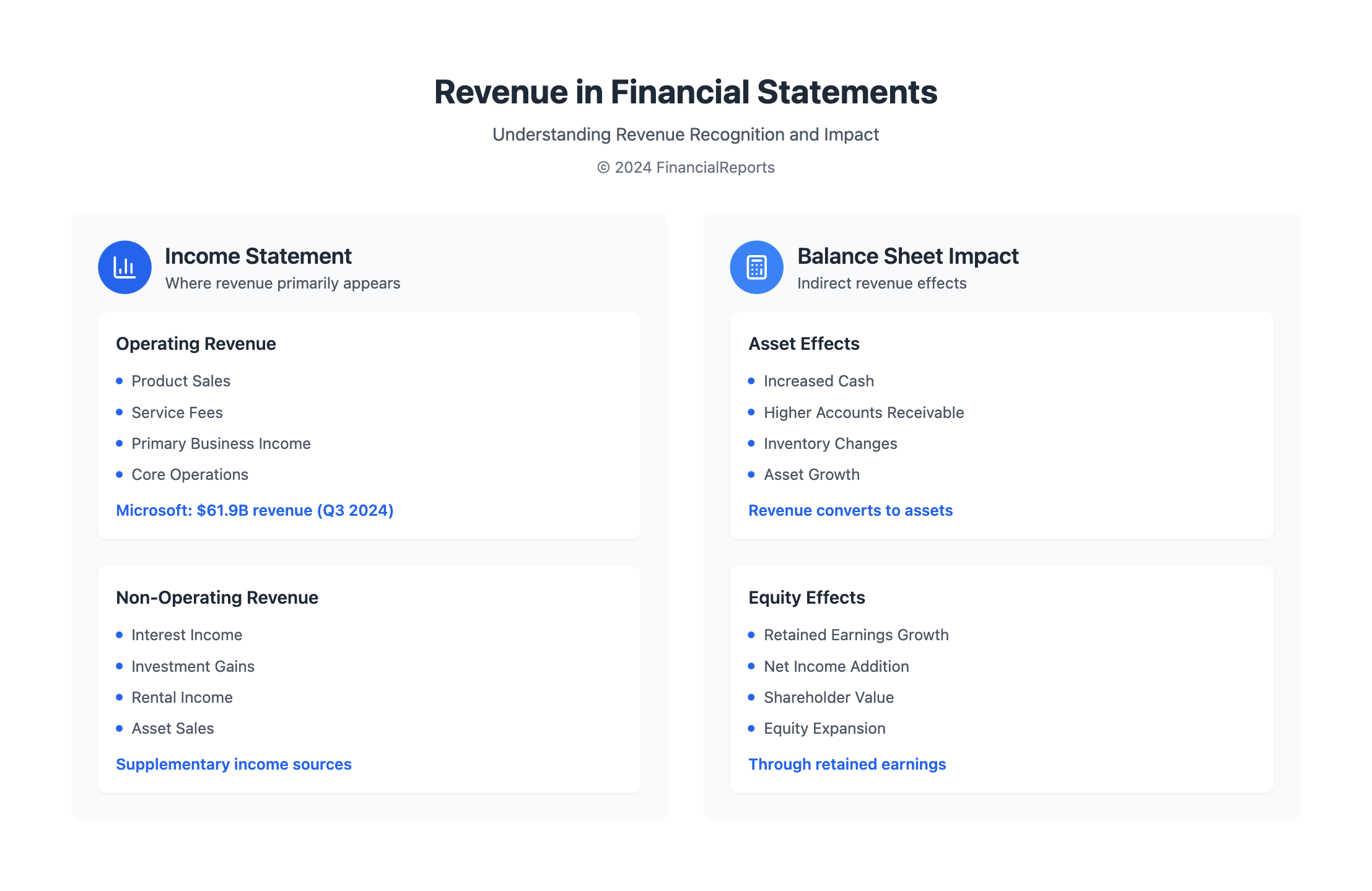
After it's earned, revenue impacts equity, especially in retained earnings after paying expenses. Sometimes, when revenue means getting more cash or having higher accounts receivable, it looks like an increase in assets. However, revenue is separate from assets. It causes changes in asset accounts and in stockholders' equity. It doesn’t sit with assets on the balance sheet.
Key Takeaways
- The balance sheet gives a look at a company's financial standing, showing assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity.
- Revenue changes equity and asset amounts but isn't an asset itself; it's shown on the income statement.
- Balance sheets help derive financial ratios. These ratios evaluate a company's financial health.
- Investors use balance sheets for calculating returns and analyzing a company's capital structure. This offers insights into financial health.
- If a balance sheet's numbers don't add up, it might signal errors that need fixing.
- Examples like McDonald's $33 billion in property and gear, or Domino's $18 billion in net sales, show how assets and revenue play together on a huge scale.
- Airbnb's way of recognizing revenue provides a special look at the asset-revenue relationship on balance sheets.
Understanding the Basics of a Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a key part of a company's financial statement. It shows a company’s financial status at a certain time. It lists assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity. This tells us what the company has, what it owes, and the value shareholders have put in.
Assets: Definition and Examples
Assets are important parts of the balance sheet. They show value that a business controls. Assets are split into current and long-term, based on how quickly they can be used or turned into cash. Current assets like cash, accounts receivable, and inventory, are expected to turn into cash within a year. As an example, Walmart had $14.8 billion in cash and $54.9 billion in inventory in 2024. Long-term assets, such as buildings and machinery, are used for more than a year and can’t be quickly turned into cash.
Liabilities: What You Need to Know
Liabilities show what a company owes. They are a key part of a company's debts, divided into current and long-term. Current liabilities, like accounts payable or short-term debts, must be paid within a year. Long-term liabilities, including bonds payable or lease obligations, are due after a year. Knowing about these helps assess a company’s financial health and future.
The Role of Equity in the Balance Sheet
Shareholders' equity tells us the company’s value to its owners. It shows what’s left for shareholders after all debts are paid. This includes invested capital, retained earnings, and reserves. For example, in 2024, Walmart's shareholders’ equity was over $81.3 billion. This indicates strong investor trust and financial health.
In summary, knowing about balance sheet components and their types is crucial. It gives us insight into asset liquidity and a company’s financial position. This information is valuable for investors, financial experts, and managers. It helps them make smart decisions for a company’s growth and stability.

The Revenue Section of Financial Statements
When we look into financial statements, the revenue part shows us how well a business is doing. It's important to understand what revenue is, its types, and how it's recognized. This knowledge helps us in analyzing finances and making smart decisions.
Definition of Revenue
Revenue is also known as sales or turnover. It's the total money made by a company before taking out returns or discounts. This amount is crucial because it sets the stage for calculating net income. It plays a big role in breaking down the income statement.
Types of Revenue: Operating vs. Non-Operating
Revenue is split into operating and non-operating types. This helps tell apart regular business earnings from other gains. Operating income comes from the main business activities. For example, Apple makes a lot from selling its products. Non-operating income includes things like interest or dividends. Apple might get such income from its investments.
Revenue Recognition Principles
According to U.S. GAAP, revenue should be recorded when it's earned and can be measured. This rule keeps financial reports honest and consistent. It makes sure income statements show real earnings times. This helps in better understanding a company's financial health and making wise economic choices.
| Financial Metric | Apple Inc. (2017) | J.C. Penney (2018) |
|---|---|---|
| Total Operating Revenue | $229 billion | $12.5 billion |
| Non-Operating Income | Interest & Dividend Income | Net Interest Expense |
| Total Net Income | $48.4 billion | -$116 million |
The table shows the effect of focusing on operations on a company's revenue and profit. Apple, with high operating revenue, has strong sales. Meanwhile, J.C. Penney faces profitability issues due to high non-operating expenses. Analyzing the income statement well offers deep insights into how a company is doing. It helps stakeholders make informed decisions.
How Revenue Is Reported
Learning about revenue recognition on financial statements is key to understanding a company's financial wellness. The income statement is critical in showing how revenue affects a company's financial situation.
Reporting Revenue on the Income Statement
When revenue appears on the income statement, it splits into operating and non-operating types. This split is crucial. It lets investors see how well a business runs at its core. Take Microsoft's quarterly earnings up to March 31, 2024, as an example. They showed a revenue of $61.9 billion from different products, highlighting the power of revenue reporting methods.
Direct vs. Indirect Revenue Reporting
Companies use both direct and indirect ways to share revenue info. This approach ensures financial clarity. Direct revenue comes from the main business operations, whereas indirect revenue might come from things like interest. Grasping these differences is crucial for a true revenue impact on the income statement.
| Revenue Category | Examples | Impact on Income Statement |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Revenue | Sales revenue (product sales, service fees) | Primary indicator of business performance |
| Non-Operating Revenue | Interest, dividends, royalties | Supplemental to main business activities; varies by period |
| Additional Revenue Streams | Subscriptions, grants, asset sales | Can signal growth or diversification of revenue sources |
Total revenue includes both regular and one-time revenue types. It's found by multiplying the average sale price by the number sold. This figure is a big deal for companies. It affects decisions about prices, new products, and entering new markets. It also shows directly on the revenue recognition on financial statements.
This knowledge lets finance pros get a complete picture of company health. They can adopt strong revenue reporting methods and stick to important standards. The Financial Accounting Standards Board's Topic 606 is one such standard. Following it helps depict an honest financial view of a company. This in turn helps people make well-informed choices.
The Relationship Between Revenue and Assets
Understanding how revenue affects a company's assets is key. Revenue, when well-managed, affects the balance sheet positively. It impacts asset growth and the relationship between assets and revenue.
How Revenue Impacts Asset Valuation
Revenue generation has a clear link to asset valuation. More sales can increase cash or accounts receivable. This change is reflected on the balance sheet. Stakeholders, like investors and analysts, rely on these numbers to make decisions. They look at asset valuation to assess a company's health and future.
Revenue Generation and Asset Growth
Revenue and asset growth are connected. Successful companies turn sales into tangible assets. This shows good financial management. The rate of this conversion is crucial for investors. It shows how efficiently a company operates.
An illustrative table shows how revenue changes affect assets:
| Revenue Increase (%) | Change in Cash Assets ($) | Change in Accounts Receivable ($) | Total Asset Growth ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 20,000 | 15,000 | 35,000 |
| 10% | 45,000 | 30,000 | 75,000 |
| 15% | 70,000 | 50,000 | 120,000 |
This table shows how more revenue increases asset categories. It shows a clear pattern of asset growth with increased revenue. These insights are vital for informed financial decisions and growth strategies.
Debunking Common Accounting Myths
It's vital to correct common accounting mistakes to keep financial records straight. Many people get confused about where to put revenue in financial statements. This confusion can lead to poor decision-making and errors in financial reports.
Misconceptions About Revenue on Balance Sheets
Many think revenue belongs under assets on a balance sheet. However, revenue from sales or services goes on the income statement. Revenue vs. assets must be clearly understood. It affects the equity section through retained earnings, not just the asset accounts like cash or receivables.
The Difference Between Revenue and Assets
Mixing up revenue and assets can mess up financial analysis and choices. Assets are controlled by a company because of past events and are expected to bring in future benefits. Revenue is what the company earns from main activities, such as selling goods or services. Knowing how they differ on financial statements helps avoid mistakes and gives a clearer view of a company's financial health.
Key Takeaways:
- Revenue is shown on the income statement, separate from assets on the balance sheet.
- It's crucial to know the difference between assets and revenue to keep financial statements accurate.
- Performing regular reviews, using detailed financial checks, and maybe getting professional accounting help can prevent errors and keep records accurate.
So, correcting the idea of revenue vs. assets is about more than fixing entries. It's about building strong financial habits. These habits lead to smart decisions and growth for businesses.
The Impact of Revenue on Financial Ratios
Understanding how revenue affects financial ratios is key for analyzing a company's health. Latest accounting rules, like ASC 842, have changed how we look at these numbers. This change affects important measures like the debt-to-equity ratio and profitability scores.
Key Ratios Involving Assets and Revenue
Financial ratios such as debt-to-equity and current ratio are deeply shaped by revenue reporting. For example, ASC 842 makes companies list more assets and liabilities. This has a big impact on leverage and liquidity ratios. These ratios are crucial for assessing profitability and overall business performance metrics.
Assessing Business Performance Through Ratios
Revenue's effect on financial ratios tells us a lot about a company's financial and operational strength. With ASC 842, the way revenue is reported changes performance metrics. For example, profitability ratios change due to how leases are handled. This changes the earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT).
So, understanding the relationship between revenue and financial ratios highlights how accounting standards affect a company's story. By paying close attention to these changes, stakeholders get a clearer picture of the company's financial health and strategy.
Long-term vs. Short-term Assets
Knowing if assets on a balance sheet are short-term or long-term is key for managing them well. This depends on how quickly an asset can turn into cash. The speed at which assets can be converted affects the company's finances and planning.
Differentiating Between Asset Types
Current assets, like cash and inventory, are used or turned to cash within a year. They help with daily operations and meeting short-term debts. Non-current assets, such as real estate and equipment, are used over many years. They are vital for the company's long-term success and big projects.
The Influence of Revenue on Asset Classification
How much money a company makes influences asset classification. More revenue can increase current assets, like cash and what customers owe. This makes a company more liquid. Being more liquid helps a company quickly take advantage of new opportunities or pay debts. This shows how making money and managing assets are connected.
Managing assets based on their liquidity and role is key. Doing this well leads to strong company finances.
| Asset Type | Examples | Liquidity | Impact of Increased Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current Assets | Cash, Accounts Receivable, Inventory | High | Increases in liquidity; can improve immediate financial flexibility |
| Non-Current Assets | Land, Buildings, Equipment | Low | Long-term investment; less immediate liquidity but essential for sustained growth |
Understanding current vs. non-current assets and their effect on liquidity of assets is crucial. It helps create asset management strategies that boost short-term and long-term growth.
Accounting Standards and Revenue Reporting
In today's financial world, sticking to rules like GAAP and IFRS is key. These rules help companies manage their money reports right. They make sure everything is reported correctly and follows the law.
GAAP vs. IFRS: Differences in Revenue Treatment
GAAP and IFRS are key to reporting money across borders. They set how to recognize, measure, and share revenue info. GAAP uses strict rules for reporting. IFRS focuses more on the deal's true nature.
The Importance of Compliance with Standards
Following GAAP and IFRS is crucial for businesses. It keeps things clear and builds trust with investors. It also avoids legal problems and bad reputations.
| Key Element | GAAP | IFRS |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue Recognition | Focused on specific rules for scenarios | Based on broader principles assessing contract terms |
| Financial Reporting Frequency | Quarterly and annually | Annually, with interim reporting as needed |
| Example Case | Revenue from sale of goods recognized upon delivery | Revenue recognition at the point of transferring control and benefits |
The examples in FSP 33-1, FSP 33-2, and FSP 33-3 show how different deals are handled. For example, FSP 33-1 treats the sale of demo cars as revenue. FSP 33-3 does the same with patent sales, but only in routine cases. This shows how context matters in financial reporting.
Knowing and using these standards is crucial for clear financial reports. Look at ExxonMobil's detailed numbers. They show not just health but also strict rule-following. Good financial reporting is key to managing money and keeping investors happy.
Case Studies: Revenue and Balance Sheets
Looking at financial statement analysis through case studies shows trends and changes in corporate financial strategies. It's key to understand real-world financial checks using actual company data for investors and financial pros. We'll closely review how big companies show revenue on reports and its effect on balance sheets.
Analyzing Real Companies' Financial Statements
Amazon's report format starts with the cash flow statement. It details operations, investments, and financing. This setup and detailed breakdown aid financial statement analysis a lot. Let's look into Amazon's financial activities:
- Operating activities show key aspects like depreciation and stock-based pay.
- Investing activities include big sales of securities and buying other companies.
- Financing activities shed light on managing debt and lease duties.
The analysis digs into operations and spotlights corporate financial strategies Amazon uses. These strategies help keep its balance sheet healthy and support growth.
Lessons Learned from Financial Reporting
By examining real-world financial evaluation, we learn from how top companies handle their money. Key insights from Amazon’s report include:
- Net product sales and services shape the revenue model, focusing on areas like tech and marketing costs.
- Interest income and expenses are carefully figured out, affecting net income before and after tax.
- Liquidity and leverage ratios give a clear view of Amazon's financial strength short-term and long-term.
- The efficiency ratios, like how quick assets and inventory turn over, show how well Amazon uses its assets.
Joining these dots, it’s clear that in-depth financial analysis helps peel back the layers of complex financial data of big companies. Also, evaluating these details offers essential insights for optimizing corporate financial plans. Thus, it guides making smart choices that boost value and secure lasting growth amidst competition.
Conclusion: The Interplay of Revenue and Assets
We've thoroughly explored how revenue and assets are linked. This link shows a company's financial health. Revenue doesn't sit with assets on the balance sheet. Instead, it affects asset values and shareholder equity over time.
Changes in net income and expenses affect both the balance sheet and cash flow statements. It's crucial to understand financial statements well.
Summarizing Key Takeaways
We found that net income and expenses impact retained earnings and cash flow. For example, consider Clear Lake Sporting Goods. It had a net income of $35,000 and starting retained earnings of $15,000.
After a $30,000 dividend payout, we see how fluid financial statements are. Capital expenditures also influence property and equipment accounts, affecting investing cash flow.
Future Trends in Revenue Reporting and Asset Management
Looking ahead, technology and new standards will change how we manage finances. Using past financial data is crucial for predictions. Clear Lake Sporting Goods' reports, covering three years, are a good example.
Net working capital adjustments and financing events show the link between revenue, cash management, and asset valuation. For those in finance, getting this broader perspective is key to success and innovation in financial data use.
FAQ
Does revenue go under assets on a balance sheet?
No, revenue does not fall under assets on a balance sheet. Instead, it appears on the income statement. It impacts the balance sheet through cash or accounts receivable and equity via retained earnings.
What are the components of a balance sheet?
A balance sheet shows assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity. These elements give a full view of a firm's financial state at a certain time.
How are liabilities defined in financial statements?
Liabilities are what a company must pay in the future. They are split into current liabilities, payable within a year, and long-term liabilities, payable after a year.
How does revenue impact a company's equity?
Revenue boosts retained earnings after expenses are taken out. This is part of shareholder equity on the balance sheet, showing in the company's net worth.
What is the difference between operating and non-operating revenue?
Operating revenue comes from core business activities, like product sales. Non-operating revenue comes from things like investments, not related to the main business.
Why is revenue not directly reported on the balance sheet?
Since revenue shows a firm's performance over time, it belongs on the income statement. The balance sheet, on the other hand, gives a snapshot of financial standing at a certain point.
What financial ratios involve revenue and assets?
Ratios like return on assets (ROA) and asset turnover show how well a company uses its assets to make money.
What is the significance of classifying assets on the balance sheet?
Putting assets as current or non-current shows a company's liquidity. It tells us how quickly assets can turn into cash for immediate needs.
How do accounting standards like GAAP and IFRS affect revenue reporting?
GAAP and IFRS give rules for recognizing revenue. They ensure reports are consistent, clear, and accurate, which is critical for comparing financial statements.
Why is compliance with revenue reporting standards important?
Following standards like GAAP or IFRS keeps financial reports trustworthy. This builds investor confidence to make investment decisions in a company.
What insights can be gained from analyzing other companies' financial statements?
Studying other firms' financial statements uncovers useful revenue reporting and balance management methods. It reveals ways to grow and plan finances better.
How do trends in revenue and asset management affect financial reporting?
Trends like new technologies and evolving accounting rules can influence financial reports. They change the way revenue and assets are recognized and reported.