Define Revenue Account: Understanding the Basics
Defining a revenue account in accounting shines light on a key part of financial reporting for businesses. They record the income from daily operations and extra activities. Managing these accounts right ensures compliance and gives businesses helpful insights.
These accounts keep track of money from sales and services. This is vital for a business's financial health. The income statement shows revenues, a crucial metric as pointed out by the Corporate Finance Institute. It shows how well a company sells and its market position. Microsoft made an impressive $61.9 billion in Q3 of 2024, showing the importance of managing revenue streams well, no matter the business size.
Revenue accounts include both operating and non-operating revenues. Operating revenues come from main activities like sales. Non-operating revenues come from other sources like rent. Understanding these helps in planning and carrying out strategic decisions based on solid financial benchmarks.
Revenue accounting's complexity involves different transactions. This requires advanced software for easy tracking. But the basic rules of accounting still apply. Revenues increase with credits and decrease with debits. This keeps financial stories clear and coherent.
In deep analysis, revenue accounts are more than just number storage. They tell the story of a business's financial journey. This story needs careful and insightful recording.
Key Takeaways
- Revenue accounts catalogue the income from core and auxiliary business activities, establishing a base for financial health.
- Operating revenues emerge from principal operations like sales, while non-operating revenues come from secondary sources.
- Microsoft's 2024 Q3 revenue underlines the importance of segregating diverse revenue streams for analytical clarity.
- The fundamental tenet of revenue accounts is their increase through credits and decrease through debits, maintaining the ledger's balance.
- Effective revenue management using contemporary accounting software can dramatically enhance financial accuracy and insight.
- Analyzing revenue accounts is vital for strategic business decisions, influencing everything from budget allocations to investment strategies.
- A deep understanding of various revenue accounts helps in accurately calculating a company's profitability and market valuation.
What is a Revenue Account?
"What is a Revenue Account?" This question points to the need to grasp its essence in financial systems. Revenue accounts are key in noting the income a firm earns, whether through selling products or providing services.
Definition of Revenue Account
A revenue account is vital for tracking money inflows from company activities, mainly from sales or services. It is where businesses jot down every transaction that boosts (credits) or cuts (debits) their income. To put it simply, a revenue account is crucial in financial statements. It records business earnings before taking out costs or expenses to find the net income.
Purpose of Revenue Accounts
Revenue accounts do more than just track; they analyze how well marketing and sales plans are working. These accounts give insight into a business's operational success. They help in making key decisions by breaking down income sources. They play a big part in:
- Looking at income types by department or product.
- Evaluating new projects or investments financially.
- Adjusting strategies by watching revenue trends.
Moreover, revenue accounts are crucial for continuously updating a company's financial approach. This ensures a business can adapt to market changes or shifts in its operations.
Types of Revenue Accounts
It's crucial for businesses to understand the different types of revenue accounts. Seeing the difference between operating revenue and non-operating revenue is key. It splits the main financial activities from extra income, giving a clear financial story. This clarity is vital for accurate analysis and smart management.
Operating Revenue Accounts
Operating revenues form the core of a company's finances. They come mainly from the business's main operations. For example, a retail store records sales of goods as operating revenues. Service companies, like consultancies, note service revenue as a big part of their operating income. These figures show if a business can make money from its main work, which is critical for planning and growth.
Non-Operating Revenue Accounts
Non-operating revenue is money made from side activities. This includes interest income, dividends, or profits from selling an asset. Even though it's usually less steady and smaller than operating revenue, it's still important. It clues in on possible investment opportunities and strategies.
Handling both revenue types correctly is a must for businesses. Operating revenue shows how healthy and competitive a business is. On the other hand, non-operating revenue can help soften the blow of business slumps. Hence, the use of advanced accounting software is growing. It can handle up to 75% of accounting work, ensuring accurate tracking and reporting.

Importance of Revenue Accounts in Accounting
Revenue accounts play a huge role in making financial matters clear and accurate for businesses. They help companies keep their finances in check and move quickly on decisions.
Financial Reporting
The accuracy of accounting revenue accounts is crucial for financial experts. These accounts shed light on where a business's money comes from. This helps with following rules and showing true financial status to those interested.
They're key for sticking to standards like FASB's Topic 606. This ensures stakeholders get a real picture of financial health.
- Monitoring Revenue Streams: Financial statements clearly show various types of income. This clarifies where money comes from.
- Automated Solutions: Modern billing systems make revenue accounting smoother by automating tasks. This cuts down mistakes.
- Materiality Consideration: Focusing on important financial facts helps in making smart choices. It highlights key financial information.
Business Decision Making
Accounting revenue accounts are vital for smart business choices. They're the base for planning, predicting future finances, and looking into new chances for investment. Managing these accounts well ties directly to saving money and making more profit.
| Revenue Source | Description | Annual Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Sales | Income from goods sold or services rendered | Direct reflection on Gross and Net Annual Revenue |
| Rent Revenue | Income from property leases | Affects both operating and non-operating segments |
| Dividend Income | Returns on shareholdings in other companies | Typically recorded under non-operating revenue |
| Interest Revenue | Earnings from interest on investments | Classified under non-operating revenue for clearer financial analysis |
| Sales Return and Discounts | Adjustments reducing initial sales figures | Reflected in Net Annual Revenue to provide realistic financial outlook |
Doing revenue accounting well is powerful for guiding a company's direction and growing steadily. Teams in finance use their knowledge on managing revenue and recognizing it properly. This leads to better business operations and higher profits.
How Revenue Accounts Impact Financial Statements
Revenue accounts deeply affect how we see a business's financial story. They play a key role in the income statement and balance sheet. Understanding this helps stakeholders make better decisions.
Income Statement Significance
On the income statement, revenue is the start. From there, we subtract costs to find net income. Take Microsoft's fiscal year ending June 30, 2023, as an example. Microsoft made a gross margin of $171.0 billion. After taking out costs for research, sales, and more, its total expenses were $135.7 billion. This led to an operating income of $109.4 billion. These numbers show how managing costs after making revenue is crucial for profit.
Balance Sheet Relation
When we look at the balance sheet, revenue affects assets and liabilities. Good revenue growth increases asset values, seen in cash and investments. Standards like GASB Statements 3, 28, 31, and 40 require clear reports on asset management. It's important to balance cash on hand and receivables for a stable financial picture.
| Financial Metrics | FY 2022-2023 ($ in billions) |
|---|---|
| Total Gross Margin | 171.0 |
| Operating Income | 109.4 |
| Research & Development Expenses | 29.5 |
| Sales & Marketing Expenses | 24.4 |
| General & Administrative Costs | 7.6 |
Looking at the income statement and balance sheet together shows the broad impact of revenue performance. Every number tells a story of business health and strategy. It's vital for understanding the company's current state and future direction.
Recording Revenue in Accounts
Recording revenue is key for correct financial statements. It must follow accounting rules. The method used changes with the accounting system.
Understanding when to record revenue is very important. It helps in accurately managing and reporting money matters.
Revenue Recognition Principles
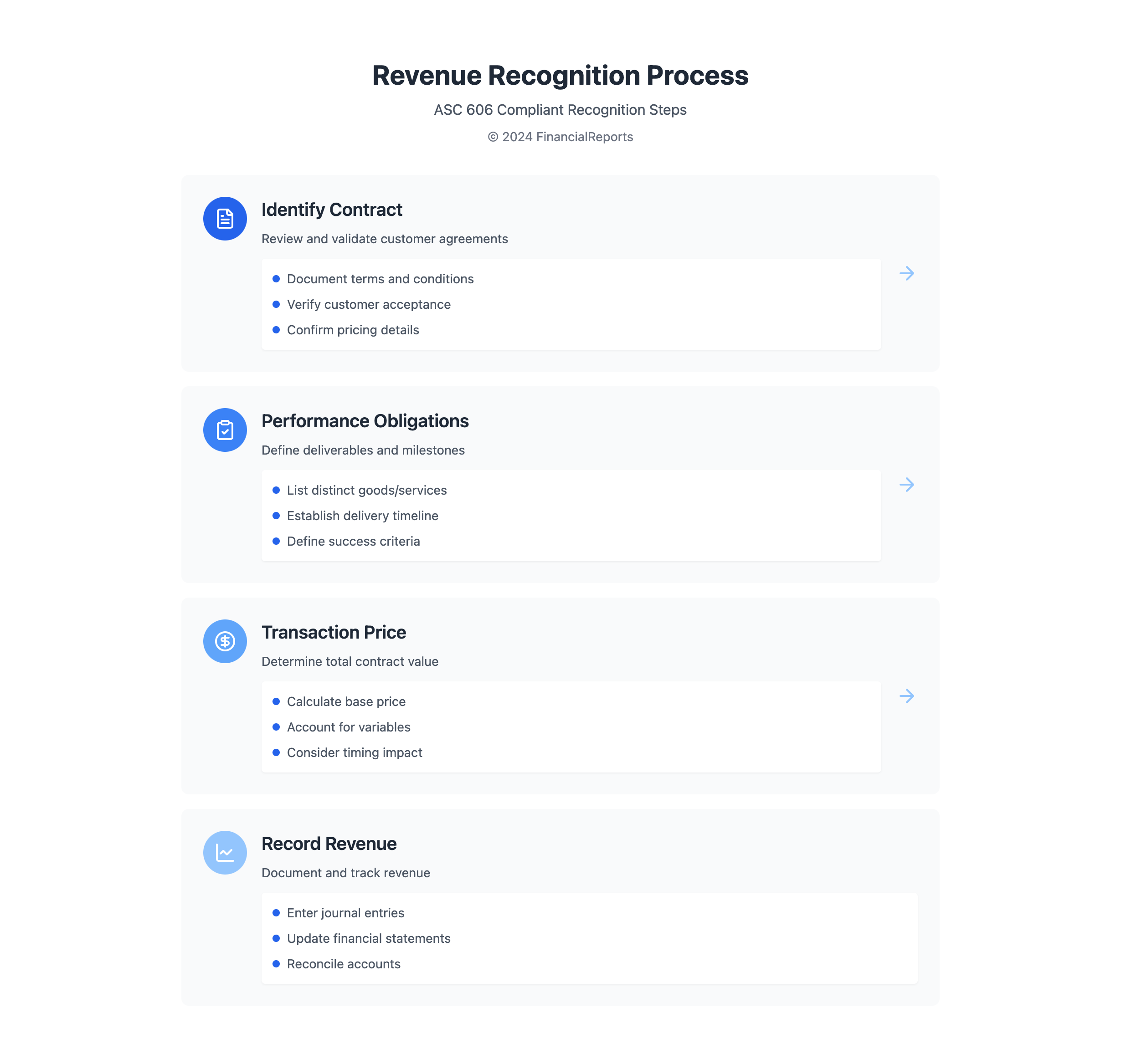
Revenue recognition has complex rules. They make sure revenue reflects business transactions accurately. The rules come from ASC 606. They say revenue is recorded when goods or services are given to the customer.
ASC 606 has five important steps. They help in recording revenue correctly. This ensures accurate financial reporting.
Common Methods of Recording Revenue
Choosing how to record revenue is crucial. It affects how a company's finances are seen. Accrual accounting is suggested by GAAP. It records revenue when it is earned, not just when cash is received.
This means revenue for provided services is recorded when they are done. Cash-basis accounting is simpler but not as accurate. It records revenue only when cash is received.
| Revenue Type | Recognition Under Accrual Accounting | Recognition Under Cash-Basis Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Tuition Revenue | Over the corresponding term for which it is earned | When payment is received |
| Sponsored Program Revenue | As expenses are incurred | When cash is received |
| Commonwealth Appropriations | Monthly on a straight-line basis over the fiscal year | When funding is received |
| Contributions | In the period received, including unconditional promises to donate at estimated net present value | When donation cash is received |
The approach to recording revenue meets revenue recognition principle needs. It greatly improves the clarity and reliability of financial reports. This lets stakeholders understand an organization's financial status better.
Differences Between Revenue and Income
Understanding the differences between revenue and income is key to knowing a business's financial health. This section uses real data to explain these differences. They're vital for figuring out profits.
Revenue Defined
Revenue is the total money a business makes before any costs are subtracted. It's the starting point for calculating profits. It includes money from selling goods or services. For example, Apple's total revenue in Q4 of 2023 was $119.5 billion. This shows how much it sold before paying any expenses.
Income Defined
Income, or net income, comes after deducting all costs from revenue. It shows how much profit a company makes after paying its bills. Apple's net income in Q4 of 2023 was $40.3 billion. This was after paying for sales costs, operating expenses, and taxes.
Comparing these numbers helps us see how well Apple turns revenue into profit. To understand better, let's look at a table. It compares revenue and income of Apple with smaller businesses. This shows different benchmarks in various industries:
| Entity | Annual Revenue | Total Expenses | Net Income |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple Inc. (Q4 2023) | $119.5 billion | $86.3 billion | $40.3 billion |
| Small Restaurant (Annual) | $500,000 | $450,000 | $50,000 |
| Individual Investor (Annual) | $10,000 | $3,000 | $7,000 |
This analysis shows how revenue and income differ depending on the business size. It highlights the need for good cost management and planning. Even with high revenues, net income is what really shows if a business is doing well financially. It's crucial for smart business decisions.
Key Terms Related to Revenue Accounts
In finance, revenue accounting terms are crucial. They include sales revenue and service revenue. These are key for evaluating a company's performance. They help track and analyze revenue, offering insight into an organization's financial health.
Sales Revenue
Sales revenue comes from selling goods, like products or digital items. It's vital for a company's profits and success. The formula is simple: the number of units sold times the average price per unit. For example, selling 10,000 units at $150 each equals $1.5 million in sales.
From giant companies to small ones, everyone tracks sales revenue. It aids in planning and making necessary adjustments. Like Amazon's $118.6 billion product sales in 2017 show the importance of keeping an eye on sales figures.
Service Revenue
Service revenue comes from providing services, not physical products. It's usual in finance, insurance, IT, and consulting. Companies in these fields rely on their knowledge and specialized services to earn. Think of a cloud company charging $100 for a service to 1,000 clients. That's $100,000 right there.
This approach matters where selling goods isn't the main game. Service quality and client happiness are what count.
Knowing revenue accounting terms is essential for financial work or business management. Terms like sales revenue and service revenue ground income statements. They are the base for strong financial reports and wise business moves.
Challenges in Managing Revenue Accounts
Modern accounting standards such as ASC 606 bring big challenges in revenue management and accurate reporting. Companies must follow revenue recognition guidelines closely to keep their financial reports true and reliable. Not doing so can lead to misleading stakeholders and messing up financial decisions.
Ensuring Accurate Reporting
Reporting accurately depends on identifying and meeting performance obligations on time. The point when revenue is recognized is key. This depends on careful analysis of when obligations are met in business deals.
For instance, identifying the right standalone selling prices (SSP) and handling contract changes often requires deep knowledge of complex principles. This process is vital for accurate revenue reporting.
Revenue Recognition Issues
Revenue recognition becomes more complex with large transaction volumes and connecting adjustments to original financial events. Keeping consistent internal data records helps avoid mismatches between calculated billings and financial reports. This is crucial in a global market, where currency changes affect financial statements in different currencies.
In specific sectors like automotive and consumer products, the challenges are even more complex. For example, automotive companies handle yearly price reductions in contracts. Meanwhile, consumer products companies face retailer allowance issues, affecting how revenue is recognized.
Handling revenue properly as a finance professional means recording revenue net of price, volume, and mix effects. This clarity is essential for understanding revenue trends correctly.
Thus, tackling these challenges requires a strong, integrated method. It must ensure accurate reporting and follow revenue recognition rules. It also needs to adjust to the ever-changing demands of global markets and different industries.
Best Practices for Revenue Accounting
Using smart revenue accounting methods is key for true financial reports. This helps trust in a company's financial statements grow. By keeping up with regular checks and neat records, firms can be more clear and follow rules better.
Regular Reconciliation
Checking your books often is a big part of good revenue management. It's important for making sure that what's in the books matches the real bank activity. A lot of finance leaders, about 40%, say they spend more than 10 hours every month just on this task. This hard work helps find and fix mistakes that could mess up financial understanding.
The reconciling work means making sure your ledger and bank statements agree. This is super important for any business that deals with a lot of money moving around.
Proper Documentation
Keeping good records is crucial for revenue accounting. It not only keeps you in line with laws like GAAP and ASC 606 but also helps during audits. A solid plan for documenting includes recording transactions right away, following a certain model for recognizing revenue, and keeping important papers like contracts and receipts.
This careful way of handling records makes sure financial reports are accurate. This supports important business choices and plans for the future.
- Transaction Records: Keep detailed notes of all money matters, with dates and types clearly marked.
- Contracts and Agreements: Hold onto signed deals showing how revenue will be handled, which are key for figuring out prices and duties.
- Auditing Trails: Make detailed audit paths that help with both outside and inside checks, increasing trust and clarity.
Putting these key steps in revenue accounting into your daily work can greatly help with getting financial reports right and making money matters more efficient. By giving extra attention to regular checking and keeping neat records, companies set themselves up for smoother audits, keeping up with rules, and laying a strong base for smart business decisions.
Conclusion: The Role of Revenue Accounts in Business Success
Managing and analyzing revenue accounts is key for any business's financial health and growth. Revenue is what a company earns from selling products and services, before taking out expenses. It shows how good a business is at making money and where it can improve. Let's look back at why revenue accounts are so important for success.
Summary of Key Points
Revenue accounts are vital for keeping track of money, helping businesses update their income reports often. Using smart pricing strategies can greatly increase income. This is seen in industries like ridesharing and hotels. Having different ways to make money also adds stability against market changes.
Businesses can better manage their revenue with the help of analytics and technology, like ERP and CRM systems. This boosts sales and marketing efforts and ensures spending matches earning, following accrual accounting rules.
Future Considerations in Revenue Accounting
The future of revenue accounting will be influenced by new rules, creative pricing, and more data for forecasting. Companies need to stay flexible and up-to-date with their financial tracking. Embracing new rules and advanced accounting tools helps maintain clear and correct financial records. This link between making more money and staying profitable highlights revenue accounts' role in long-term success.
FAQ
What is the definition of a revenue account?
A revenue account helps track the money a business makes. It includes income from sales or services in financial reports. This account shows how much benefit a company gets in an accounting period. It's like the starting point on an income statement.
What is the purpose of revenue accounts?
Revenue accounts help keep track of money made from a company's main activities. They show how well sales and marketing efforts are working. This info is key for making good business decisions and figuring out net income.
What are examples of operating revenue accounts?
Operating revenue accounts cover income from main business activities. This includes money from services, merchandise sales, or making products. They are crucial to understanding a business's core operations.
What are non-operating revenue accounts?
Non-operating revenue accounts cover secondary income. This includes earnings like dividends, interest from investments, or asset sales. It captures money made outside of day-to-day business operations.
How do revenue accounts play a role in financial reporting?
Revenue accounts detail the financial gains of a company in reports. They are essential for assessing a company's performance. They also meet regulatory needs and show the company's financial health to its stakeholders.
How can business decision-making be influenced by revenue accounts?
Revenue accounts offer insights into how well a company is selling and growing. By examining these accounts, businesses can plan their budgets and strategies better. This helps in making smart choices for profit and operations.
Why is the income statement significant in the context of revenue accounts?
The income statement starts with revenue and subtracts costs to find net income. Revenue accounts affect the top line, impacting the company's profitability. This shows how vital they are in the big picture of business finance.
How do revenue accounts relate to the balance sheet?
Revenue accounts impact the balance sheet by changing assets and liabilities. Recognized revenue can boost assets or lower liabilities. These changes reflect in the overall financial health on the balance sheet.
What are the principles of revenue recognition?
The principles of revenue recognition involve identifying customer contracts and their obligations. It includes setting the price and recognizing revenue when obligations are met. These rules guide how revenue is recorded accurately.
What are some common methods for recording revenue?
Revenue recording often uses journal entries by crediting sales. Cash or other accounts may be debited depending on the situation. The revenue is recognized based on cash received or accrual methods, which depend on service delivery or payment timing.
How do revenue and income differ?
Revenue is the total money made before taking out any expenses. Income is what's left after paying all costs associated with making that revenue. So, while revenue shows gross earnings, income shows the net earnings.
What distinguishes sales revenue from service revenue?
Sales revenue comes from selling goods, sometimes adjusted for discounts or returns. Service revenue comes from providing services, varying by industry and service type. The key difference lies in what the customer is paying for.
What challenges do companies face in managing revenue accounts?
Companies struggle with ensuring their reporting and recognition guidelines are correct. Mistakes can lead to wrong financial results and decisions. Accurate timing and recording are crucial to prevent such issues.
What constitutes best practices in revenue accounting?
Good revenue accounting involves regularly checking revenues against actual transactions. It requires keeping accurate sales records and following revenue recognition rules closely. These practices help ensure honesty and compliance.