Calculating the Cost of Preferred Shares: The Formula
The cost of preferred shares is the return needed by preferred shareholders. It's found by dividing the annual dividend by the current market price. This is key for companies to find the best way to get capital. It also helps in figuring out the Weighted Average Cost of Capital.
Knowing the cost of preferred shares formula is important for finance experts and investors. It helps them make smart choices about investments and funding. Preferred stock is seen as safer than common stock. Its value is found using the formula, which divides the annual dividend by the market price per share.
Key Takeaways
- The cost of preferred shares formula is calculated as the annual preferred dividend paid out divided by the current market price.
- The cost of preferred shares is a key part of the Weighted Average Cost of Capital calculation.
- Preferred stockholders get dividends and payments first in case of liquidation.
- The cost of preferred shares helps figure out the cost of capital. This is important for companies to find the best way to raise capital.
- The cost of preferred shares formula is Rp = D (dividend) / P0 (price). It's a basic idea in corporate finance.
- Understanding the cost of preferred shares formula is key for finance experts and investors. It helps them make informed decisions about investments and funding.
Understanding Preferred Shares
Preferred shares are a type of equity used for funding projects or developments. They offer more flexibility than common equity and debt. To calculate the cost of preferred stock, knowing the characteristics of preferred shares is key.
Preferred shares get priority in dividend payments and asset claims, making them safer than common stock. But, they usually don't give voting rights, which might not appeal to all investors. Knowing how to calculate preferred stock is vital for investors to gauge their investment's return.
Definition of Preferred Shares
Preferred shares are a mix of equity and debt, representing a claim on a company's assets and earnings. They rank higher than common stock but lower than debt, making them unique.
Characteristics of Preferred Shares
Some key traits of preferred shares include:
- Priority in dividend payments
- Claims on assets
- No voting rights
- Fixed dividend payments
Knowing these traits is critical for investors. It helps them make smart choices when figuring out how to calculate preferred stock and its return.
Importance of Cost of Preferred Shares
Figuring out the cost of preferred stock is key for companies to find the best way to get capital. It's a big deal in corporate finance because it shapes how a company gets money and what it owns. Preferred stockholders get dividends or assets before common stockholders, but not as much as bondholders.
The cost of preferred shares is important for a company's overall financial plan. Companies use different ways to get money, like debt, common shares, or preferred shares. Knowing the cost of preferred shares helps management decide how to finance their plans. The calculation includes things like dividends, current price, and growth rate.
Impact on Corporate Financing
The cost of preferred shares can change how easy it is for a company to get money. A high cost might mean a company is seen as risky. But a low cost could show the company is stable and attractive to investors.
Comparison with Common Shares
Preferred shares are different from common shares. They don't get to vote much, but they get dividends or assets first. The cost of preferred shares is fixed, unlike common shares which can change. Knowing these differences helps investors and companies make smart choices.
The Basic Formula for Cost of Preferred Shares
The cost of preferred shares formula is key in finance. It shows the return needed by preferred stock holders. To find this, we use: Cost of Preferred Stock = Preferred Stock Dividend Per Share (DPS) / Current Price of Preferred Stock. This formula is vital for investors and finance experts.
The formula's main parts are the dividend per share (DPS) and the current price of the stock. First, we figure out the DPS. Then, we use the current price per share (PPS) to find the cost. This cost is a percentage, making it easy to compare with other investments.
Breakdown of the Formula
The formula has two main parts: DPS and PPS. DPS is the yearly dividend to the preferred shareholder. PPS is the stock's current market price. Dividing DPS by PPS gives us the cost of preferred stock. This shows the return needed by the stock holder.
Key Variables Explained
The table below explains the key variables in the cost of preferred shares formula:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| DPS | Dividend per share, which is the annual dividend payment made to the preferred shareholder |
| PPS | Current price per share, which is the current market price of the preferred stock |
| Cost of Preferred Stock | Rate of return required by the holder of the preferred stock, calculated by dividing the DPS by the PPS |
Knowing the cost of preferred shares formula is critical for investors and finance pros. It helps them compare returns with other investments. By using this formula, investors can make better choices and improve their portfolios.
Components of the Cost of Preferred Shares
To figure out the cost of preferred stock, we need to look at its parts. The cost is what a company pays for the money it gets from selling these shares. It's found by dividing the annual dividends by the total money from the stock issue.
The dividend per share (DPS) is usually a set percentage or amount. For example, if a company's preferred stock pays $4 a year and costs $25, the cost is 16%. This is found by dividing the yearly dividends by the stock's current price.
Dividend Payments
Dividend payments are key in the cost of preferred shares. Preferred stock often has higher and more regular dividends than common stock. This gives investors a steady income. The cost of preferred stock formula includes the annual dividends, the stock's current price, and sometimes a growth rate.
Market Value Considerations
Market value is also important in figuring out the cost of preferred shares. The stock's value is the present value of its dividends, with a discount rate for risk and opportunity cost. Knowing how to calculate preferred stock involves these market value factors for smart investment choices.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Dividend Payments | Annual dividends paid on preferred shares |
| Market Value Considerations | Current market price of the stock and discount rate |
How to Calculate Cost of Preferred Shares
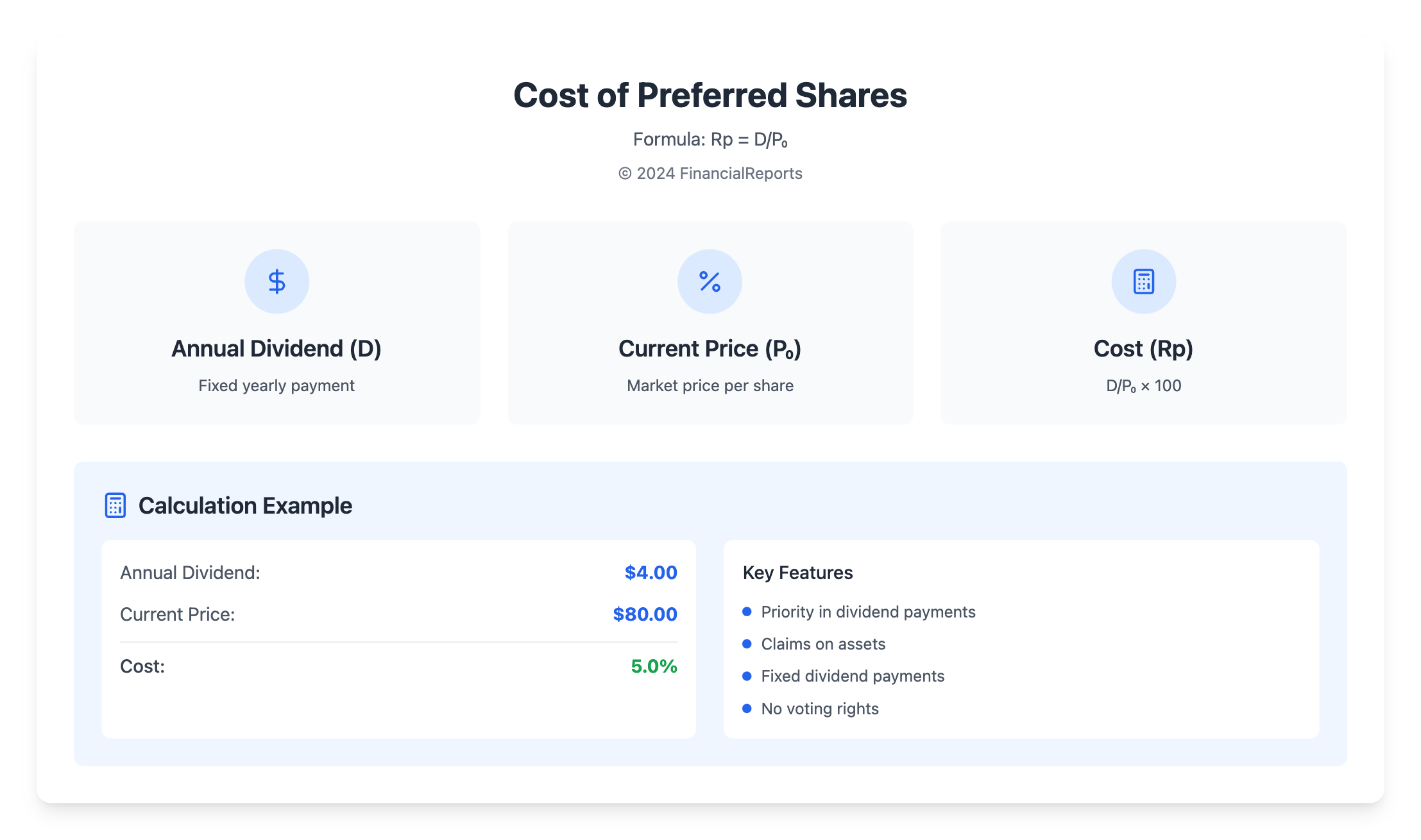
To figure out the cost of preferred shares, you need to know the formula and its parts. The cost of preferred stock calculation is key to finding the value of these shares. The formula is: Cost of Preferred Stock = Annual Dividend / Current Price.
For example, let's say a company's preferred stock has a fixed dividend of $4.00 per share. If the stock's current price is $80.00, the cost of preferred stock is 5.0%.
The calculation is simple. You just divide the annual dividend by the stock's current price. In our example, the dividend is $4.00 and the price is $80.00. This gives us a cost of preferred stock of 5.0%.
This calculation is vital for figuring out the value of preferred shares. It helps investors and financial experts make smart choices.
Here's how to do it step by step:
- Determine the annual dividend per share
- Determine the current price of the stock
- Divide the annual dividend by the current price to get the cost of preferred stock
Understanding the cost of preferred stock calculation is important. It helps investors and financial experts make informed decisions about their investments.
| Annual Dividend | Current Price | Cost of Preferred Stock |
|---|---|---|
| $4.00 | $80.00 | 5.0% |
Factors Influencing Cost of Preferred Shares
The cost of preferred shares is affected by many things, like market conditions and credit ratings. Knowing these factors is key to figuring out the cost of preferred shares formula. This formula considers the preferred dividends and the net issuing price. It's calculated as: Cost of Preferred Stock = Preferred Dividends / Preferred Stock Price.
Market conditions, such as interest rates and economic cycles, greatly influence the cost of preferred shares. Interest rates are very important because they can change the dividend yield investors expect. A company's credit rating also matters, as it can affect how easily it can issue preferred stock at a good price.
Other things that can change the cost of preferred shares include:
- Dividend rate
- Convertibility options
- Call provisions
These elements can alter the cost of preferred stock and a company's overall capital cost. By grasping these factors and applying the cost of preferred shares formula, companies can make better choices about issuing preferred stock and managing their finances.
Implications of High vs. Low Cost
Understanding the cost of preferred stock is key. A high cost can limit a company's financial options and raise its overall cost of capital. But, a low cost can help a company get more capital and boost its financial health.
To grasp the impact, knowing how to calculate preferred stock is vital. The cost of preferred shares is tied to the market interest rate. If interest rates go up, the value of preferred shares drops. This is because investors look for better returns elsewhere.
The benefits of a low cost of preferred shares include:
- Improved financial ratios
- Enhanced ability to raise capital
- Increased financial flexibility
But, a high cost of preferred shares can cause problems:
- Reduced financial flexibility
- Increased cost of capital
- Decreased ability to raise capital
| Cost of Preferred Shares | Implications |
|---|---|
| High | Reduced financial flexibility, increased cost of capital |
| Low | Improved financial ratios, enhanced ability to raise capital |

Adjusting Cost of Preferred Shares
It's key to keep the cost of preferred stock in check for a strong capital structure. Companies use different ways to manage and adjust this cost.
Refinancing Options
Refinancing preferred shares means swapping old securities for new ones with better terms. For example, a company might issue new preferred stock at a lower dividend rate if the market improves. This can cut the cost of preferred stock, improving financial flexibility.
Market Timing Strategies
Timing is everything when it comes to the cost of preferred stock. Issuing or buying back shares when the market is good can get better deals. For instance, issuing preferred stock when interest rates are low can lower costs, making capital management more efficient.
Common Mistakes in Calculation
Calculating the cost of preferred shares formula needs to be precise. Mistakes often come from not understanding key parts.
Misunderstanding Dividend Yield
Dividend yield is key in the cost of preferred shares formula. It's found by dividing the annual dividend by the current market price. For example, a $5 dividend on a $100 share gives a 5% yield. Getting this wrong can cause big mistakes in valuation.
Overlooking Market Value
Using par value instead of market value is a common error. Market value shows the real cost of preferred shares. For instance, if a preferred share is priced at $95 with a $5 dividend, the yield goes up to about 5.26%. Getting the market value right keeps the cost of preferred shares formula accurate.
Being precise with data is vital. Even a small mistake can change the cost analysis. This can affect investment choices and financial plans.
| Mistake | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Dividend Yield | Inaccurate cost estimation | Verify dividend and market price data |
| Using Par Value | Misvaluation of shares | Use current market value |
Real-World Applications of Cost of Preferred Shares
Knowing how to calculate preferred stock is key for companies and investors. It shapes their financing plans and investment choices. This ensures they perform well financially.
Case Studies from Corporations
Big names like Apple Inc. and Johnson & Johnson use the cost of preferred stock in their plans. For example, Apple issued shares with a 5% dividend rate at $105. This made their cost of preferred stock about 4.76%. This helps them balance their debt and equity, improving their WACC.
Investor Decision-Making
Investors use the cost of preferred stock to check their investment returns. By looking at the cost of preferred shares, they can compare different options. For instance, if a share has a higher dividend yield, it might be more appealing, as long as the company's credit is good.
Also, knowing the cost of preferred stock helps investors see a company's financial health. Preferred shareholders get paid first in dividends and in case of liquidation. This makes their investment safer.
Conclusion: Mastering the Cost of Preferred Shares
Understanding the cost of preferred stock is key in corporate finance and making investment choices. It helps see how a company's capital structure works. It also shows the balance between debt, equity, and preferred shares.
Knowing how to calculate the cost of preferred shares helps finance experts. They can make better choices about funding, look at investment chances, and improve their company's WACC. Private equity firms, for example, like the balance of risk and return in preferred stock.
The cost of preferred shares changes based on market conditions, credit ratings, and the stock's features. This includes if it can be converted or if it participates in profits. Finance teams need to keep up with these changes to manage the cost of capital well.
Being good at figuring out and understanding the cost of preferred shares is important. It lets financial leaders handle complex markets, make smart funding decisions, and help their companies grow. Using data and analysis can help your company get the most from its preferred stock investments.
FAQ
What is the cost of preferred shares formula?
The cost of preferred shares is found by dividing the preferred dividend per share by the current market price per share.
How do you calculate preferred stock?
To figure out preferred stock, learn about its key traits. These include its priority in getting dividends and its claim on assets.
Why is the cost of preferred stock calculation important?
Knowing the cost of preferred shares is key in finance. It helps in making financing choices, shaping a company's capital structure, and calculating its weighted average cost of capital (WACC).
What are the components of the cost of preferred shares formula?
The cost of preferred shares formula includes two main parts. These are the preferred dividend per share and the current market price per share.
How do dividend payments and market value affect the cost of preferred shares?
The cost of preferred shares changes with dividend payments and market value. Market value is affected by interest rates and credit ratings.
Can you provide an example of how to calculate the cost of preferred shares?
Yes, we can show how to use the formula with a real example. This will help you understand how it works in practice.
What factors can influence the cost of preferred shares?
Several things can change the cost of preferred shares. These include market conditions, like interest rates, and the company's credit and financial health.
How does the cost of preferred shares compare to the cost of other financing options?
Comparing the cost of preferred shares to other financing options is important. It helps understand their implications and how they stack up against common shares, debt, and other capital sources.
Are there strategies to adjust the cost of preferred shares?
Yes, companies can use strategies like refinancing and market timing. These can help improve the cost of their preferred shares and their overall capital structure.
What are common mistakes in calculating the cost of preferred shares?
Mistakes often include confusing dividend yield with cost of preferred shares. Also, forgetting to use the current market value instead of par value is a common error.
Can you provide real-world examples of how companies use the cost of preferred shares calculation?
Yes, we can look at case studies of companies. They show how the cost of preferred shares metric guides their financing and investment plans.