Another Name for the Income Statement | Key Financial Terms
The income statement is key for showing a company's financial health over a set time. It details everything from money made to money spent, showing if a company is making a profit or a loss. Another name for it includes Profit and Loss Statement or Statement of Operations. It turns net revenue into net earnings by factoring in revenue, expenses, gains, and losses.
Companies like Microsoft Corporation use income statements to give detailed financial reports to the SEC. These reports show important figures like gross margin and operating expenses. They help figure out numbers such as operating income. The importance of the income statement in financial reporting is huge, pushing us to make global financial data easier to access.
Key Takeaways
- The income statement is a principal financial statement, revealing a company's financial status over a reporting period.
- A multi-tiered analysis is often evident in multi-step income statements, providing different profitability measures such as gross, operating, and pre-tax income.
- Key financial metrics derived from the income statement, like Gross Profit and EBITDA, facilitate investor and creditor assessment of business health.
- Financial reporting standards by governing bodies like the SEC necessitate precise inclusion of elements on an income statement.
- Spanning from revenue generation to net income, the income statement encapsulates the financial outcome of company operations and strategic decisions.
- Advanced tools and software for income statement generation endorse efficient financial analysis and elevate reporting accuracy.
- Comprehension of income statement components is critical for financial professionals and investors focused on the technicalities of financial reporting.
Understanding the Income Statement
An income statement tracks a company's financial performance over time. It shows how revenue turns into net earnings. This happens after considering all costs and expenses of running the business. This document is key for looking into business management and its financial impact.
Definition of Income Statement
The income statement is also called the profit and loss statement. It's a report that adds up the revenues, expenses, and net earnings of a company. It reveals if a company made a profit or loss in a quarter or year. This report is crucial for showing how well a company is doing.
Purpose of the Income Statement
The main goal of the income statement is clear. It gives stakeholders a look into the company's financial and operational health. It plays a few important roles:
- Assessing Business Performance: It compares revenues to expenses to check efficiency and cost control.
- Informing Investment Decisions: Investors use it to decide if a company is worth investing in.
- Strategic Business Management: It guides decisions on budgeting, cost-saving, and growth plans.
Below is an example of an income statement from Coffee Roaster Enterprises Inc. It shows various financial metrics. This table and the numbers in it help us understand the income statement's real-world use.
| Financial Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Total Revenue | $57,050.68 |
| Gross Profit | $32,065.89 |
| Operating Income | $21,016.34 |
| Net Income | $6,016.34 |
| Gross Profit Margin | 56% |
This detailed look helps show the financial outcomes clearly. It supports business strategy by connecting financial numbers to company operations. Every figure provides insights into the company’s health and efficiency. This information helps stakeholders make smart decisions.
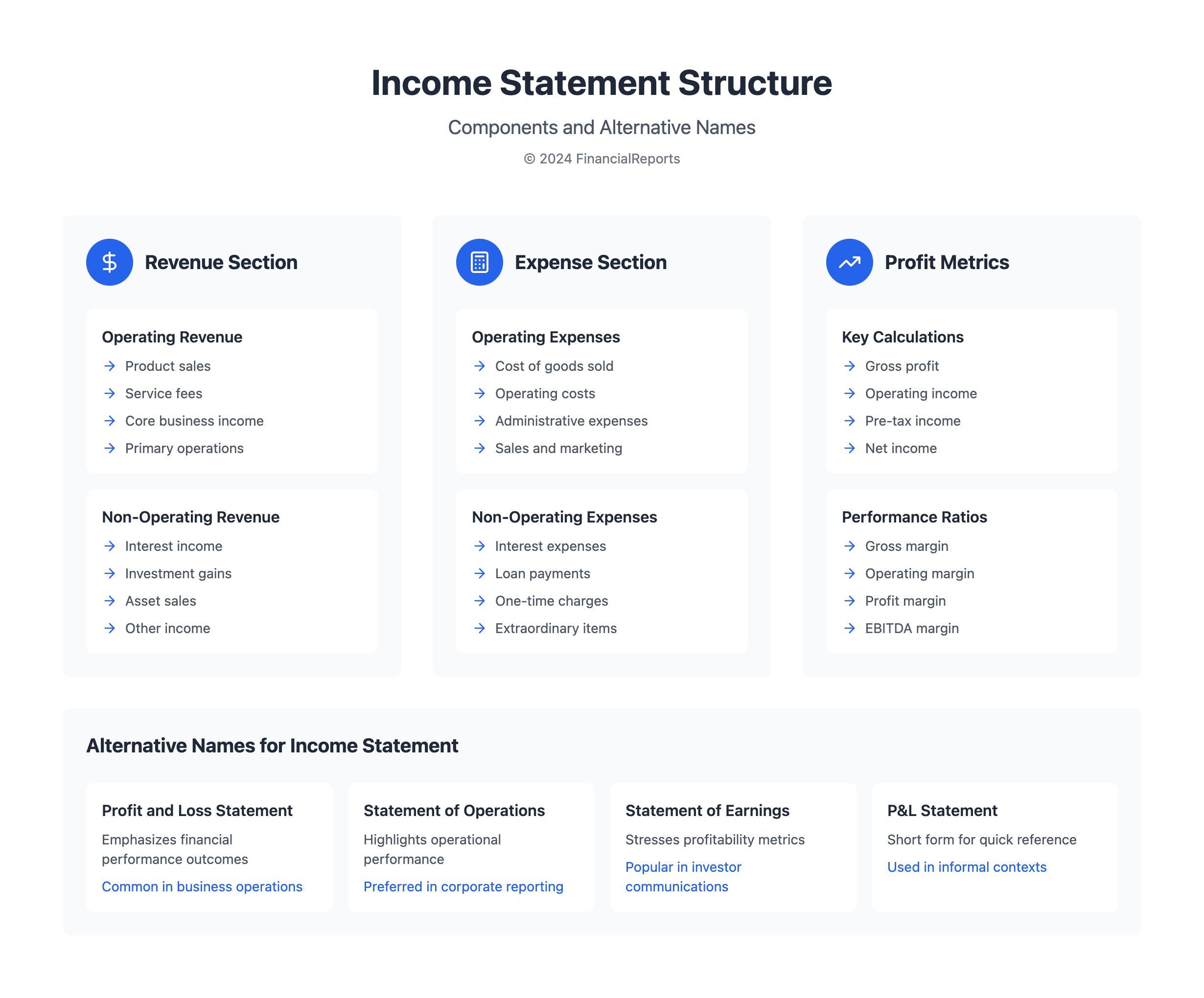
Alternate Names for the Income Statement
The Income Statement is key in showing how well a company did financially over time. It goes by different names, each one highlighting a special part of what the document offers.
Profit and Loss Statement
The profit and loss (P&L) statement, as it's often called, shows profits made and losses faced during a certain period. For example, GreenHarbor LLC's P&L for the year ending December 31, 2010, showed a net income of €100,882. This was after counting total revenues of €296,397 against expenses of €195,515. This report details costs like sales, goods, and R&D, painting a clear picture of the company's financial moves.
Statement of Earnings
This is also known as the statement of earnings. It zooms in on the net financial results - either profit or loss. It includes every kind of revenue and expense. That means everything from regular operations to one-off items for a full view of what a company can earn.
Statement of Operations
The statement of operations focuses on what a company does day to day versus one-time financial gains, like selling assets. It separates everyday business income from other types of earnings. This makes it easier for people to see how well the core business is doing on its own.
| Year | Total Revenue (€) | Total Expenses (€) | Net Income (€) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 296,397 | 195,515 | 100,882 |
Knowing these different names helps those interested in a company's finances get a clearer picture. Different names underline the income statement's diverse roles in business finance.
Importance of the Income Statement
The income statement is super important for both managing a business and analyzing its finances. It shows how well a company is doing, looking at its money-making and spending to figure out its financial health and strategy. Understanding this document is key to making smart decisions for the future.
Assessing Business Performance
For managers, the income statement is crucial for checking if their plans are working. It points out the strong and weak spots. Managers then know where to make changes. This document helps them see how their choices affect the company's money-making and expenses. Keeping an eye on these numbers helps improve how the business does overall.
Financial Planning and Analysis
This statement lays the foundation for deep diving into a company's finances. It shows where money comes from and where it goes. Analysts use it to figure out important financial health signs, like gross and net profit margins. These insights guide future plans and investments, leading to a smart way of running the business.
Especially for small business owners, frequent checks of the income statement are vital. It guides them in making fast, crucial decisions. This data lets them grasp market trends and compare their business to others, helping them dodge common mistakes and grow their business.
In the end, the income statement is not just about numbers. It's a strategic asset for boosting operational performance and standing out in the market. Keeping this document updated and analyzed is key for a clear financial view and for driving the business toward ongoing success and profit.
Components of an Income Statement
An income statement shows how a company did financially in a certain time. It lists revenues, expenses, and net income. These details give a clear view of the company's financial health to those interested.
Revenues
Revenue is split into operating revenue and non-operating revenue. Operating revenue comes from the main business activities, like selling products or services. Non-operating revenue is from other sources, such as interest on investments, or selling assets. Knowing the difference helps understand where the money comes from.
Expenses
Expenses on an income statement are divided into two types. There are primary operating expenses, like the cost of goods sold (COGS) and selling, general and administrative expenses (SG&A). Then, there are non-operating expenses, like interest payments. It's crucial to keep track of these to measure how well the company is doing.
Net Income
Net income is what you get when you subtract total expenses and losses from total revenues and gains. It shows if the company made a profit during that period. A positive net income means the company earned more than it spent. This is a sign of good management and business success.
From calculating gross profit margin by subtracting COGS from operating revenue, to figuring out net income, each step is important. It helps people understand a company's financial condition. This knowledge is key for making smart decisions and planning for the future.
Relationship with Other Financial Statements
The income statement is a key part of corporate financial statements. It connects directly to the balance sheet and the cash flow statement. Through analysis, we see how the income statement affects and relates to key aspects of financial health and financial liquidity.
Connection to the Balance Sheet
Net income impacts the balance sheet's retained earnings. For example, Clear Lake Sporting Goods saw retained earnings increase from $15,000 to $20,000. This shows the company's skill in handling debt obligations and boosting shareholder value.
Also, income statement actions affect asset values. This is seen in changes to property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) on the balance sheet.
Role in the Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement's operations section benefits from the income statement. Adding back non-cash charges like depreciation shows real cash flow from operations. For Clear Lake Sporting Goods, shifts in operating activities cash flow, like managing a $1,500 utility bill, show how well they're doing in financial planning and operations.
Linking income statement results with balance sheet and cash flow data helps financial pros guide a company towards growth and better capital efficiency. These connections are key for evaluating a company's financial health and management.

How the Income Statement Affects Stakeholders
The income statement is crucial for various stakeholders in finance, affecting investment decisions and credit risk evaluations. It offers a detailed look at a company's financial activities over a certain time, like a quarter or year. It's essential for evaluating the company's financial solvency and aligning interests with the organization's well-being.
Investors’ Perspective
Investors use the income statement to gauge a company's profit-making and efficiency. They look at how the company grows revenue, manages expenses, and generates net income. These factors help them decide if the company is worth investing in.
- Revenue: Shows the total money made from the main business activities, indicating market demand and pricing strength.
- Expenses: Higher expenses may show possible inefficiencies or investment in growth. Analyzing these can reveal long-term impacts.
- Net Income: A clear measure of profitability, affecting stock prices, dividends, and company reinvestment plans.
Creditors’ Assessment
Creditors check the income statement to see the credit risk of lending to a company. They focus on the company's ability to pay off its debts with its earnings. This shows if the company is financially solvent.
- Operational Efficiency: They look at how well the company handles its cash flow through metrics like the cash conversion cycle.
- Debt Servicing: They assess if the company can earn enough profit to cover its debts. Retained earnings and net income are key indicators.
- Financial Health: Income and expense details help creditors judge the risk of giving credit or continuing financial agreements.
For all involved, the income statement is a key tool. It helps align stakeholder interests with the company's financial health and plans. Whether it's for assessing credit risk, investment potential, or strategic decisions, the income statement provides essential data. This data aids financial decision-making in the complex business finance world.
Key Metrics Derived from the Income Statement
The Income Statement is crucial for analyzing a company's profits. It provides essential insights through key financial ratios. These are important for evaluating a company's financial condition and how well it operates.
Gross Profit Margin
Gross Profit Margin shows how effectively a company uses labor and materials to produce goods. The formula is: (Gross Profit / Revenue) x 100. This ratio indicates basic profitability from making and selling products. It also plays a big role in a company's overall profit analysis.
Operating Income
Operating Income tells us about the profit from regular business activities. You can find it using this formula: (Operating Income / Revenue) x 100. It looks only at the earnings from main operations, not including things like taxes. This gives a clear view of how well the company operates without other financial factors.
Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT)
EBIT is key for understanding a company's financial results without interest and tax effects. The formula for it is: (EBIT / Revenue) x 100. It's crucial for seeing how the operations perform by themselves. Both company management and outside analysts use it to look at operational success without tax or financing distractions.
| Financial Metric | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Profit Margin | (Gross Profit / Revenue) x 100 | Measures the production efficiency beyond the costs of goods sold. |
| Operating Profit Margin | (Operating Income / Revenue) x 100 | Assesses profitability from core business operations. |
| EBIT Margin | (EBIT / Revenue) x 100 | Indicates profit before the influence of tax and interest expenses. |
Using these key metrics in financial analysis makes profit analysis more precise. It also helps in making strategic decisions. Companies that calculate these ratios often can monitor their operational improvements. They can also better understand their financial status.
Common Mistakes in Income Statement Preparation
In the world of financial reporting, making sure income statements are right is crucial. Mistakes can cause big financial reporting errors. They can mess up revenue accounting and make expense management hard. This can lead to serious compliance issues. Knowing these common mistakes helps protect a company's financial health.
Overlooking Revenue Recognition
Not handling revenue recognition correctly is a common mistake. This can mean recording revenue too soon or too late. This messes up how a company's health looks financially. For example, saying you made money too early can make earnings seem bigger. This gives a false image of how well the company is doing. To avoid these mistakes, improving your knowledge with programs like the Master of Business Administration with a focus in Accounting at Longwood can help.
Misclassification of Expenses
Messing up expense categories is another big issue. This could be with operating costs, non-operating costs, or big purchases. Doing it wrong can give a wrong idea of how much profit a company is making. For instance, Wipfli LLP found many major journal adjustments were needed during audits. This shows a big flaw in how financial statements are made. These mistakes can make you need big corrections and can cause big compliance problems.
Both of these mistakes show why it's important to have tight control and a good understanding of accounting rules. Being very careful with financial documents is not just advised, it's critical. It helps keep financial practices strong. And it makes sure a company's financial reporting is clear and trustworthy.
Regulatory Standards for Income Statements
Creating income statements follows strict rules. These rules are vital for accounting compliance and making financial reports standard worldwide. Mainly, GAAP in the U.S. and IFRS internationally are the guideposts. They make sure that financial statements can be trusted and compared across different regions and economies.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
In the U.S., GAAP outlines how income statements should be structured. Key sections like ASC 205 and ASC 225 offer details on presenting comprehensive income. A common method used by businesses is the "two-step" format. This format, required by rules like S-X 5-03 for SEC filings, lists essential income statement items. Such structure helps keep reports clear and consistent, aiding stakeholders in analysis and decisions.
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
Worldwide, IFRS sets rules for income statements with standards such as IAS 1. This is called the 'statement of profit or loss.' Companies can choose how they show their financial results. They may use a single statement of comprehensive income or two separate statements. This choice supports the varied practices and rules of different countries, helping in global report standardization.
| Year | Net Sales ($M) | Gross Profit ($M) | Operating Expenses ($M) | Net Income ($M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20X3 | 120,000 | 40,000 | 30,000 | 25,000 |
| 20X2 | 110,000 | 35,000 | 28,000 | 22,000 |
| 20X1 | 100,000 | 30,000 | 25,000 | 20,000 |
These income statement standards are key for deep financial analysis and comparison over time. By sticking to GAAP and IFRS, companies not just follow the rules. They also make their financial reporting more credible and reliable.
Analyzing Trends in Income Statements
In today's fast-changing business world, financial trend analysis and performance metrics from income statements are vital. They help decision-makers understand market competitiveness and sustainability. This section explores how such analysis boosts strategic planning and benchmarking efforts.
Year-over-Year Comparisons
Reviewing income statements year-over-year (YoY) lets organizations track their financial health. It shows trends in income, expenses, and profit. Look at Company B's last year's financial performance for example:
| Financial Aspect | FY Ending 2019 | % Change |
|---|---|---|
| Net Sales | $4,358,100 | N/A |
| Operating Income | $765,227 | N/A |
| Net Income | $483,232 | N/A |
| Gross Profit | $1,619,386 | N/A |
| Income Before Taxes | $740,874 | N/A |
Even without specific percentage changes, historical data can illustrate financial growth rates.
Industry Benchmarking
Comparing with industry peers highlights strengths and improvement areas. For instance, consider Coca-Cola’s recent financial gains:
| Financial Metric | Value Increase | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Income | $218 million | 2.6% |
| Net Sales | $4,129 million | 13.3% |
| Gross Margin | $2,524 million | 12.7% |
This highlights the outcomes of Coca-Cola’s strategic decisions, showing how it compares to industry norms. Such analysis defines success and aids in aligning strategies with industry best practices.
Using financial trend analysis, including year-over-year comparisons and industry benchmarking, helps stakeholders make better choices. It ensures a competitive stance in the market.
Tools and Software for Creating Income Statements
In today's world, there are many tools and software to help with financial documents. They make data management easier and improve the accounting system's integrity. This ensures companies follow rules and perform excellently.
Accounting Software Options
There are lots of accounting software choices for businesses. For example, Oracle NetSuite offers a full set for financial insights. It works well with Salesforce and Shopify. This helps with smooth data management for good accounting. QuickBooks is great for smaller businesses. It's easy to use and not too expensive, costing between $30 and $200 a month.
Spreadsheet Applications
While new software is popular, Microsoft Excel is still very important. Spreadsheets let you move data around easily. They are perfect for detailed financial analysis and initial accounting checks.
| Software | Pricing | Target User | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cube | $1500/month for Cube Go $2800/month for Cube Pro Custom for Enterprise |
Medium to Large Businesses | FP&A software, integrates with Google Spreadsheets, Sage, Workday |
| Oracle NetSuite | Contact for Quote | Large Enterprises | Comprehensive finance insights, integrates with Salesforce, SAP, Shopify |
| QuickBooks | $30/month for Simple Start $200/month for Advanced |
Small Businesses, Freelancers | User-friendly for beginners, ideal for small-scale operations |
| Sage Intacct | Contact for Quote | Nonprofits, Medium Enterprises | Cloud-based, core financial management applications |
To pick the right software, financial pros must think about their needs. They should consider how big their company is and how complex their accounting needs to be. Choosing wisely helps with financial documents and improves business strategy through better data management.
Educational Resources for Understanding Income Statements
Getting ahead in finance means you must understand key documents like income statements well. There's a wealth of educational tools for those wanting to grow their finance and accounting skills. These resources help explain the complex stories numbers tell about a company's health and its place in the market.
We aim to make global financial data easy for everyone to access. We do this by sharing knowledge.
Online Courses and Webinars
Online courses and webinars can really boost your financial education. They cover everything from basics to advanced topics in income statement analysis. These digital platforms give detailed insights.
Live webinars let you interact in real time with experts and learn the latest practices. They're crucial for understanding detailed accounting topics. This includes knowing about revenue, expenses, and deduction strategies.
Recommended Books and Articles
Books and articles also offer deep insights into income statements. Some books dissect income statements very precisely. They examine the financial details of companies, like Coffee Roaster Enterprises Inc. and Dead Simple Coffee Inc.
Articles and journals provide case studies and compare different companies. They highlight key figures like gross profit, operating earnings, and net income. Engaging with these resources is essential for staying sharp in financial analytics and decision-making.
FAQ
What is an income statement?
An income statement shows a company's financial performance during a time frame. It's also called a profit and loss (P&L) statement. This report details the company’s revenues, expenses, gains, and losses, showing the net income.
What is the main purpose of the income statement?
Its main purpose is to give a clear picture of a company's profitability and efficiency over time. This helps stakeholders assess financial health and guide planning and decisions.
What are some alternate names for the income statement?
It can also be called the profit and loss (P&L) statement, statement of earnings, or statement of operations.
Why is the income statement important?
It's vital for showing how well a company can earn money, control costs, and make profits. It guides strategies and decisions with its in-depth financial analysis.
What are the key components of an income statement?
Major parts include revenues, expenses (broken down into COGS, operating expenses, and non-operating expenses), gains, losses, and net income.
How does the income statement connect to the balance sheet?
It affects the retained earnings in the shareholders' equity on the balance sheet. Net income, after dividends, adjusts retained earnings from the prior period.
What role does the income statement play in the cash flow statement?
It helps show the profit from company operations, affecting the cash flow's operating activities. This illustrates adjustments for non-cash items and capital changes to show the net operating cash flow.
How do investors and creditors use the income statement?
Investors check it to gauge profitability and growth potential, affecting their choices and the stock price. Creditors evaluate credit risk and repayment capacity, influencing their lending.
What are some key metrics derived from the income statement?
Key metrics include gross profit margin, operating income, and EBIT. These help in comparing financial performance and profitability analysis with peers.
What are common mistakes in income statement preparation?
Mistakes often involve incorrect revenue reporting that misrepresents performance and expense misclassifications. These can affect profitability views and lead to accounting issues.
What regulatory standards govern the preparation of income statements?
In the US, GAAP guides income statement preparation. Globally, IFRS standards apply. Both ensure financial statement consistency and reliability.
How are trends in income statements analyzed?
Analysis involves year-over-year reviews and industry comparisons. This helps identify trends in growth, profitability, and efficiency relative to similar companies.
What tools and software can assist in creating income statements?
Accounting software like QuickBooks and Xero, along with Excel, help with accurate calculations, data management, and following standards.
Where can one find educational resources for understanding income statements?
There are many resources online including courses and webinars. Books and publications on accounting and financial analysis are also helpful.